Zebrafish facilitates drug screening: potential of 3-deoxyandrographoside from Chuanxinlian (Herba Andrographitis Paniculatae) as an anti-inflammatory agent
2022-10-14HEXuemeiXIAOJunjieFANChunlinLUZibinCAOHuihuiYULinzhongZHENGYuanruLIUJunshan
HE Xuemei,XIAO Junjie,FAN Chunlin,LU Zibin,CAO Huihui,YU Linzhong,ZHENG Yuanru,LIU Junshan
HE Xuemei,XIAO Junjie,LU Zibin,CAO Huihui,YU Linzhong,ZHENG Yuanru,LIU Junshan,Third Level Research Laboratory of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine,School of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510515,China
HE Xuemei,XIAO Junjie,LU Zibin,CAO Huihui,YU Linzhong,ZHENG Yuanru,LIU Junshan,Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Pharmaceutics,Guangzhou 510515,China
FAN Chunlin,Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Pharmacodynamic Constituents of TCM and New Drugs Research,College of Pharmacy,Jinan University,Guangzhou 510632,China
ZHENG Yuanru,School of Pharmacy,Guangdong Pharmaceutical university,Guangzhou 510006,China.
LIU Junshan,Department of Pharmacy,Zhujiang Hospital,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510515,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE: To systematically evaluate the in vivo antiinflammatory potential of diterpene lactones from Chuanxinlian (Herba Andrographitis Paniculatae) (AP).METHODS: We firstly adopted zebrafish,a novel and ideal animal model for high-throughput drug screening,to investigate the in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of 17 diterpene lactones isolated from AP.RESULTS: The results showed that most of diterpene lactones displayed significant anti-inflammatory effects in lipopolysaccharide microinjection-,copper sulfate exposure- or tail transection-induced zebrafish inflammation models.Moreover,diterpene lactone 3-deoxy-andrographoside (AP-5) was firstly found to attenuate inflammatory responses,which was closely associated with the myeloid differentiation primary response 88/nuclear factor-kappa B and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathways.CONCLUSION: Our research sheds light on the inestimable roles of zebrafish in high-throughput drug screening,elucidates the potent inhibitory effects of diterpene lactones against inflammation and indicates that AP-5 may serve as a potential alternative agent for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: diterpenes lactones;inflammation;zebrafish;myeloid differentiation factor 88;NF-kappa B;STAT3 transcription factor
1.INTRODUCTION
Inflammation,a self-protective mechanism of the organism to detrimental stimulation,is a basic pathophysiological process owing to its function of eradicating pathogens and healing damaged tissues.1However,continuous inflammatory response or acute unsettled inflammation may result in the occurrence of many serious diseases,such as bronchial asthma,2rheumatoid arthritis,3pneumonia4and so on.The presently available repertoire of approved antiinflammatory agents mainly incorporates nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,glucocorticoids,immunosuppressant drugs and biologicals.Despite this arsenal,therapy is often not effective enough or is hampered by insufferable side effects.5Therefore,the discovery or development of safe and effective natural products as innovative anti-inflammatory agents is urgently required.
Accumulating evidence demonstrates that traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) with heat-clearing and detoxification properties could eliminate the pathogenic response caused by excessive inflammation.6Chuanxinlian (Herba Andrographitis Paniculatae) (AP),one of the most commonly used antipyretics in TCM,has been widely applied for the treatment of inflammationrelated diseases such as flu,upper respiratory tract infection,diarrhea and dysentery.7Previous phytochemical studies on AP have revealed that it contains a representative type of constituents named as diterpene lactones.8Among which,andrographolide is the most abundant diterpene lactone in AP and has been reported to restrain inflammation by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation.9Dehydroandrographolide,3-dehydroandrographolide and so on also display anti-inflammatory activities through the NF-κB/Akt signaling pathway.10,11However,the other diterpene lactones isolated from AP have not been extensively studied especially in terms of their antiinflammatory effects in anin vivomodel.
