Drug response biomarkers of Pien Tze Huang (片仔癀) treatment for hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride
2022-07-20ZHANGDiWEIMuyunCHENLuanWUHaoWANGTingZHANGZhiruoZHANGYingYUJuanHUANGJinmingZHUJinhangQINShengying
ZHANG Di,WEI Muyun,CHEN Luan,WU Hao,WANG Ting,ZHANG Zhiruo,ZHANG Ying,YU Juan,HUANG Jinming,ZHU Jinhang,QIN Shengying
ZHANG Di,ZHU Jinhang,School of Life Sciences,Anhui Medical University,Hefei 230032,China
ZHANG Di,WEI Muyun,CHEN Luan,WU Hao,WANG Ting,ZHANG Zhiruo,ZHANG Ying,ZHU Jinhang,QIN Shengying,Bio-X Institutes,Key Laboratory for the Genetics of Developmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders,Ministry of Education,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200030,China
YU Juan,HUANG Jinming,Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Pien Tze Huang Natural Medicine Research and Development,Zhangzhou Pien Tze Huang Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,Zhangzhou 350000,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE:To explore biomarkers of Pien Tze Huang(片仔癀) that ameliorated the symptoms of hepatic fibrosis.METHODS:Two groups of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis (HF) mice model were constructed in our study:one group received PZH treatment and another group received no treatment.We performed this study to investigate the role of PZH in the regulation process of hepatic fibrosis.RESULTS:We identified 31 down-regulated and 39 upregulated miRNAs using small RNA-seq analysis.Combining RNA-Seq data analysis,our study revealed 7 significant target genes (Sp4,Slc2a6,Tln2,Hmga2,Ank3,Pax9,Fgf9).The results of real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis suggested that the expression level of 6 genes (Sp4,Tln2,Hmga2,Ank3,Pax9,Fgf9) were down-regulated compared to control group.On the other hand,the expression level of Slc2a6 appeared to be up-regulated.The protein mass spectrometry showed that PZH group had lower protein expression of Tln2 compared to control group.CONCLUSION:We identified 7 genes that were significantly related to PZH response in HF mice using multiple conjoint analysis methods.These genes could participate in underlying regulation mechanism of hepatic fibrosis during PZH treatment.
Keywords: liver cirrhosis;biomarkers;RNA-Seq;carbon tetrachloride;fibroblast growth factor 9;Pien Tze Huang
1.INTRODUCTION
Hepatic fibrosis (HF) is a spontaneous healing reaction caused by chronic or acute hepatitis,medical damage and immune attack.1In addition,HF plays an important role in development of the liver cancer.It is the main cause of terminal hepatocellular carcinoma.Recent studies have shown that the occurrence of HF increased the morbidity rate of liver cancer.3It has been noticed that the liver tissues generated inflammatory response that often developed into HF if the patients were not treated in time.4A recent study has found that suppressing hepatic inflammation response may be one effective therapeutic intervention point for HF treatments.6However,there are still no satisfactory therapies for this disease up till now.
Previous studies have revealed multiple signaling pathways that played important roles in the development of hepatic fibrosis,such as transforming growth factor β(TGF-β) signaling pathway,PI3K-AKT signaling pathway,Rap1 signaling pathway,platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling pathway and mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway.5Additionally,excessive deposition of the extracellular matrix (ECM) has been found to damage hepatic tissue and the organic functions,resulting in hepatic fibrosis.6Pien Tze Huang (片仔癀) is a traditional herbal Chinese formula that was first documented in the Ming Dynasty.It has been widely applied to treat various types of cancer,inflammation and liver diseases.7PZH is primarily consisted of musk,gallstone of the ox,San qi and snake’s gall.8Currently,the use of PZH drug to treat HF is only limited to China and Southeast Asia regions.9In a recent study using carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induced mice model,PZH has been shown to relieve the severity of the hepatic injury symptoms.14Similarly,a number of reports have indicated that PZH drug exerted a preventive influence on CCl4-induced liver injury or fibrosis.16,17
MicroRNA,also called miRNA,is a type of non-coding RNA with length ranging from 20 to 24 nucleotides.18,19It has been shown to have a negative influence on expression of genesviabase-pairing complementary sequences combination at the 3’ ends of mRNA molecules.20The main functions of miRNA are regulation of the gene expression in post-transcriptional level and suppression of gene transcription and degradation of mRNA through RNA silencing.20-22MiRNA regulates most of the cellular metabolic processes that are highly involved in the emergence of various diseases and abnormal metabolic status in both human and animals.23It has been demonstrated that the expression level of miRNA was significantly changed in HF patients24,25and miRNA might actively participate in the development process of HF.
A number of studies have demonstrated that PZH drug ameliorated hepatic injury and fibrosis.However,the role of miRNA in the regulation process in the PZH treatment of HF remained unveiled.It is still unclear how miRNA regulate the development process of HF.Currently,effective treatment strategies for patients with hepatic diseases are still yet to be designed.Therefore,this study aimed to identify important miRNA and gene biomarkers of the therapeutic effect of PZH in hepatic fibrosis mice.Our results provide critical perspectives for future studies of PZH treatment for hepatic fibrosis patients.
2.MATERIALS AND METHOADS
2.1.Ethical statement
The mice used in the experiment was obtained from Shanghai Southern Model Animal Center.The animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health of China for the care and use of laboratory animals.All the animal works were approved and conducted under the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,China.
