Protective efficacy of dark chocolate in letrozole-induced ovary toxicity model rats: hormonal,biochemical,and histopathological investigation
2022-10-14NaserMiraziSheidaHesamiAlirezaNourianAbdolkarimHosseini
Naser Mirazi,Sheida Hesami,Alireza Nourian,Abdolkarim Hosseini
Naser Mirazi,Sheida Hesami,Department of Biology,Faculty of Basic Sciences,Bu-Ali Sina University,Hamedan 6517433391,Iran
Alireza Nourian,Department of Pathobiology,Faculty of Veterinary Science,Bu-Ali Sina University,Hamedan 6517433391,Iran
Abdolkarim Hosseini,Department of Animal Sciences and Biotechnology,Faculty of Life Sciences and Biotechnology,Shahid Beheshti University,Tehran 1983969411,Iran
Abstract OBJECTIVE: To assess the protective effect of dark chocolate (DC) on the letrozole-induced rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).METHODS: In this experimental study,32 female Wistar rats,weighing (200 ± 20) g,were randomly categorized into 4 groups including control,letrozole (1 mg·kg-1·d-1),metformin (500 mg·kg-1·d-1) along with letrozole,and DC (500 mg·kg-1·d-1) along with letrozole for 28 d by oral gavage.Twenty-four hours after the last supplementation,direct blood sampling was taken from the heart to obtain blood serum for evaluation of sex hormones and gonadotropins,oxidative parameters,inflammatory cytokines,and ovarian tissue was examined for histology.RESULTS: The DC treatment significantly improved PCOS signs,as demonstrated by the significant restoration of ovarian morphology and physiological functions as compared with the letrozole group.DC treatment also decreased ovarian interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α levels and improved total oxidative/antioxidative status as compared with the letrozole group.CONCLUSIONS: Treating the animals with DC could alleviate the PCOS symptoms and reduced the toxic effects of letrozole in the ovary.This effect may mediate through antioxidant and antiinflammatory properties.
Keywords: chocolate;letrozole;metformin;polycystic ovary syndrome;antioxidants; anti-inflammatory agents
1.INTRODUCTION
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine and metabolic disorder in women at reproductive age with a genetic origin.1PCOS is a heterogeneous multifactorial disorder that is genetically complex and is associated with endocrine disorders,characterized by menstrual disruption,clinical and biochemical manifestations,and polycystic ovaries.The detrimental and numerous effects of this syndrome on physiology and metabolism of the body have led to its recognition as a metabolic syndrome with observable abnormalities such as dyslipidemia,obesity,and hypertension which in the long term produce serious side effects,such as type 2 diabetes,cardiovascular diseases,as well as endometrial and breast cancers.2This syndrome is influenced by environmental factors including diet,lifestyle,and social status.Common clinical symptoms in PCOS include insulin resistance,hyperandrogenism,anovulation,and ultimately infertility.3The progression of the disease results in anovulation,which prevents the follicles in which the egg grows from opening,thus forming a cyst.3,4In PCOS,several endocrine disorders reinforce and intensify each other.These disorders include impaired hypothalamicpituitary-ovarian function and adrenal function.In fact,PCOS is associated with abnormal secretion of gonadotropins [luteinizing hormone (LH),folliclestimulating hormone (FSH)],increased secretion of ovarian steroids,and insulin resistance.5Currently,PCOS treatment is based on chemical mediators such as clomiphene citrate,tamoxifen,metformin,and glucocorticoids;however,the efficiency of these treatments is inadequate because of their major side effects,including psychological perturbation,suboptimal pregnancy rates,muscle pain,nausea,and diarrhea.6So,need for finding new strategies and treatments alternatives with fewer adverse effect is more growing.