Numerous studies in cells and animal models have contributed greatly to our understanding of inflammation,but there are limitations.Thein vitrocell experiments are poor to simulate the internal environment,while rodent or other mammalian experiments are relatively lowthroughput,time-consuming and high cost,which may delay the progress of drug development.12,13In the past 20 years,zebrafish (Danio rerio) has been broadly adopted as a reliable model of inflammatory diseases for its similar innate immune system like human,high conservation of signal transduction pathways related to disease,high number of offspring,short reproductive cycle and low-cost maintenance.14,15Notably,the optical transparency of whole larvae permits noninvasive and dynamic imagingin vivo,16and the transgenic type labeled fluorescent neutrophils or macrophages also facilitate and accelerate the progress of drug discovery.17Because of these characteristics,zebrafish holds considerable promise as a high-throughputin vivodrug screening model for the studies of inflammatory-related diseases.18
In this research,three different zebrafish models were firstly applied to screen out thein vivoanti-inflammatory components among 17 diterpene lactones isolated previously from AP,19,20and the participating roles of NF-κB and STAT3 pathways were also investigated in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced zebrafish.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Material and reagents
Totally 17 diterpenoid lactones with high purities (≥ 95%)were previously isolated from AP.19,20Methylene blue was from Meilunbio (Dalian,China) and tricaine was from Macklin (Shanghai,China).Copper sulfate (CuSO4)was obtained from Chemical Reagent Factory(Guangzhou,China).Dexamethasone (Dex) was purchased from Tianxin (Guangzhou,China).Dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO),LPS (E.coli,O55: B5,L2880) and other reagents were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis,MO,USA).
2.2.Zebrafish maintenance
Transgenic zebrafishTg (mpo:GFP)exhibiting fluorescence on neutrophil17were obtained from Professor Zhang Wenqing at South China University of Technology (Guangzhou,China) and maintained in a flow-through aquaria at 28.5oC on a 14/10 h (light/dark)photoperiod.All experiments were performed in compliance with the standard guidelines for maintenance protocols.21Embryos were gathered by natural spawning at a male-to-female ratio of 1∶2 and then kept in egg water (containing 0.02 mg/mL methylene blue) up to 3 d post fertilization (dpf).
2.3.LPS-induced inflammatory model
To develop the inflammatory zebrafish model,2 nL of LPS was microinjected into the yolk sac of zebrafishviaCell microinjector (PM1000,MicroData Instrument,Inc.,South Plainfiled,NJ,USA) as described previously.12,22,23Negative control larvae were microinjected with an equal volume of phosphatebuffered saline (PBS).The recruitment of neutrophils was recorded using a fluorescent microscope (Olympus,MVX10,Tokyo,Japan).
2.4.CuSO4-induced inflammatory model
CuSO4-induced inflammatory model was developed according to the previously described method.23Briefly,3-dpf larvae were randomly assigned to a 24-well plate(n=20) and soaked in 20 μM CuSO4containing different diterpenoid lactones or Dex for 2 h at 28.5 ℃.Then these larvae were rinsed off with fresh egg water and anesthetized with 0.02% tricaine before observation under the fluorescent microscope (Olympus,MVX10,Tokyo,Japan).
2.5.Tail transection-induced inflammatory model
Zebrafish larvae at 3 dpf were subjected to a transection at the end of the spinal cord using a stereomicroscope(Olympus,SZX7,Tokyo,Japan),23which were then immersed in the egg water containing diterpenoid lactones or Dex for 6 h.Finally,the migration and accumulation of neutrophils at injured areas were detected under the fluorescent microscope (Olympus,MVX10,Tokyo,Japan).
2.6.Survival analysis
The LPS-stimulated larvae with or without the treatment of diterpenoid lactones were evaluated on the morbidity and mortality within 72 h post injection (hpi).Dead embryos were numbered and discarded to depict the survival rate curves.23
2.7.Histopathological analysis
Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was performed as described before.19,23Briefly,the whole larvae at 12 hpi were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde,routinely embedded in paraffin (Leica,Wetzlar,Germany) and crosssectioned to 4-μm slices.The obtained histological sections were dewaxed with xylene,dehydrated with increasing concentrations of ethanol and stained using the standard procedure of HE (Yuanye Biotech,Shanghai,China).Microscopic observations were performed on an IX 53 light microscope (Olympus,Tokyo,Japan).