2.2.HFmouse model using CCl4,the dose and treatment duration of PZH
Thirty mice received intraperitoneal injection of 10 µL/g solvent mixture of CCl4and 10% corn oil twice a week.
These mice were randomly assigned to ‘PZH group’ and‘Control group’.The 15 mice in PZH group received 0.25 mg/g of the PZH intragastric administration once a day.In comparison,the other 15 mice in the Control group received double distilled water intragastric administration once a day.The treatment duration of PZH was 8 weeks.Three mice were killed every two weeks from first to sixth weeks in both groups.Finally,all the remaining mice were killed in the eighth week.
2.3.Staining methods of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA)
Liver tissue fragments of approximately 1 cm3extracted from mouse livers were fixed using 10% formalin.After liver tissues were sliced,all sections were incubated overnight with α‐SMA antibody in a 4 ℃ humidified box.The anti-α-SMA antibody was used to make α-SMA immunofluorescence and sections were counterstained with DAPI.
2.4.Reagents preparation
PZH medicine was provided and authenticated by Zhangzhou Pien Tze Huang Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.(China Food and Drug Administration approval no.Z35 020242;Zhangzhou,China).The α-SMA antibody was obtained from Solarbio Science &Technology Co.,Ltd.(Beijing,China).Phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS),Dulbecco Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were purchased from Thermo fisher technology co.,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).We purchased 30 mice from Shanghai Southern Model Animal Center.
2.5.Small RNA library construction,miRNA of genome and database annotation
After 8 weeks,the liver tissues of remaining 12 mice were harvested and small RNAs were extracted.The tissue was stored at low temperature (Minus 80 degrees Celsius) before performing miRNA sequence analysis.According to manufacturer’s instructions,the total small RNA from each sample was extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Camarillo,CA,USA).The small RNA library was constructed using the authoritative methods of Illumina TruSeq Small RNA kit.The libraries were sequenced on an HiSeq 2000 by Fujun Bioinformatics Technology Co.,Ltd.,and 50 bp singleend reads were generated.3’ adaptor was TGGAATTCTCGGGT-GCCAAGG.Sequence adaptor was trimmed to ensure the quality of the data.
We used Fastqc (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/)) and Cutadapt (https://pypi.org/project/cutadapt/) softwares to filter the raw data (The original data obtained from NCBI website GSE137100)of miRNA sequences.The BWA software (https://sourceforge.net/projects/bio-bwa/files/)) was used to map the data to genome of mouse.Finally,we used both miRbase (http://www.mirbase.org/) and Rfam(http://rfam.xfam.org/) database to map the data into genome to obtain the final reads count and the types of small RNA.
2.6.Differential expression analysis of miRNA,miRNA target prediction
DESeq2 package in R was used to identify the differentially expressed miRNA.The miRNAs with log2FC (Fold change) >1 or log2FC <-1 and adjustedPvalue <0.05 were defined as threshold of differentially expressed miRNAs.The 3’ UTR,5’ UTR and CDS region of target gene were regarded as miRNA binding sites.Target genes were identified using 3’ UTR plus CDS,5’ UTR plus CDS and 5’ UTR plus 3’ UTR methods by miRwalk 3.0 version website (http://mirwalk.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/).The genes that were annotated using both TargetScan and MiRanda were defined target gene.
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)enrichment analysis was performed to explore the roles of these identified miRNAs using David website(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/).We then identified the differentially expressed genes using RNA sequencing that were also found by all 3 methods (3UTR plus CDS,5UTR plus CDS and 5UTR plus 3UTR).26-28The shared genes were considered as biomarker candidates of PZH treatment response in hepatic fibrosis mice in further analysis.
2.7.Differential expression analysis of mRNA
We used the RNA-seq data from a study that used the same modeling method (PZH treatment and without treatment groups) to reduce miRNA target genes numbers (GEO:GSE133481).The clean data was obtained after removing the adaptor,trimming low quality reads and fragment from raw data using the Trimmomatic software (http://www.usadellab.org/cms/index.php?page=trimmomatic).The FastQC software was used to assess the quality of the clean data(http://darlinglab.org/ tutorials/fastqc/).The fragments of clean reads from raw data were mapped to the genome of mouse using HiSat version 2.1.0 (http://ccb.jhu.edu/software/hisat2/ index.shtml).The HTSeq version 0.11.1 was used to estimate the gene expression counts and perform gene name annotation (https://htseq.readthedocs.io/en/release_0.11.1/) using GTF files.Differentially expressed genes were identified using the DESeq2 package in R.The genes with log2FC >1 or log2FC <-1 and adjustedPvalue <0.05 were defined as threshold of significance.
2.8.Analysis of target genes using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR)
Validation of the up-regulated target genes were necessary to study the protective functions of PZH medicine treatment for HF.First,TRIzol® (Invitrogen;Camarillo,CA,USA) was used to isolate total RNA from LX-2 cell (ATCC company,Rockefeller,Marylabd,USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.The cDNA was synthesized with a PrimeScript RT Reagent kit (Takara;Shanghai,China) in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions.The quantitative PCR(qPCR) was carried out on an ABI7500 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems,Carlsbad,CA,USA) using a SYBR® Green PCR Master Mix (Solebao,Tokyo,Japen).TheGADPHwas regarded as the reference gene.The primer sequences of target genes are listed in the Table 1.