Natural products and generally antioxidant-rich substances has consistently been shown to have had significant effects on the prevention,control,and in some cases,treatment of various diseases.Medicinal herbs are rich in polyphenolic and flavonoid compounds.These compounds improve PCOS due to their antioxidant and phytoestrogenic properties by decreasing cystic follicles(CF) and increasing mature follicles as well as corpus luteum (CL).7,8Antioxidants neutralize the effect of free radicals and prevent lipid peroxidation and other processes caused by free radicals.9Cocoa,scientifically known asTheobroma cacao,is a tree from the Malvaceae family that is 4-10 m high.Cocoa contains flavonoids and polyphenols including catechins,epicatechins,procardinsand,and procyanidins.10The epicatechin content of cocoa is primarily responsible for its favorable pharmacological effect on vascular endothelium,which is the result of both acute and chronic upregulation of nitric oxide (NO) production.Epicatechins improve vascular function,decrease blood pressure,improve insulin sensitivity,and decrease platelet activity.11Also,catechin and epicatechin have been shown to stimulated testosterone production by acting on rat Leydig cells via the mechanism of increasing the action of cAMP.12
Since the effects of dark chocolate (DC) on the improvement of or protection against PCOS have not been studied to date,this study investigated the effects of DC on PCOS and changes in serum levels of gonadotropin hormones.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Animals and their maintenance
In this experimental study,32 female Wistar rats[weighing (200 ± 20) g,60-70 d old] were purchased from Hamadan University of Medical Sciences and transferred to the animal room of Bu-Ali Sina University.The rats were maintained at (22 ± 3) °C and 50%-60%humidity with 12 h light cycle and 12 h dark cycle.The rats had free access to water and food.To acclimatize the animals with the new atmosphere,the experiments were performed two weeks after the rats were accommodated.All conducted experiments pertaining to animal rights and conservation in this study were in accordance with the standard ethical guidelines (European Communities Directive 2010/63/EU) and were approved by the Local Ethics Committee at the Bu-Ali Sina University (ethic code number: IR.BASU.REC.1398.036).
2.2.Determination of estrous cycle and induction of PCOS
For 10 d before the experiment,the estrous cycle was examined by obtaining vaginal smear and light microscopic observation of the estrous cycle stages(proestrus,estrous,metestrous,diestrous) in the respective animals.After a vaginal smear test,the animal which having 2 or 3 regular estrous cycles,was used for the study.The induction of PCOS was followed based on previous work;each rat was given 1 mg·kg-1·d-1body weight letrozole to induce PCOS.13Vaginal smears were examined daily,and the animals were considered to be developing follicular cysts if cornified cells were observed in the smears for 10 consecutive days.14Also,at the end of the experiment in the estrous stage the animal sacrifice and samples were taken from them.
2.3.Experimental design and grouping
Letrozole and metformin were obtained from Arya Pharmaceuticals Company (Tehran,Iran).DC,containing 96% cocoa solids (cocoa butter,cocoa mass,cocoa powder,E322,and vanilla),was obtained from Parmida Company (Tehran,Iran).The rats were randomly divided into four groups of eight: Group I(control) received normal saline only,Group II received normal saline and letrozole (1 mg·kg-1·d-1),Group III received metformin (500 mg·kg-1·d-1) along with letrozole,and Group IV supplemented with DC (500 mg·kg-1·d-1) along with letrozole for 28 d by oral gavage.Metformin and DC doses were selected based on previously published work.15,16At least a one-hour interval between letrozole supplementation and metformin or DC was observed.
2.4.Determination of animal body weight
The body weight of the rats was measured at the beginning and at the end of the experiment for monitoring the effect of treatments on body weight.
2.5.Blood sampling and isolation of animal serums
The rats were euthanized 24 h after the last treatment using a chamber prefilled with carbon dioxide (CO2) gas with a concentration of 70% which,is a common and safe method for euthanizing.17Approximately,5 mL of blood samples were taken by cardiac puncture of each animal and poured into the test tubes and the names of each group were recorded.After one hour,the samples were centrifuged for 10 min by blood centrifugation at 3000 rpm and their serums were separated for measurement of hormonal,oxidative,and inflammatory cytokines levels.
2.6.Assessment of hormonal,oxidative,and inflammatory cytokines levels
For measurement of serum LH,FSH,testosterone,and estradiol levels the ELISA Kit (ZellBio GmbH,Lonsee,Germany) and ELISA reader device (BioTek ELx808,San Diego,CA,USA) were used.The sensitivity of the kit for rat LH,FSH,testosterone,and estradiol was 0.05 mIU/mL,0.12 mIU/mL,0.02 ng/mL,and 4.45 pg/mL respectively;also,the intra-assay coefficients of variation (CV) for these hormones were less than 10%based on manufacturer instruction.