2.8.qRT-PCR (quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction) analysis
Total RNA was isolated from the whole larvae at 12 hpi using RNAiso Plus as recommended by the manufacturer,and reversely transcribed into cDNA using the PrimeScriptTM RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser.Thereafter,qRT-PCR analysis was carried out on a Roche LightCycler®96 system using TB GreenTMPremix Ex TaqTMII (Takara,Shiga,Japan).The 2-ΔΔCtmethod was applied to quantify the relative expressions of genes using β-actin as the internal control.The sequences of the primer used in the present study were listed in Table 1.

Table 1 Sequences of the primers in qRT-PCR analysis
2.9.Statistical analysis
Statistical software GraphPad Prism 5.0 (San Diego,CA,USA) was used for statistical analysis.Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s) from parallel triple experiments.The results were analyzed statistically using one-way analysis of variance andaPvalue < 0.05 was considered to denote statistical significance.
3.RESULTS
3.1.Most of diterpenoid lactones exerts significant antiinflammatory effects
The chemical structures of 17 deterpenoid lactones are shown in Figure S1.To expediently and rapidly screen out thein vivoanti-inflammatory compounds among these isolated compounds,LPS microinjection-,CuSO4exposure-or tail transection-induced inflammatory models were employed on the transgenic zebrafishTg(mpo:GFP)expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP)in neutrophils.
In this study,the LPS-induced zebrafish inflammatory model was firstly used to rapidly screen out thein vivoanti-inflammatory components by the real-time track of neutrophils recruitment.As shown in Figure 1,large numbers of neutrophils migrated to the yolks after the stimulus of LPS,indicating the inflammatory model was established successfully.All these diterpenoid lactones could significantly inhibit LPS-induced migration of neutrophils toward the yolks,demonstrating that all 17 diterpenoid lactones have anti-inflammatory effects during the early phase of inflammation.Remarkably,compounds AP-1,AP-4 and AP-5 show the most potent activities among all these diterpenoid lactones.
CuSO4and tail transection can chemically or physically cause robust inflammation in zebrafish,which can be characterized by neutrophils recruitment to the injured lateral line neuromasts or tails.24,25Then the inhibitory effects of 17 diterpenoid lactones on neutrophil migration were further confirmed by using the CuSO4exposure and tail transection method.As shown in Figures 2,3,recruitment of neutrophils to the lateral line neuromasts or cut site was markedly increased following the treatment of CuSO4or tail amputation,implying the occurring of inflammation.While most of diterpenoid lactones except AP-3 and AP-17 significantly reduced the number of neutrophils surrounding the injured sites.These findings further verify the potent antiinflammatory effects of most diterpenoid lactones,which is in line with the major results in LPS-induced zebrafish model.
In order to further understand the relationships between chemical structures and anti-inflammatory activities of 17 diterpenoid lactones,the structure-activity relationship (SAR) of these compounds were investigated.We find that AP-4 showed more potent antiinflammatory effects than AP-3,demonstrating that the introduction of a hydroxyl group may be favorable to the anti-inflammatory activity.Besides,the introduction of a hydroxymethyl group may reduce the anti-inflammatory activity,as evidenced by the differences in the antiinflammatory activities of AP-7 and AP-17.
It is worth noting that compounds AP-4 (andrographolide)and AP-5 (3-deoxy-andrographoside) exhibit significant anti-inflammatory effects in all three kinds of inflammatory models.Consistent with the existing literature,AP-4 shows a promising anti-inflammatory activity and has been well studied.9AP-5,by contrast,has been far less investigated.Therefore,thein vivoantiinflammatory effect and mechanism of AP-5 were firstly illustrated by survival analysis,histopathological evaluation and qRT-PCR assay in LPS-stimulated zebrafish.