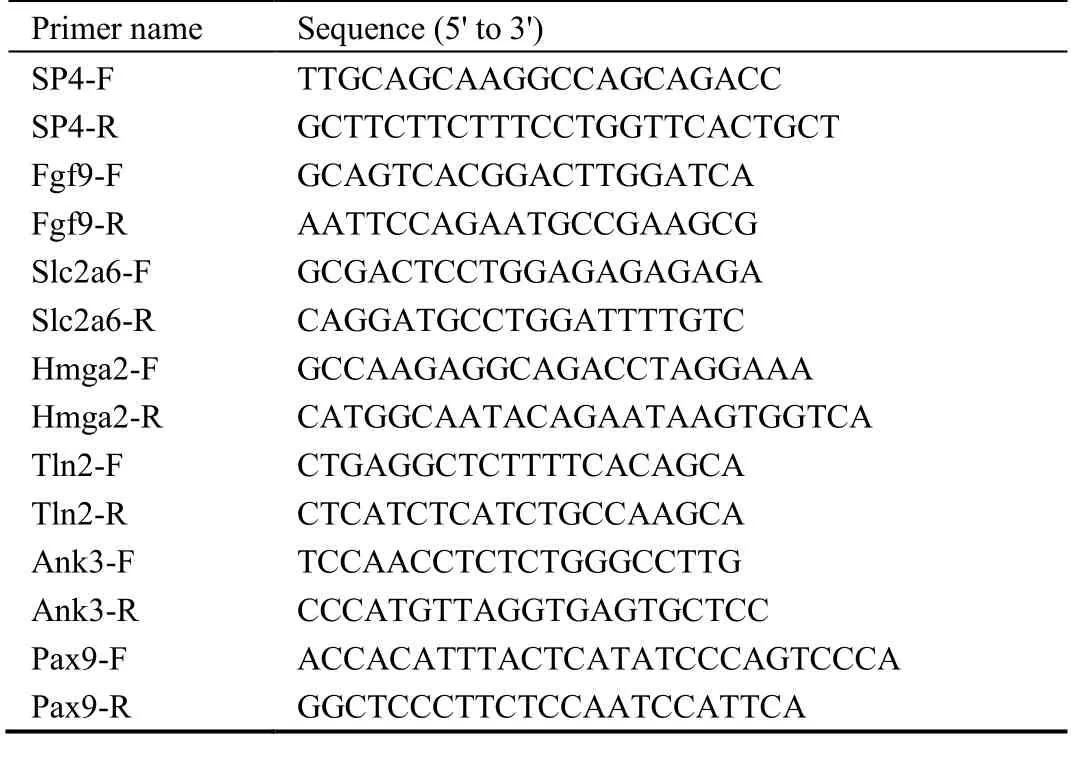
Table 1 Primer sequence of target genes
2.9.Cell culture,immunofluorescence assay and Protein mass spectrometry
PBS solution was used to wash the culture flask.The LX-2 cells (Human Hepatic Stellate cell) were cultured in DMEM and supplemented with 10% FBS.PZH medicine was configured into 20 mg/mL PZH.LX-2 cells were added to 6 well plates to culture for 0 to 48 h in the different concentrations medium.The cell line was grown at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2.Paraffin sections were cut into 4 µm slices,fixed in xylene,and dehydrated using grades ethanol reagents (from 70% to 80%,next 90%,95%,100%).Finally,tissue sections were made successfully.The immunofluorescence assay was conducted to detect the differential expressions of α-SMA of PZH and Control groups.Protein profiling was performed using liver tissues of mice after the 8 weeks of treatment.
3.RESULTS
3.1.Hepatic fibrosis model in mice
The immunofluorescence staining results of α-SMA are shown in Figure 1.They included immunofluorescence staining results using the liver tissues collected from mice treated by CCL4from the second,fourth,sixth and eighth week.The expressions of α-SM A,compared PZH with Control group,had no obvious difference in the second week.However,the expression levels of α-SMA were significantly lower than Control group from the fourth to eighth week.