In order to gauge the amount of serum superoxide dismutase (SOD),malondialdehyde (MDA),levels the ELISA Kit (ZellBio GmbH,Lonsee,Germany) and ELISA reader device (BioTek ELx808,San Diego,CA,USA) were used.The sensitivity,intra-assay CV,and inter-assay CV of the kit for SOD were 1 U/mL,5.8%,and 7.2% respectively.The sensitivity,intra-assay CV,and inter-assay CV of the kit for MDA were 0.1 μmol/mL,5.8%,and 7.6% respectively based on manufacturer instruction.
For assessment of serum interleukin (IL)-1β and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α levels in serum the ELISA Kit(Diaclone SAS,Besancon Cedex,France),and ELISA reader device (BioTek ELx808,San Diego,CA,USA)were used.The sensitivity of the kit for rat IL-1β and TNF-α were 4.4 and 15 pg/mL respectively;also,the intra-assay CV for these parameters was < 10%,and 8.2%respectively based on manufacturer instruction.
2.7.Histopathological staining
After the incision of the abdomen of each animal,the ovary tissue was removed and washed with ice cold saline and transferred to a 10% formalin-containing container (having 10 times of the sample volume).In the next step,tissues were dehydrated and embedded for histological examination.From these tissues,5μ-size sections (10 sections for each block) were prepared and stained through the hematoxylin-eosin method.The elicited slides magnified at 100 were scrutinized for microscopic studies.
2.8.Statistical analyses
The data were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) or median (min,max).The normality of data was checked by the normality test.The data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism version 8.0.0 for Windows (GraphPad Software,San Diego,CA,USA,www.graphpad.com) and based on the nature of normality result,variables compared with the one-way analysis of variance or Kruskal-Wallis test was used to determine the level of significance.If significant,then the Tukey or Dunn's post-test would be used.The significance level was set at 0.05 to interpret the results of the tests used.
3.RESULTS
3.1.Effect of different treatments on the body weight
As shown in Table 1 at the beginning of the study there were no significant differences between different groups in terms of body weight.Abnormal gaining of weight was observed in letrozole treated groups (P< 0.001).Treatment with either DC or metformin alleviates this condition and animal return to normal body weight in comparison with the letrozole group.
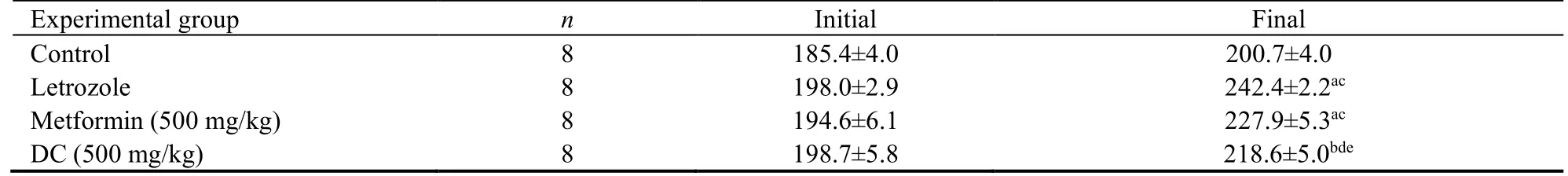
Table 1 Comparison of the body weight in the experimental groups at beginning and end of experiment
3.2.Results of histopathological studies
Ovaries of the control group demonstrated histological characteristic of a typical ovary,with no CF (Figure 1A).Letrozole group had ovaries lacking of large secondary follicles (SF),graafian follicles (GF),or CL,and were characterized by the existence of CF (Figure 2B).Metformin group had SF and a few CL (Figure 2C).DC group displayed the same characteristics as the metformin group,plus they had GF,and having less CF in compare to the metformin group (Figure 2D).This suggests that treatment with DC (500 mg/kg) displayed a more protective effect in the ovary of rats with PCOS.Figure 2A-2F shows the quantitative examination of ovarian histology.The percentage of CF in the letrozole group was significantly greater as compared with the control group (P< 0.001).Also,animals in the letrozole group had a significantly lower percentage of CL compare to the control group (P< 0.001);also,there was a significant difference between the letrozole and the groups treated with DC (P=0.001).The mean GF was significantly lower in the letrozole rats as compared with the control group (P< 0.001).Treatment with DC normalizes the GF,such that the difference in the number of GF was significant between DC-treated groups and the letrozole group (P=0.021).There are no significant differences in the mean percentage of either in primordial follicles (PMF),primary follicles (PF),or SF from the ovaries of letrozole or DC treated as compared with the control group.