3.2.AP-5 protects the zebrafish challenged by LPS
Death is the most important indicator of severe inflammation and the survival rate is commonly used to directly characterize and evaluate the efficacy of antiinflammatory drugs.22To determine whether AP-5 could protect zebrafish from the death caused by LPS stimulation,the survival test was initially performed on LPS-induced zebrafish.As shown in Figure 4A,the mortality of LPS model group was markedly declined to zero at 72 hpi compared with the PBS group,while AP-5 significantly elevated the survival rate of LPS-induced zebrafish larvae to 50%,thereby demonstrating the defensive roles of AP-5 in the inflammatory zebrafish insulted by LPS.
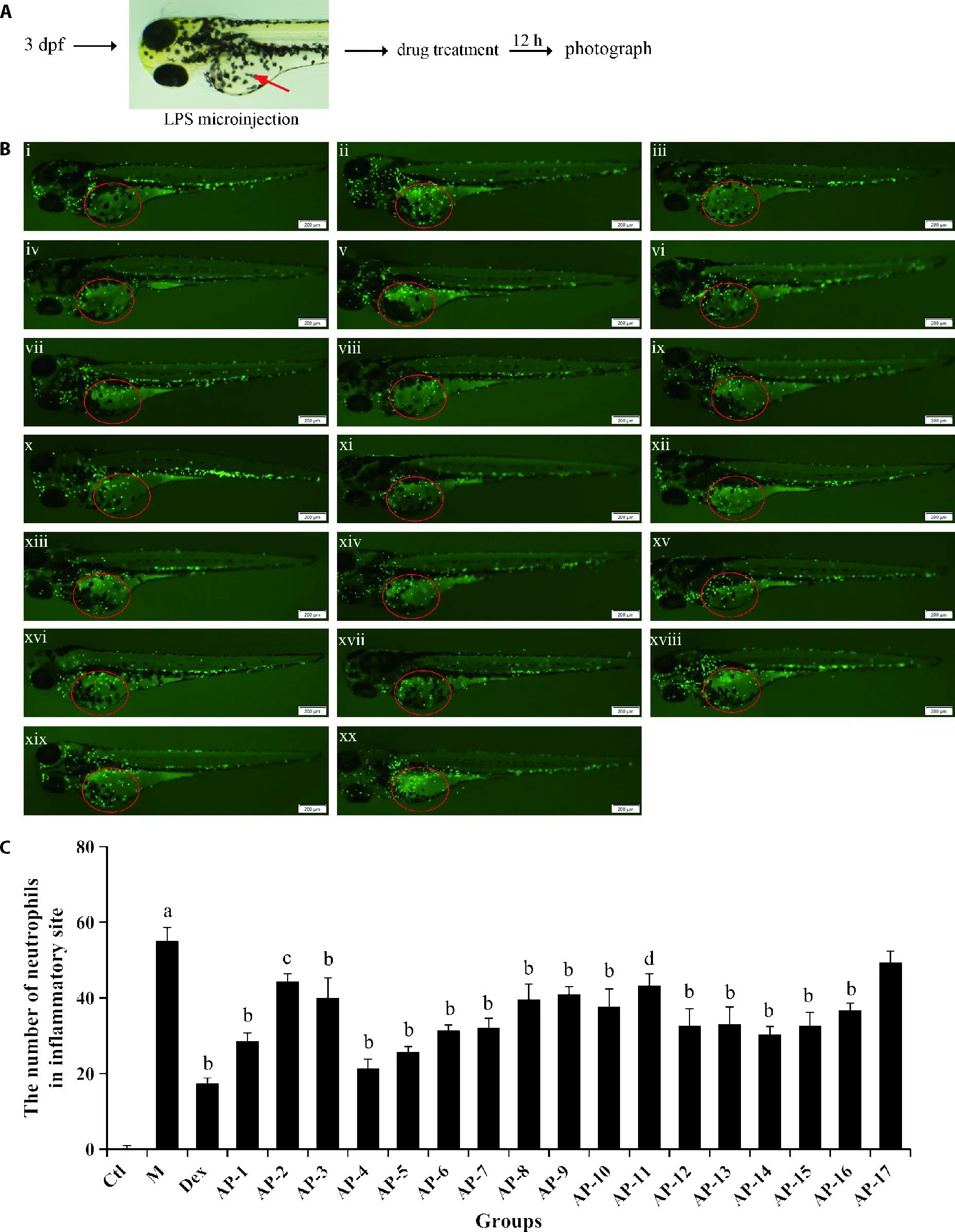
Figure 1 Inhibitory effects of 17 diterpenoid lactones on LPS-stimulated inflammation in 3-dpf zebrafish larvae
The infiltration of inflammatory cells are key features of acute inflammation,which can be stained and labeled by HE to indicate the presence and intensity of inflammatory response.26Therefore,the protective effects of AP-5 on zebrafish histopathological changes were visually examined by HE staining.The results showed that a significant infiltration of inflammatory cells was observed with the stimulation of LPS.However,prominent infiltration of inflammatory cells induced by LPS could be lessened by the treatment of AP-5 (Figure 4B),which further verifies the protective effects of AP-5 against LPS-induced inflammation.