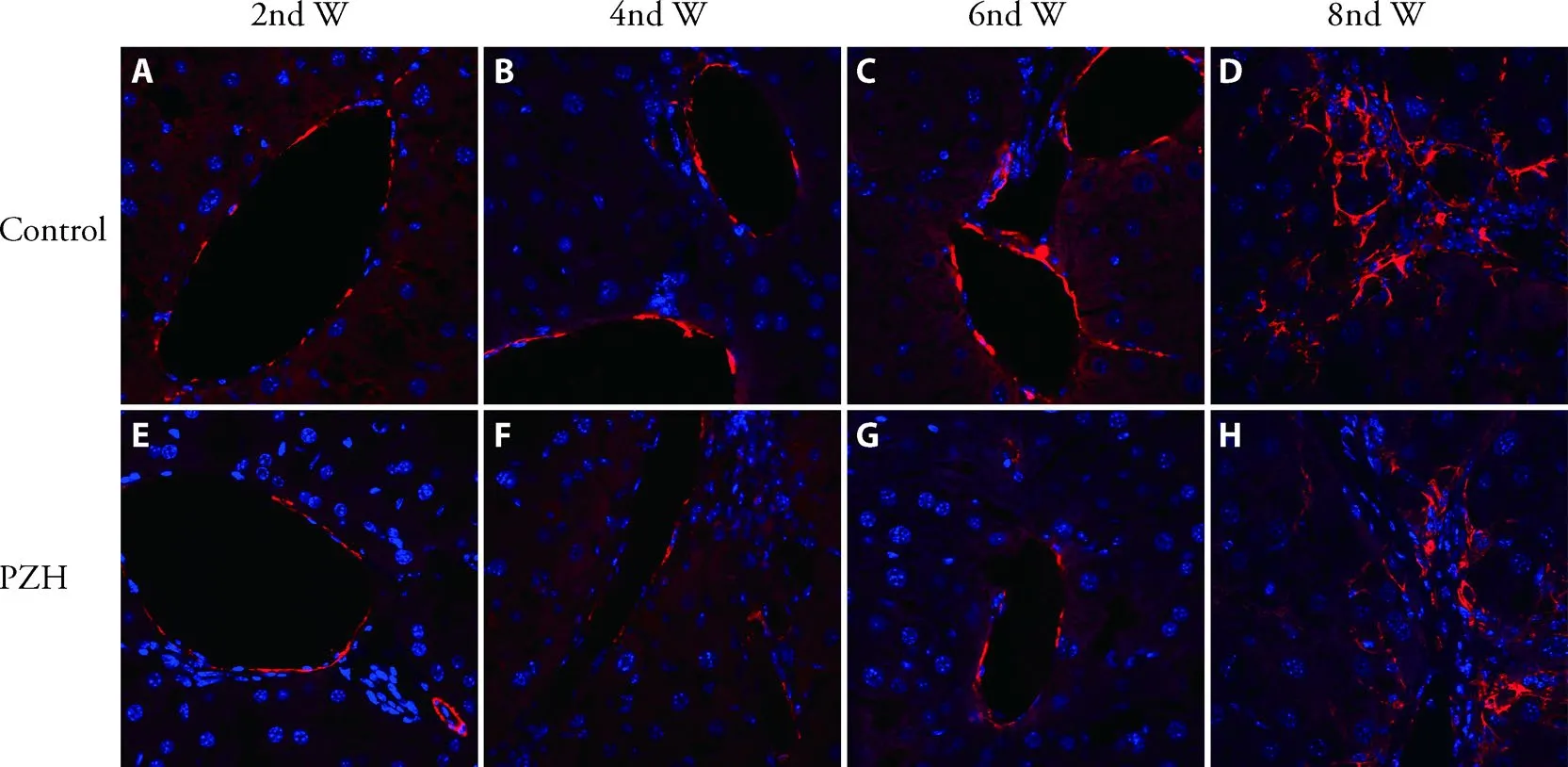
Figure 1 Expression level changes of α-SMA from second to eighth week (×400)
3.2.Sample quality,mapping ratio,ncRNA types,overall expression levels after quality control
Clean data was obtained after removal of the adaptor and Ploy-N of raw data and trimming the alleles with low quality.The quality control results are shown in Figure 2A,B.The median of the quality control (QC) score of the 12 samples was larger than 35,which assured the quality of the sequence data for further analysis.The distribution of miRNA lengths ranged from 19 to 25 nt and the peak of reads was 22 nt.The sequenced clean data was mapped to the mouse genome.The mapping ratios of 12 sample are shown into Figure S1.Samples with the smallest numerical value of mapping ratio was greater than 87%.The ratio of total samples mapped to genome ranged from 87% to 93%.The annotated miRbase dataset was classified by Rfam database again to obtain the percentage of every type of RNA in small RNAs (Figure 2C).The miRNAs were identified in every sample and their statistics satisfied the basic requirements for miRNA sequence analysis.Therefore,we adopted the log2(Nreads+1) to normalize the expression levels in every sample.In every sample,the total expression of miRNAs,represented by log2(Nreads+1),was smaller than 20 (Figure 2D).
3.3.Total cluster graph,clustering top 20 miRNAs and the volcano plot of differentially expressed miRNAs
The overall miRNA expression data was visualized using Pheatmap package in R (Figure 3A).The result suggested that specific miRNAs were differentially expressed in PZH-treated mice compared to the mice in Control group.The top 20 mostly differentially expressed miRNAs are shown in Figure 3B.Our results suggested that the expression levels of 5 miRNAs (mmumiR-370-3p,mmu-miR-377-3p,mmu-miR-434-5p,mmu-miR-541-3p,mmu-miR-409-5p) were upregulated and the remaining 15 miRNAs were downregulated in PZH-treated mice.In particular,mmu-miR-370-3p may serve as an important miRNA biomarker of PZH response in hepatic fibrosis mice.The expression levels of miRNA were visualized using volcano plot.The differentially expressed miRNA was defined as the miRNA with the log2FC >1 or log2FC <-1.The significance threshold of adjusted P-value was set to be 0.05.Subsequently,31 down-regulated and 39 upregulated miRNAs were identified,as shown in Figure 3C.The names and values of these differentially expressed miRNAs are listed in Table S1.
3.4.Results of KEGG functional enrichment analysis
The results of the functional enrichment analysis were visualized by bar graphs using ggplot2 package in R.The top 15 mostly enriched pathways are shown in the Figure 4A-4C.The results of KEGG analysis suggested that PI3K-Akt signaling pathway,TGF-beta signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Rap1 signaling pathway,MAPK signaling pathway were highly enriched in the identified miRNA biomarkers using all 3 methods (3’ UTR plus CDS,5’ UTR plus CDS and 5’UTR plus 3’ UTR).It was noted that AMPK signaling pathway was only enriched using the genes identified by 5’ UTR plus CDS method.

Figure 2 Results of sequenced data from quality control to miRNA expression
3.5.Validation of the target genes by identification of the common biomarkers among the miRNAs target genes and differentially expressed genes obtained from RNA-seq and qPCR analysis
Seven genes were identified to have significant influence on PZH treatment for hepatic fibrosis response using all 3 different methods as discussed above (3’ UTR plus CDS,5’ UTR plus CDS and 5’ UTR plus 3’ UTR),which are shown in Figure 5.These genes included Sp4,Slc2a6,Tln2,Hmga2,Ank3,Pax9,Fgf9.The expression level of the miRNAs,the predicted expression level of the target genes and the pathways that had been known to be related with these genes are listed in Table 2.The miRNAs that regulated the 7 genes (Sp4,Tln2,Hmga2,Ank3,Pax9,Fgf9) were selected to produce miRNAtarget gene network chart (Supplementary Figure 1).The qPCR technology was used to validate the target gene expression level of these 7 genes.The results of qPCR analysis suggested the expression levels of 5 genes (Sp4,Hmga2,Ank3,Pax9,Fgf9) were downregulated compared to control in the different drug concentration (0.25,0.75,1.50 mg/mL).In comparison,Slc2a6was found to be up-regulated compared to control group.It was noted that while the expression level ofTln2gene was down-regulated in the 0.75 and 1.50 mg/mL drug concentration,its expression level was up-regulated in 0.25 mg/mL drug concentration(Supplementary Figure 2).Protein profiling was performed using liver tissues of the mice after 8-week treatment.We found that the protein expression of Tln2 in PZH group was lower than that in Control group (P<0.01).
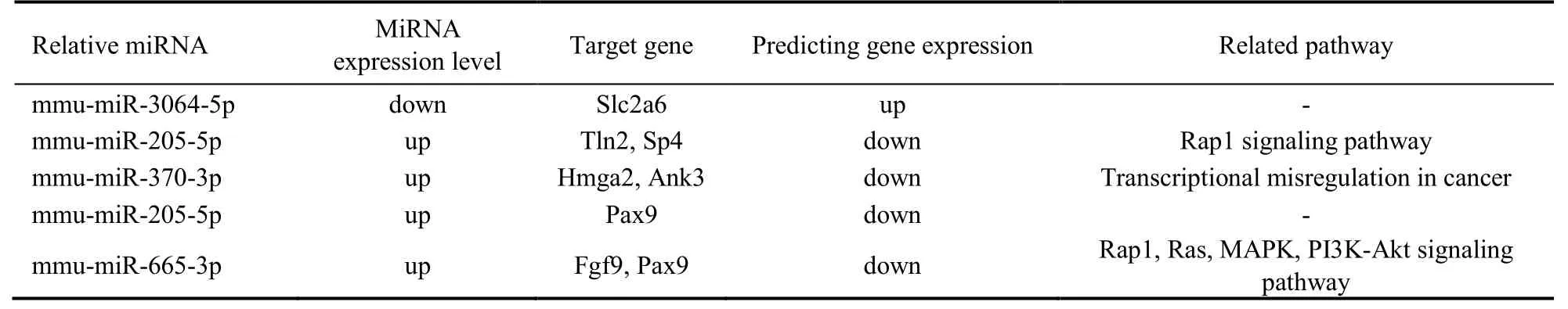
Table 2 Important miRNAs,their pathways and prediction expression level related with target genes
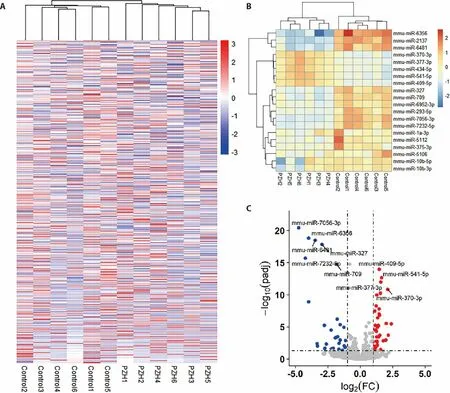
Figure 3 Analysis results of samples and differential expression miRNAs
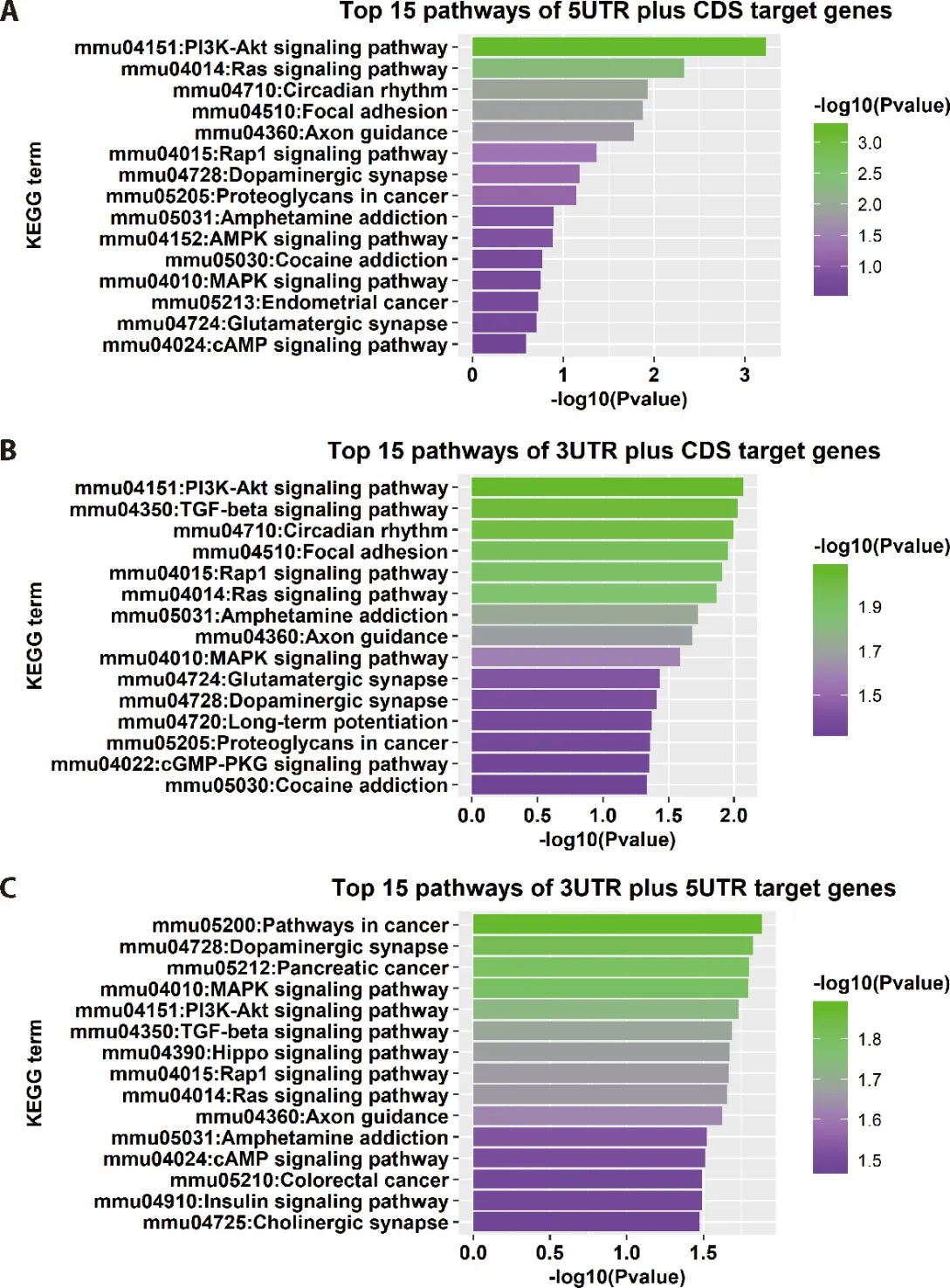
Figure 4 Analysis results of KEGG enrichment

Figure 5 Intersection of the genes differentially expressed miRNAs target genes and differentially expressed genes obtained from RNA-seq
4.DISCUSSION
PZH has been pervasively used as therapy of multiple cancer,inflammation and liver disease in China and Southeast Asia.10Although miRNAs have been known to play an important role on regulating the development of hepatic fibrosis,11there were no detailed miRNA studies of the effects of PZH in hepatic fibrosis.In this study,two groups of CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice model were constructed.One group received PZH treatment and another group did not receive any treatment.According to the staining result of α-SMA analysis,the expression levels of α-SMA appeared to be significantly lower than Control group in fourth,sixth and eighth week.This result of α-SMA staining suggested that PZH significantly alleviated the process of hepatic fibrosis.Using small RNA-seq analysis,we successfully identified 31 down-regulated and 39 upregulated miRNAs that may be related with PZH treatment effect in hepatic fibrosis mice.