3.3.Effect of DC on the sexual hormone and gonadotropins level
Figure 3A-3E shows the changes in the serum levels of the sexual hormone and gonadotropins after treatments either with letrozole or DC.The amount of LH in the letrozole-treated group revealed a significant increase(P< 0.001).Treatment with metformin or DC showed a significant decrease compared to the letrozole group(P=0.002 andP< 0.001,respectively) (Figure 3A).The amount of FSH in the letrozole-treated group unveiled a significant decrease (P< 0.001).This hormone in the experimental metformin group compared with the letrozole group did not show a significant increase,butthere is a significant increase in the experimental DC group compared to the letrozole group (P< 0.001)(Figure 3B).The level of LH/FSH ratio in the letrozoletreated group demonstrated a significant increase (P<0.001);the level of this ratio in the experimental metformin group was higher compared to the control group (P=0.015).DC demonstrated a significant decrease compared to the letrozole group (P< 0.001) in term of the LH/FSH ratio (Figure 3C).The amount of testosterone in the letrozole-treated group revealed a significant increase (P< 0.001).Treatment with DC showed a significant decrease compared to the letrozole group (P< 0.001) (Figure 3D).The amount of estradiol in the letrozole-treated group unveiled a significant decrease (P< 0.001).This hormone in the experimental metformin group compared with the letrozole group did not show a significant difference.However,there is a significant increase in the experimental DC group compared to the letrozole group (P=0.010) (Figure 3E).
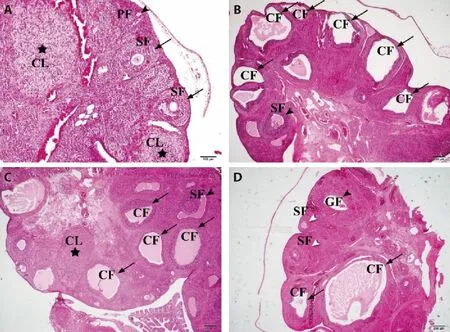
Figure 1 Micrographs of the ovary in the different experimental groups
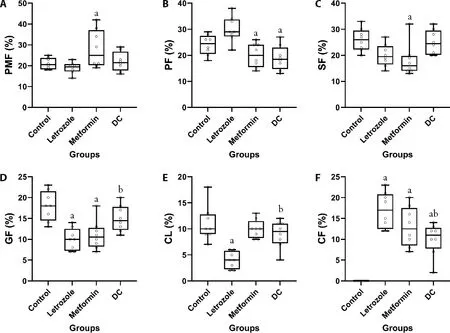
Figure 2 Quantitative examination of the histology of ovarian tissue in the control,letrozole,metformin,and DC group
3.4.Effect of DC on the oxidative damage
The evaluation of serum levels of SOD revealed that letrozole significantly decreased the enzyme levels in rats (P=0.006).Treatment with metformin although did increase SOD,did not show a significant difference with the letrozole group.This result for the group receiving DC significantly increased SOD enzyme compared to the letrozole group (P=0.039) (Figure 4A).The results of the serum levels of MDA in the tested rats indicated that the use of letrozole significantly augmented the serum level of MDA in rats (P< 0.001).This was significantly reduced in the DC treatment group compared to the letrozole group (P=0.010) (Figure 4B).
3.5.Effect of DC on the inflammatory cytokines
Findings of the serum levels of IL-1β in the blood of the tested rats designated that letrozole significantly increased IL-1β levels in the group treated by this drug(P< 0.001).On the other hand,the use of metformin significantly decreases the IL-1β,compared to the letrozole groups (P=0.010).However,the use of DC significantly decreased the IL-1β in comparison with the letrozole group (P< 0.001) (Figure 5A).The results of serum levels of TNF-α in the assessed rats indicate that while the use of letrozole in the treatment of rats significantly increases the serum level of TNF-α in this group in comparison with the control (P=0.003),the use of metformin in the tested rats did not cause a significant decrease in the serum level of TNF-α in comparison with the letrozole group.The results also unveiled that the levels of TNF-α serum in the blood of rats receiving the DC were significantly decreasedvs.the group receiving the letrozole (P=0.040) (Figure 5B).