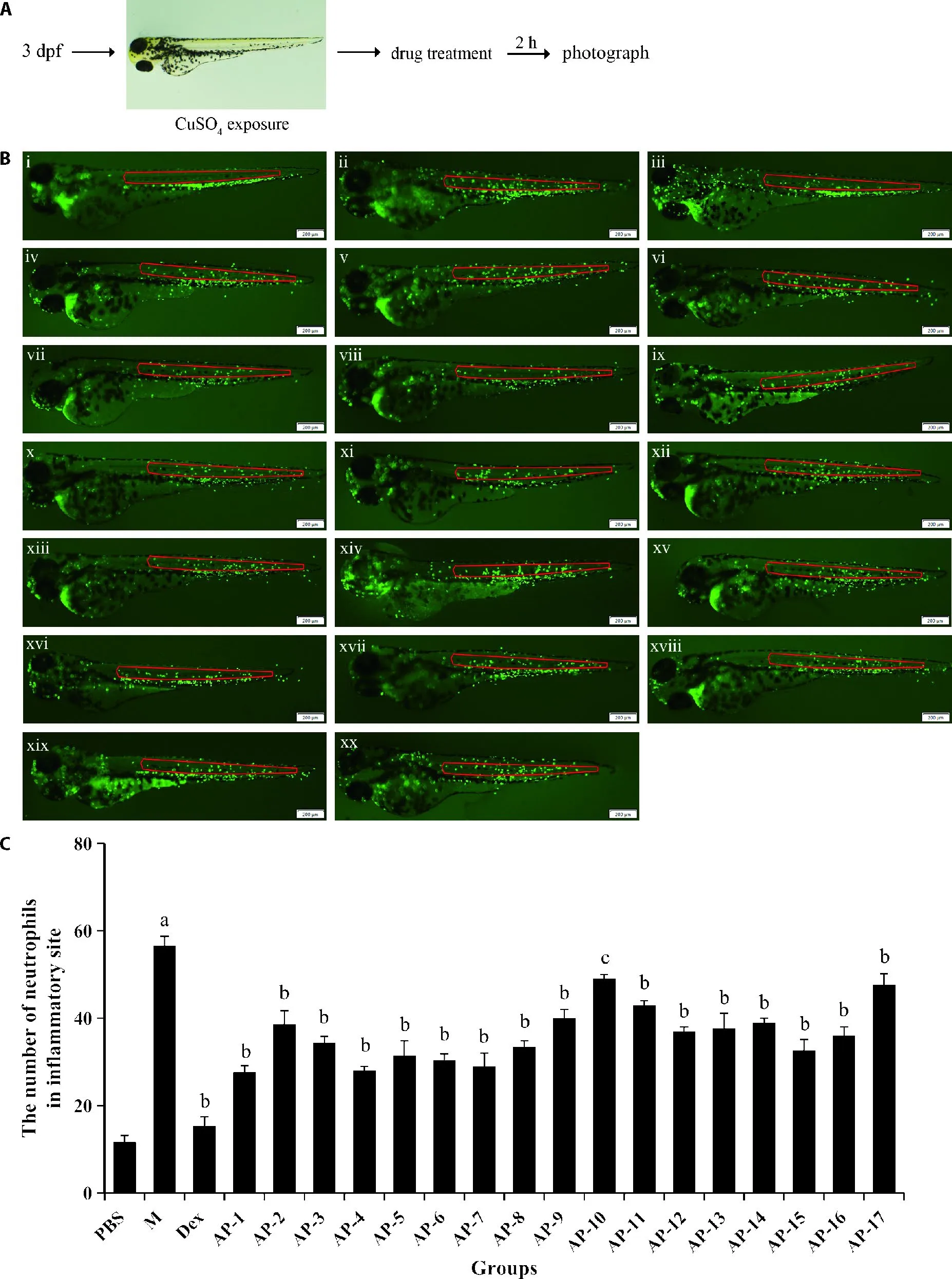
Figure 2 Inhibitory effects of 17 diterpenoid lactones on CuSO4-induced inflammation in 3-dpf zebrafish larvae
3.3.AP-5 suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated zebrafish
LPS can induce the release of numerous proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α),which are known as the important mediators involved in the progress of many inflammatory diseases.27It is a compelling method to tightly regulate the secretion levels of these cytokines during an inflammatory response.To explore the underlying molecular mechanisms of AP-5,the mRNA expressions levels of IL-6 and TNF-α were firstly determined by qRT-PCR in LPS-induced zebrafish.The results showed that LPS increased the mRNA expression of IL-6 to approximately 3.0-fold,which was reduced to only 1.7-fold by AP-5 (Figure 4C).Similarly,the mRNA expression of TNF-α was boosted to approximately 13.0-fold by LPS alone,while AP-5 reduced TNF-α expression to only 6.0-fold (Figure 4D).These data suggest that AP-5 exerts an anti-inflammatory activityviathe suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α in LPS-stimulated zebrafish.