The results of the pathway enrichment analysis suggested that the identified genes were actively involved in the regulation processes,including PI3K-Akt pathway signaling pathway,TGF-beta signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Rap1 signaling pathway,MAPK signaling pathway,APMK signaling pathway and antiinflammatory pathway.These pathways have been reported to have associations with the mechanism underlying hepatic fibrosis.In this study,these pathways were also annotated as important players in therapeutic effects of PZH drug treatment of hepatic fibrosis in mice.In addition,we found that some of these enriched pathways were related to the therapeutic functions of PZH drug,such as improving the immune system,reducing cell death and position regulation of gene silencing by miRNA.Therefore,PZH might regulate the anti-inflammatory,apoptotic and environmental pathway related genes in mouse model of CCl4induced hepatic fibrosis.PZH appeared to alleviate the severity level of hepatics fibrosis and improve the tolerance of CCl4induced hepatic fibrosis in liver cells.Our results suggested that there was a therapeutic effect of PZH in the CCl4induced hepatic fibrosis mice.
We identified 7 genes (Sp4,Slc2a6,Tln2,Hmga2,Ank3,Pax9,Fgf9) that were significantly related to the PZH response in HF mice using multiple conjoint analysis.The expression levels of these 7 genes were validated by qPCR method.The expression level of 7 genes were significantly changed after the subjects received PZH medication.Among them,two genes (Fgf9,Hmga2)have been reported to be related with hepatic fibrosis32,33in previous literatures.Fgf9,a sub-member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family,has been found to play an important role in regulating the development of Hepatic Stellate Cells (HSCs).Fgf9 increases the rate of hepatocyte proliferation and regeneration upon injury on CCl4environment exposure.12Hmga2,a gene encoded a protein that belonged to the non-histone chromosomal high mobility group (HMG) protein family,has been known to be relevant to the development process of hepatic fibrosis.13In addition,our study identified 5 novel genes (Sp4,Slc2a6,Tln2,Ank3,Pax9),including the transporter,transcription factor and protein coding genes,that have never been reported to be associated with hepatic fibrosis.These genes were identified to be targeted by mmu-miR-205-5p,mmu-miR-3064-5p,mmu-miR-205-5p,mmu-miR-370-3p,mmu-miR-665-3p in our study.Hmga2 and Ank3 were regulated by the mmu-miR-370-3p.Interestingly,two target genes among these 7 genes,Fgf9 and Tln2,were annotated by the Rap1 signaling pathway.
Through literature research,we found that 16 out of 70 miRNAs identified in our analysis had been previously reported to be closely associated with fibrosis.In particular,5 of them have been reported to be related with hepatic fibrosis.14A recent report has suggested that the expression of HF-related miRNAs changed in the process of fibro-genesis of liver tissue.9It has been revealed that the up-regulation of mmu-miR-370 attenuated the extent of CCl4induced hepatic fibrosis in previous study.39The results of this study discovered that PZH medication led to up-regulation of mmu-miR-370 and down-regulation of expression of corresponding target gene of mmu-miR-370.Therefore,PZH medication might has a preventive effect in the development of hepatic fibrosis.PZH medication might influence the expression level of those miRNAs or corresponding target genes to relieve the process of hepatic fibrosis.
Although we found several biomarkers related to PZH response in HF mice,these findings were not based on human liver tissue but the liver tissue of mouse.
Therefore,additional validation studies using human liver tissue are necessary before any conclusions are drawn about these influences of the candidate biomarkers on PZH drug response in human.
In sum,we utilized the mice hepatic fibrosis model to identify the genetic biomarkers of PZH response and to investigate the prevention mechanism of PZH in hepatic fibrosis.Our result suggested that the expression level of Fgf9 and Hmga2 genes might be independently regulated by mmu-miR-665-3p and mmu-miR-370-3p in the development process of hepatic fibrosis.The mmu-miR-370 can serve as potential marker of PZH treatment response to hepatic fibrosis.PZH drug alleviated the development of hepatic fibrosis by the Rap1 signaling pathway.Although the other 5 genes have not been reported to have association with hepatic fibrosis in previous study,we discovered that they could be separately regulated by these miRNAs (mmu-miR-205-5p,mmu-miR-3064-5p,mmu-miR-370-3p,mmu-miR-665-3p) that were involved in mechanism of PZH response in the hepatic fibrosis.Our discoveries provided important biomarker candidates of PZH drug response in hepatic fibrosis and liver injury.
5.REFERENCES
1.Friedman SL.Hepatic fibrosis:emerging therapies.Dig Dis 2015;33:504-7.
2.Toosi AE.Liver Fibrosis:causes and methods of assessment,a review.Rom J Intern Med 2015;53:304-14.
3.Xu F,Liu C,Zhou D,Zhang L.TGF-β/SMAD pathway and its regulation in hepatic fibrosis.J Histochem Cytochem 2016;64:157-67.
4.Kong LJ,Li H,Du YJ,et al.Vatalanib,a tyrosine kinase inhibitor,decreases hepatic fibrosis and sinusoidal capillarization in CCl4-induced fibrotic mice.Mol Med Rep 2017;15;2604-10.
5.Poilil Surendran S,George Thomas R,Moon MJ,Jeong YY.Nanoparticles for the treatment of liver fibrosis.Int J Nanomedicine 2017;12:6997-7006.
6.Altamirano-Barrera A,Barranco-Fragoso B,Mendez-Sanchez N.Management strategies for liver fibrosis.Ann Hepatol 2017;16:48-56.
7.Kagan P,Sultan M,Tachlytski I,Safran M,Ben-Ari Z.Both MAPK and STAT3 signal transduction pathways are necessary for IL-6-dependent hepatic stellate cells activation.PLoS One 2017;12:e0176173.
8.Wu L,Zhang Q,Mo W,et al.Quercetin prevents hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation and reducing autophagyviathe TGF-beta1/Smads and PI3K/Akt pathways.Sci Rep 2017;7:9289.
9.Ying HZ,Chen Q,Zhang WY,et al.PDGF signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis pathogenesis and therapeutics (Review).Mol Med Rep 2017;16:7879-89.
10.Huang Y,Fan X,Tao R,et al.Effect of miR-182 on hepatic fibrosis induced by Schistosomiasis japonica by targeting FOXO1 through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol 2018;233:6693-704.
11.Jung YK,Yim HJ.Reversal of liver cirrhosis:current evidence and expectations.Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:213-28.
12.Li SX,Mu Y,Zheng FY.Influence of gastrointestinal digestion and edible plant combination on oral bioavailability of triterpene saponins,using a biomimetic digestion and absorption system and determination by HPLC.J Agric Food Chem 2013;61:10599-603.
13.Qiu X,Luo H,Liu X,et al.Therapeutic potential of Pien Tze Huang on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis rat.J Immunol Res 2018;2018:2952471.
14.Qi F,Zhou S,Li L,et al.Pien Tze Huang inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by upregulating miR-16 expression.Oncol Lett 2017;14:8132-37.
15.Zhao J,Hu H,Wan Y,Zhang Y,Zheng L,Hong Z.Pien Tze Huang Gan Bao ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury,oxidative stress and inflammation in rats.Exp Ther Med 2017;13:1820-26.
16.Lee KK,Kwong WH,Chau FT,Yew DT,Chan WY.Pien Tze Huang protects the liver against carbon tetrachloride-induced damage.Pharmacol Toxicol 2002;91:185-92.
17.Yang Y,Chen Z,Deng L,et al.Pien Tze Huang ameliorates liver injury by inhibiting the PERK/eIF2alpha signaling pathway in alcohol and high-fat diet rats.Acta Histochem 2018;120:578-85.
18.Xin X,Zhang Y,Liu X,Xin H,Cao Y,Geng M.MicroRNA in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2014;19:1418-24.
19.Wang L,Zhu W,Dong Z,Song F,Dong J,Fu J.Comparative microRNA-seq analysis depicts candidate miRNAs involved in skin color differentiation in red tilapia.Int J Mol Sci 2018;19:1209.
20.Rupaimoole R,Slack FJ.MicroRNA therapeutics:towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases.Nat Rev Drug Discov 2017;16:203-22.
21.Vishnoi A,Rani S.MiRNA biogenesis and regulation of diseases:an overview methods.Mol Biol 2017;1509:1-10.
22.Zealy RW,Wrenn SP,Davila S,Min KW,Yoon JH.microRNAbinding proteins:specificity and function.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2017;8:10.1002/wrna.1414.
23.Dong Z,Li S,Wang X,et al.lncRNA GAS5 restrains CCl(4)-induced hepatic fibrosis by targeting miR-23a through the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2019;316:G539-50.
24.Roy S,Benz F,Luedde T,Roderburg C.The role of miRNAs in the regulation of inflammatory processes during hepatofibrogenesis.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 2015;4:24-33.
25.Jiang XP,Ai WB,Wan LY,Zhang YQ,Wu JF.The roles of microRNA families in hepatic fibrosis.Cell Biosci 2017;7:34.
26.Kertesz M,Iovino N,Unnerstall U,Gaul U,Segal E.The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition.Nat Genet 2007;39:1278-84.
27.Friedman RC,Farh KK,Burge CB,Bartel DP.Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs.Genome Res 2009;19:92-105.
28.Loher P,Rigoutsos I.Interactive exploration of RNA22 microRNA target predictions.Bioinformatics 2012;28:3322-3.
29.Lin JM,Wei LH,Chen YQ,et al.Pien Tze Huang induced apoptosis in human colon cancer HT-29 cells is associated with regulation of the Bcl-2 family and activation of caspase 3.Chin J Integr Med 2011;17:685-90.
30.Kitano M,Bloomston PM.Hepatic stellate cells and microRNAs in pathogenesis of liver.Fibrosis J Clin Med 2016;5:38.
31.He X,Sun Y,Lei N,et al.MicroRNA-351 promotes schistosomiasis-induced hepatic fibrosis by targeting the vitamin D receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018;115:180-5.
32.Schumacher JD,Guo GL.Regulation of hepatic stellate cells and fibrogenesis by fibroblast growth factors.Biomed Res Int 2016;2016:8323747.
33.McDaniel K,Huang L,Sato K,et al.The let-7/Lin28 axis regulates activation of hepatic stellate cells in alcoholic liver injury.J Biol Chem 2017;292:11336-47.
34.Antoine M,Wirz W,Tag CG,et al.Expression and function of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 9 in hepatic stellate cells and its role in toxic liver injury.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007;361:335-41.
35.Cui H,Song R,Wu J,Wang W,Chen X,Yin J.MicroRNA-337 regulates the PI3K/AKT and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting highmobility group AT-hook 2.Am J Cancer Res 2018;8:405-21.
36.Xiao Y,Liu R,Li X,et al.Long noncoding RNA H19 contributes to cholangiocyte proliferation and cholestatic liver fibrosis in biliary atresia.Hepatology 2019;70:1658-73.
37.Yang YZ,Zhao XJ,Xu HJ,et al.Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate ameliorates high fructose-induced liver fibrosis in rat by increasing miR-375-3p to suppress JAK2/STAT3 pathway and TGF-β1/Smad signaling.Acta Pharmacol Sin 2019;40:879-94.
38.Li J,Xue J,Wang D,et al.Regulation of gasdermin D by miR-379-5p is involved in arsenite-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells and in fibrosisviasecretion of IL-1β from human hepatic cells.Metallomics 2019;11:483-95.
39.Lu CH,Hou QR,Deng LF,et al.MicroRNA-370 attenuates hepatic fibrogenesis by targeting smoothened.Dig Dis Sci 2015;60:2038-48.
40.Wang P,Lei S,Wang X,et al.MicroRNA-134 deactivates hepatic stellate cells by targeting TGF-β activated kinase 1-binding protein 1.Biochem Cell Biol 2019;97:505-12.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Effectiveness of redcore lotion in patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis:a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Efficacy and safety of external application of Chinese herbal medicine for psoriasis vulgaris:a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
- Effectiveness and safety of electroacupuncture for the treatment of pain after laparoscopic surgery:a systematic review
- Effect of astragaloside IV on the immunoregulatory function of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from patients with psoriasis vulgaris
- Shenqihuatan formula (参七化痰方) reduces inflammation by inhibiting transforming growth factor-beta-stimulated signaling pathway in airway smooth muscle cells
- Wenshen Yangxue decoction (温肾养血方) promotes follicular development in aged female mice via stimulation of the silent information regulator 3/forkhead transcription factor O1 3a pathway