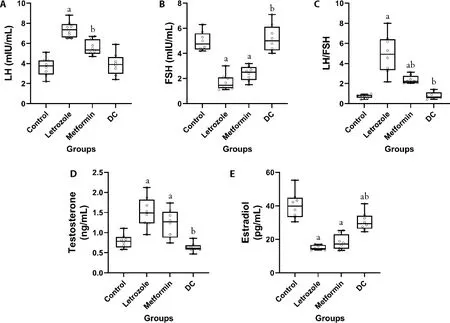
Figure 3 Comparison of the sexual hormone and gonadotropins level in control,letrozole,metformin,and DC group
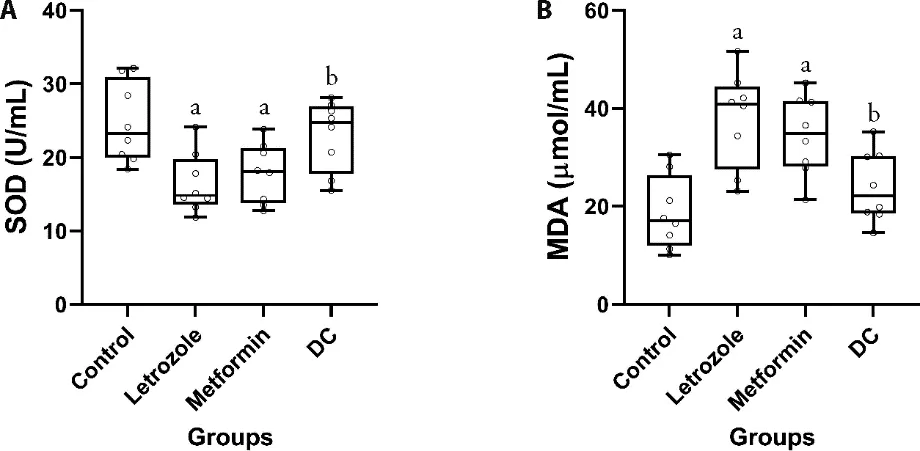
Figure 4 Comparing the serum level of SOD and MDA in the control,letrozole,metformin,and DC group
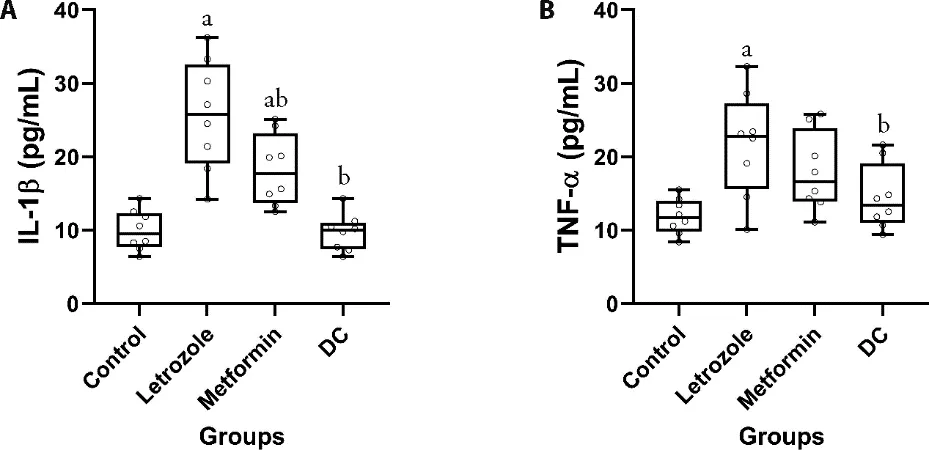
Figure 5 Comparing the serum level of IL-1β and TNF-α in the control,letrozole,metformin,and DC group
4.DISCUSSION
Observations from the present study indicate that DC has a protective role in letrozole-induced PCOS and significantly changes serum levels of markers such as gonadotropins,estradiol,testosterone,and inflammatory factors in the blood serum compared to control groups.Research findings can be summarized as follows: DC improves rats with PCOS,which is specified by decrease in LH,LH/FSH ratio,and testosterone,increase in FSH,and estradiol.Also,increase in SOD and decrease in MDA activity,decreased IL-1β,and TNF-α levels,and increase in the number of CL and a decrease in the number of CF in histological studies.