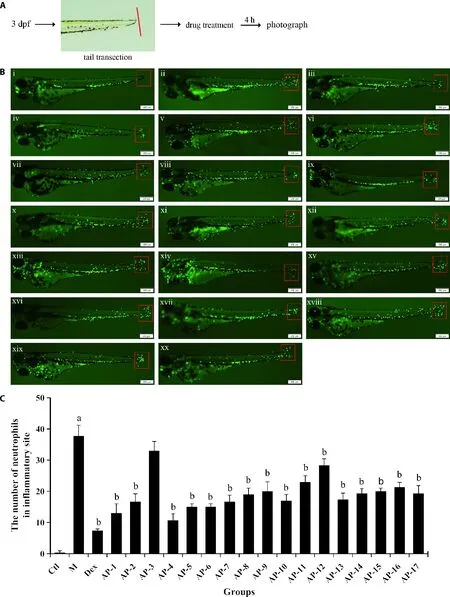
Figure 3 Inhibitory effects of 17 diterpenoid lactones on inflammation induced by tail transection in 3-dpf zebrafish larvae
3.4.AP-5 attenuates LPS-triggered inflammatory response via the myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88)/NF-κB and STAT3 pathways
To gain further insight into the mechanism by which AP-5 inhibits the inflammatory response in zebrafish,we next sought to investigate whether the MyD88/NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways are involved in the antiinflammatory effect of AP-5.Compared to PBS groups,the mRNA levels of NF-κB,IκBα,MyD88 and STAT3 in LPS groups were found to be increased by approximately 1-2 fold.However,AP-5 notably inhibited the up-regulation of NF-κB,IκBα,MyD88 and STAT3 in LPS-stimulated zebrafish (Figure 4E-4H).These results suggest for the first time that AP-5 exhibits a potent suppressive effect in LPS-induced inflammation probably through inhibiting the activation of MyD88/NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways.