The results of the present study showed that letrozole causes follicular cysts in rats.Letrozole is a non-steroid aromatase inhibitor that has great potential to inhibit the aromatase enzyme.This enzyme catalyzes the estrogen biosynthesis of androgens.Decreased aromatase activity disrupts the synthesis of estrogens in the ovarian tissue and ultimately induces PCOS.18This finding in harmony with the result of current study which is letrozole decrease the estradiol level in animal with PCOS.Also,the result of the current study indicated that DC causes augmentation of estradiol,and FSH levels,and increase in testosterone,LH/FSH ratio in treated groups compared to the letrozole group.So,DC may likely affect the estradiol,and testosterone levels,and the LH/FSH ratio and ultimately improve PCOS condition.
Since inflammation and disruption of antioxidant levels are great importance in the pathology of PCOS,19the serum levels of SOD and MDA,were measured in order to investigate the antioxidant effects of DC in the present study.The results of this study showed that DC increases SOD and decreases MDA.These findings are consistent with studies that approved antioxidant effects of DC,20-22it is expected that DC may improve PCOS in this way.Previous studies have indicated the relationship between SOD activity and estrogen level and other steroid hormones.23It has been shown that SOD is able to reduce the estrogen in Granulosa cells inin vitrocondition by blocking of CYP19 activity.24In addition,SOD cause to inhibit the LH secretion in sheep.25Therefore,due to the antioxidant property of DC and its effect on the increase of SOD activity,it is possible to justify the hormonal regulation by DC.
Chronic inflammation is one of the most important factors in PCOS pathology.The elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β,and TNF-α have been shown in many studies concerning PCOS.26,27In the present study,DC prevents increased levels of inflammatory cytokines.These results consistent with previous studies which are reported the protective effect of DC on inflammation.28,29DC contains polyphenols could inhibit nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)activation.30,31Many studies have shown that NF-κB is a transcription factor that regulates genes responsible for the inflammatory process.32,33In the current study the reduction of inflammatory cytokines by DC at least in part,may be related to the inhibition of NF-κB activation.34
Studies from morphological observation of ovarian tissue have shown that the PCOS condition is characterized by a reduction in CL and an increase in CF.8In the present study,DC reduced CF in rats with PCOS.In PCOS,increased oxidative stress,inflammation,and dysregulated hormonal level play an important role in developing the ovarian cysts.26As a consequence,it can be concluded that DC helps to inhibit OS,inflammation,and increase estradiol levels by inhibiting the release of free radicals in PCOS rats,leading to decreased CF and increases in normal follicles and CL.
Since PCOS is often associated with obesity,metabolic syndrome,gestational diabetes,cardiovascular issues,it is not surprising that PCOS patients with insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism are treated with metformin.We use metformin as a reference drug to compare the effect of metformin and DC on PCOS condition.As shown in the present study the DC is having the same results as metformin.At the cellular level,metformin has been observed to regulate oocyte maturation by activation and regulation of 5' AMPactivated protein kinase (AMPK).35Also,it has been suggested that DC like metformin could increase AMPK activity.36This observation is very important for DC as a natural product which has minimal side effect against the chemical agents such as metformin.Our study has some limitations that should be considered.As limitations,our study did not evaluate the other biochemical and molecular parameters which very important such as lipid levels,insulin,other inflammatory cytokines,gene expression of steroidogenic pathway due to limited funding,and sample size.Therefore,supplementary studies need to justify the result and beneficial effect of DC on the PCOS condition.
In conclusion,the results of this study suggest that the DC (as natural products) has protective effects on letrozole-induced PCOS,which may be pertained to the promising antioxidant capacity and anti-inflammatory activities that might ameliorate the complications,and they might be able to regenerate the ovarian morphology to the normal state.These results may pave the way for randomized clinical trials on DC,which will help researchers in introducing new treatments for PCOS patients.
杂志排行
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Effectiveness and safety of tripterygium glycosides tablet (雷公藤多苷片) for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Efficacy of green tea extract on PC3 prostate cancer cells through upregulation of miR-195 expression and suppression of epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- Qilan preparation (芪蓝颗粒) inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by down-regulating microRNA-21 in human Tca8113 tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells
- Tenglong Buzhong granules (藤龙补中颗粒) inhibits the growth of SW620 human colon cancer in vivo
- Yajieshaba prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal barrier injury via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis
- Antihepatofibrotic effect of Guizhifuling pill (桂枝茯苓丸) on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice