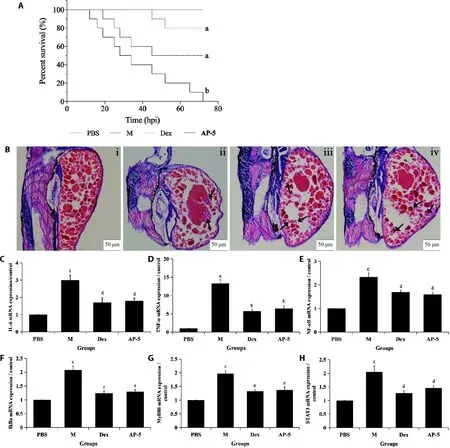
Figure 4 Protective effects of AP-5 on zebrafish larvae stimulated by LPS
4.DISCUSSION
Neutrophils are the first responders and play a crucial role in the early immune response against inflammatory stimuli.When an inflammatory reaction is initiated in injured tissue,neutrophils are activated and rapidly recruited to the inflammatory area,and the continued neutrophilic activity can lead to overenthusiastic inflammation.17Thus,the number of infiltrating neutrophils provides a measurement for the degree of inflammatory response,which can be used as a crucial target in the discovery of anti-inflammatory drugs.In the present study,zebrafish exhibiting GFP in neutrophils were used to evaluate the inhibitory effects of the isolated compounds.
LPS,also called endotoxins,can activate various cascade reactions and disturb the balance between immunity and inflammatory responses,leading to fever,systemic inflammatory response syndrome,endotoxic shock or even death.28LPS-induced zebrafish model has been initiatively developed by our research group and successfully results in the induction of local inflammation by microinjecting LPS into the yolk sac of zebrafish larvae.22Therefore,the model was applied in the study to determine the anti-inflammatory active compounds,and we found that most of the compounds exert anti-inflammatory effects by decreasing the numbers of neutrophils in related regions.
NF-κB plays a crucial role in regulating the inflammatory responses by increasing the expression of multiple genes,such as pro-inflammatory cytokines,chemokines and inducible enzymes.29MyD88,a key modulator in the inflammatory signaling cascades triggered by LPS,is also a critical adapter protein in the activation of NF-κB.30As another prominent signaling pathway involved in the inflammatory response,STAT3 transcription factors can up-regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory enzymes and mediators.31On one hand,activation of NF-κB signaling produces IL-6 cytokines,which can activate the STAT3 pathway.32On the other hand,STAT3 can prolong the existence of active NF-κB in the nucleus,suggesting that the NF-κB and STAT3 pathways mutually involved in inflammation triggered by LPS.33Thus,the NF-κB and STAT3 pathways are considered as crucial targets for controlling inflammation.The results indicated that NF-κB and STAT3 pathways are partially contributed to the antiinflammatory of AP-5.Our study not only highlights the irreplaceable role of the zebrafish inflammatory models in high-throughputin vivoscreening for the antiinflammatory drugs but also suggests that diterpene lactone AP-5 may serve as the candidate to be an antiinflammatory agent.However,we did not explore the anti-inflammatory activity of AP-5 on the corresponding protein levels,which need to be further confirmed in the future.Moreover,the research on cell and rodent models is also required to validate the anti-inflammatory effects and the participation of MyD88/NF-κB and STAT3 pathways of AP-5.
In conclusion,the zebrafish inflammatory models have been employed to rapidly screen thein vivoantiinflammatory components among 17 diterpene lactones from AP.Moreover,it is the first time to report that AP-5 possesses anin vivoanti-inflammatory activity,which is highly associated with the MyD88/NF-κB and STAT3 signal pathways.
5.ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Chen Yuyao and Xu Nishan for their assistance during HE staining.
杂志排行
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Effectiveness and safety of tripterygium glycosides tablet (雷公藤多苷片) for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Efficacy of green tea extract on PC3 prostate cancer cells through upregulation of miR-195 expression and suppression of epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- Qilan preparation (芪蓝颗粒) inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by down-regulating microRNA-21 in human Tca8113 tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells
- Tenglong Buzhong granules (藤龙补中颗粒) inhibits the growth of SW620 human colon cancer in vivo
- Yajieshaba prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal barrier injury via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis
- Antihepatofibrotic effect of Guizhifuling pill (桂枝茯苓丸) on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice
