What are the barriers to implementing nurse practitioners' role in health settings?
2020-12-31NooraAlSoqair
Noora Al Soqair
1 Nursing Research Department,Regional Nursing Administration in Alhassa Region,Ministry Of Health,Saudi Arabia.
Abstract Background:Nurse practitioners can assist the healthcare system by administering care to patients with medical or complex or chronic conditions by providing medical and nursing care in an expanded scope of practice.However,there are barriers that influence the implementation of nurse practitioners' role in health settings.Influences among systemic or organization levels have impeded nurse practitioners' role implementation.All 10 studies included in this integrative review are critically explained based on the relevant information categorised into three themes: a lack of clarity regarding nurse practitioners' role,fees for service physician remuneration and resistance from other health professionals.The 10 studies included in this integrative review reveal barriers to nurse practitioners' role implementation in health settings. Objectives: The aim of this integrative literature review is to identify the barriers to implement the nurse practitioners' role.Therefore, the following research question is posed: "What are the barriers to implementing the nurse practitioners'role in health settings?".Methods:An integrative review of the medical and nursing research literature has been conducted using a systemic search accessing CINAHL, Medline,Scopus and PubMed databases.The identified 287 articles have been narrowed to 10 articles based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria.A limitation search was applied at the beginning of the search phase to assist in identifying the range and type of studies potentially available for synthesis.The srearch was limited to human,peer reviewed and full text articles available in English language without a date limitation to obtain a large number of avilable studies that were relevant to the topic. Finding: The literature search resulted in 10 primary studies that met the inclusion criteria.All studies included in this integrative review reveal barriers to nurse practitioners' role implementation in health settings.All studies found three barriers that can impact on the implementation which are:the lack of clarity of nurse practitioners'role,fees for service physician remuneration and resistance from other health professionals.Conclusion:Health settings must prepare the surrounding environment and the culture before implementing a new role, such as that of nurse practitioners.Implementing new roles into the organization is not straightforward:multiple influences can affect the implementation,such as barriers.Understanding the involvement of nurse practitioners' role in health settings by health care providers have to be visible and clear and changes that may occur as a result of implementing the role need to be identified to ensure the successful implementation.
Keywords:Nurse practitioner,Advance nurse practice,Role,Barrier
Introduction
The healthcare system in Saudi Arabia has been given“high priority” in the government.Improving and developing the healthcare system in Saudi Arabia was clear in terms of quality and quantity of services in the past few years, included availability of high level of care administer to the community.Saudi Arabia's healthcare system is “ranked 26th among 190 of the world's health systems” according to the World Health Organization (WHO) [1].The healthcare system in Saudi Arabia was provided by the Ministry of Health(MOH) with 244 hospitals (33277 beds) and 2037 primary healthcare centres [1].The MOH in Saudi Arabia is supporting the public healthcare system,which means the government provides all the citizens and expatriates free access to all public healthcare facilities.The responsibility for MOH in Saudi Arabia is to manage, plan,formulate health policies,supervise health programs and monitor health services in the private facilities [1].The healthcare system in Saudi Arabia administers health services at “three levels:primary, secondary and tertiary”.Primary healthcare centres are the primary level providing preventive and curative services.The secondary level is the public hospitals that receive referral patients from primary healthcare centres in need of more advanced care.The tertiary level is for more complex cases that need to be transferred to specialized hospitals[1].
Many countries are considering improving their healthcare systems by increasing the efficiency of healthcare delivery [2].Healthcare systems can be improved through new or more advanced roles for health professionals.Nurses are one group of clinical professionals who can assist in optimizing healthcare delivery in health settings.Given the growing demands of healthcare systems,nurses can increase the access to care in the face of a shortage or limited number of doctors [2].Nurses are the largest profession of healthcare providers in health settings and the primary profession with patient contact [3].According to Almalki et al.[1], nurses in Saudi Arabia constitute 50.3%of the health workforce in the MOH.
As noted above, primary care involves different services that include preventative and curative care[4].New symptoms can be evaluated in a primary care setting, and the follow up and management of patients with chronic disease can occur [4].Preventing the spread of disease is also a focus of primary care through immunizations and screenings [4].Primary care is a common healthcare approach that is offered in the Middle East.Saudi Arabia is one of the leading countries that has adapted primary healthcare to administer curative and preventative care to the community[5].Primary healthcare in Saudi Arabia has been activated and developed to prevent or minimise diseases as one of the MOH health strategies.The primary healthcare centres' method focuses on eight elements: “educating the population concerning prevailing health problems and the methods of preventing and controlling them, provision of adequate supply of safe water and basic sanitation,promotion of food supply and proper nutrition, provision of comprehensive maternal and child health care,immunization of children against major communicable diseases, prevention and control of locally endemic disease, appropriate treatment of common disease and injuries and provision of essential drugs” [1].Muslims around the world make the annual pilgrimage to Mecca(more than 2000000) during the Hajj season, requiring 157 health centres to open, and each administers care for 14734 pilgrims [6].Furthermore, 82% of patients visit primary care centres frequently in Saudi Arabia because it is the first health service level in the health system due to the requirement to develop healthcare services, particularly in primary healthcare [5].However, the healthcare system is heavily reliant on international clinicians who often do not speak the local language, have a minimal understanding of Saudi culture and therefore struggle to meet the diverse healthcare needs of the Saudi population[7].
Nurse practitioners or acute care nurse practitioners can assist the healthcare system by administering care to patients with medical or complex or chronic conditions by providing medical and nursing care via their expanded scope of practice [8].Implementing nurse practitioners' role can decrease the need for general practitioners in primary care and improve patients'access to care.Nurse practitioners have been effective in the assessment and treatment of chronic disease, which decreases the need for family doctors[9].Improved teamwork within a practice is another clinical benefit that can be achieved using nurse practitioners.There is an economic advantage to nurse practitioners as well because a consultation with a nurse practitioner is more cost efficient than with a general practitioner [10].Furthermore, unnecessary duplicate work can be eliminated because clients can be seen by nurse practitioners rather than by doctors.Therefore, the autonomy of nurse practitioners has an added benefit of reducing the burden on general practitioners, fostering teamwork, and improving job satisfaction [10].However, there were barriers that influence the implementation of nurse practitioners'role in health settings.The lack of understanding the nurse practitioners' role, job description, limited community awareness and resistance from other health professional can impact the implementation[11].
This integrative review aims to identify the barriers to implementing nurse practitioners' role.Nurse practitioners have the potential to improve access to healthcare and improve clinical outcomes for patients in primary care and health settings [9].However,before implementing their role, the barriers of practice and role implementation must be identified to prevent or reduce unsuccessful implementation.Creating an environment that required to implement the nurse practitioners' role in the healthcare system, among healthcare professionals and practice settings can guide successful implementation [12].However, nurse practitioners are not a recognized profession in Saudi Arabia's healthcare system.Nurse practitioners offer advantages in improving or developing healthcare,which has led to Saudi Ministry of Health to consider improving primary healthcare.Therefore, the MOH in Saudi Arabia is attempting to improve the healthcare system and healthcare delivery by creating a role for nurse practitioners in primary care and hospitals.Thus,to ensure the successful implementation of the nurse practitioners'role in Saudi Arabia,the barriers that can influence the implementation are identified in this review.The research question is as follows: What are the barriers to implementing nurse practitioners'role?
Aim of the Review
The aim of this integrative literature review is to identify the berries to implementing the nurse practitioners' role.Therefore, the following research question is posed: “What are the barriers to implementing nurse practitioners'role?”
Methods
An integrative literature review method was applied to conduct the study to investigate the role description of nurse practitioners in primary care.A comprehensive literature search strategy is the foundation for an integrative review.It is applied to assess evidence as well as to indicate the systemic analysis and synthesis of research in this study.An integrative literature review is a broadened type of research review method that involves experimental and non-experimental research with different methodologies [13].The integrative review process occurs in five steps: 1)problem identification, 2) literature search, 3) data evaluation, 4) data analysis and 5) the presentation of the results.Integrative review method has several benefits, such as the ability to evaluate the strength of the scientific research evidence presented by each study, identify the current gap in the research and the central issues in a research area, and bridge the gap in the current research [13].The following section describes the search strategy used in this integrative review.
Search Strategy
The search was aimed to find literature that was relevant to the topic of the study and to answer the question that was raised in this study: “What are the barriers to implementing the nurse practitioners'role?”.
The article search was an electronic search within main computerized databases, such as Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature(CINAHL), MEDLINE, PubMed and Scopus databases.A limitation search was applied at the beginning of the search phase to assist in identifying the range and type of studies potentially available for synthesis.The search was limited to human,peer-reviewed and full-text articles available in English language without a date limitation to obtain a large number of available studies that were relevant to the topic.Furthermore,hand searching of the reference lists and citations of literature reviews, thesis and included studies was carried out to identify any relevant studies.
Four primary search terms (nurse practitioner,barrier, role, implement) were identified from a preliminary literature survey.The key words used during research in the database were all related to the topic.The literature search included the following key words: nurse practitioner*, community nurse*,advance practice*, advance nurse practice*, family nurse practitioner*, acute care nurse practitioner*,role*, barrier*, implement* and practice*.The next step was to include a combination of the key words using the Boolean connector “AND'and “OR” to find the most relevant and available studies in the databases.
A total of 287 articles that included research studies and non-research papers were found.As a result, a specific criterion was applied to select the relevant studies that could assist in answering the research question.Inclusion and exclusion criteria were used to narrow the search to the relevant studies.
Inclusion criteria:(1) Primary study; (2) in the English language;(3)studies on the implementation or integration of nurse practitioners' role in acute care,hospitals, primary healthcare and long-term care settings.
Exclusion criteria:(1) Studies in role development because this studies limited to designing the role only;(2) discussion papers; (3) studies on the expanded nursing role.
Search Outcomes
The preliminary search of the CINAHL, Medline,PubMed and Scopus databases resulted in 282 articles and five articles via hand searching.Following the initial search, all the articles were cross checked and screened according to the article titles.As a result,after 206 articles were removed due to duplicates, the number of articles was reduced to 81.Then, the full articles were screened and assessed for eligibility and inclusion criteria.Thirty-three articles were excluded because twenty-seven studies were about nurse practitioners'role being expanded and six studies had no clear outcome.When the search phase was complete, the 10 chosen studies were assessed based on a quality appraisal tool [14].Ten peer-reviewed primary studies were finally included in this integrative review (from the computerised databases),as shown in Table 1.Figure 1 in the Appendix provides the details of the screening process utilized to identify the final 10 articles discussed in this integrative review.

Figure1:PRISMA flow diagram of search process and numerical outcomes(Moher,Liberati,Tetzlaff,&Altman,2009)
Quality Appraisal
Four of the 10 articles included in this review were qualitative research designs, two studies were descriptive studies, two were cross-sectional studies and two case studies.
The quality appraisal tool was applied for an individual study to evaluate the studies included in this integrative review.The 10 articles included in this integrative review were apprised using the Critical Appraisal Skill Program Checklist for Qualitative Research (2017), Critical Appraisal of a Case Study and the Tool for Descriptive/Cross-Sectional Studies.There were no papers excluded from this study due to quality issues.Therefore,a critical appraisal is required for determining the quality of the selected literature,as assessing the quality of the studies is associated with the assessment of the risk of bias.Thus, the methodological quality, rigour, information value and representativeness of the studies are considered.The results of the evaluation are provided in the Appendix(Appendix Tables 1,2&3).
Analysis of the Studies
Four qualitative studies [16, 17, 22, 23] were included in this integrative review,which identifies the barriers that influence the implementation of nurse practitioners' role in different settings.The majority of these studies were done in primary healthcare and one in an emergency department.The participants in these studies included nurse practitioners, physicians,staff nurses and administrators.Two descriptive studies[19, 15] were also included in this integrative review.These two studies identified the barriers associated with the implementation of nurse practitioners'role in public health units in Ontario and four hospitals in Ontario.All the data were collected by the researchers as a survey and questionnaire.The participants in these studies included multidisciplinary teams.Twocross-sectional studies [18, 20] were included in this integrative review as well.Interviews and questionnaires were applied to collect the data, and the sample sizes were appropriate in these studies.Two case studies were also included [11, 21] that explained nurse practitioners' implementation role and the barriers that influence the implementation.Interviews and documentation analysis were conducted in these studies to collect the data, and they were applied in acute care and primary healthcare with appropriate sample sizes.The details of the quality appraisal of included studies are indicated in the Appendix(Appendix Table 1,2 and 3).

Table 1:Studies included in the review

Abbreviations:NP:Nurse Practitioner,ACNP:Acute Care Nurse Practitioner,RN:Registered Nurse,CNS:Clinical Nurse Specialties,ED:Emergency Department,PA:Physician Assistance.
Data abstraction and synthesis
The findings from each study were reviewe d to identify the barriers to implementing nurse practitioners' role in the health settings.All barriers included in the studies were then reviewed to identified themes.According to Miles and Huberman 2014 [21],the common themes identification occurs to clarify the research focus and the orientation ideas.The concepts of the themes can guide to further research in the future because it will identify the relationships in the research [21].The themes of this integrative review were identified and analysed in the finding chapters(Table 2&3).
Findings
The literature search resulted in 10 primary studies that met the inclusion criteria.Four studies were qualitative,two were case studies, two were descriptive and two were cross-sectional; all studies are described in Table 2.In this chapter, all studies are critically explained based on the relevant information categorised into three themes:the lack of clarity of nurse practitioners'role, fees for service physician remuneration and resistance from other health professionals.The studies that discuss each theme are itemized in Table 3 and the studies'characteristics in Table 2.
The 10 studies included in this integrative review reveal barriers to nurse practitioners' role implementation in health settings, such as acute care,hospitals and primary healthcare.
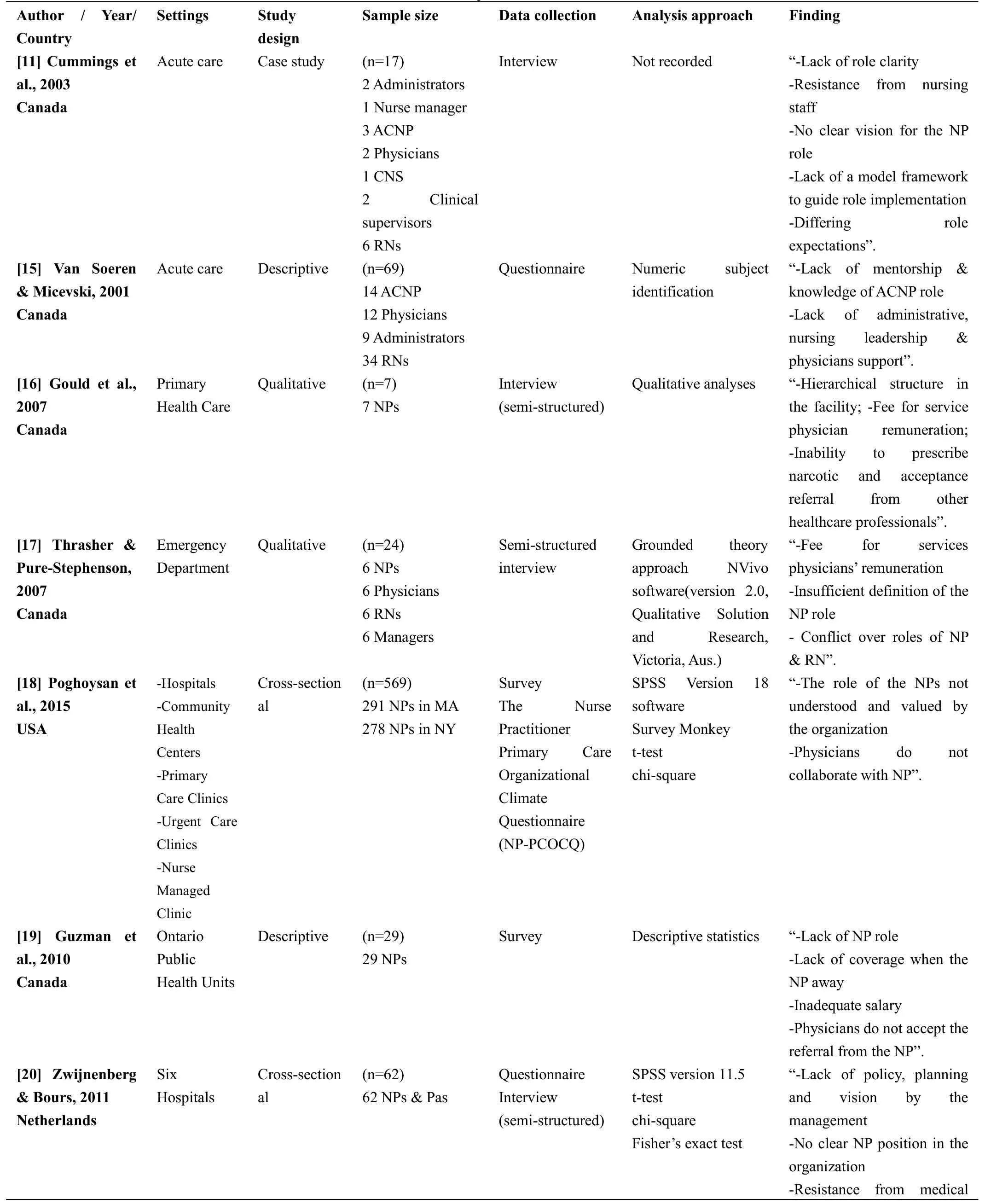
Table 5:Study Characteristics

specialists-Lack of legal framework of NP-Inadequate salary”.[21]Sangster-Gormley et al.,2013 Canada Three Primary Health Care Case study (n=16)4 Managers 3 Physicians 2 RNs 4 NPs 1 Medical office assistant 1 Community member Interview Documents review N-Vivo 8.0 “-Lack of the NP role-Resistance from medical specialists-Lack of long term plan-Community does not accept NPs as new care providers”.[22] Poghosyan et al.,2013 USA Community Health Centers Qualitative (n=23)23 NPs Group &individual interview Atlas.ti 6.2 qualitative software“-No clear understanding of the Np role and competencies-Lack clarity of NP role on the support and the relationship with other healthcare providers-Lack of work environment-Lack of organizational support”.[23]Sullivan-Bentz et al.,2010 Canada Primary Health Care Qualitative (n=44)23 NPs 21 Coparticipants including family physicians, NPs and managers Interview(semi-structure)NVivo software “-Lack of NP role-No job description or professional expectation available-NP role and scope of practice confusion-Resistance from other health professionals-Fee for service physician remuneration".

Table 6:Studies Theme
Lack of clarity of nurse practitioners'role
Nurse practitioners'role was implemented in different settings; however, there were several barriers impacting practice.The nine studies that included in this theme conducted in different health settings such as (primary health care, hospitals, acute care,emergency department).Most of the participants in these nine studies have a lack of knowledge and clarity of nurse practitioners'role in health settings[11,15,17,18, 19-23].The first study was conducted by Van Soeren and Mickevski 2001[15],among 12 physicians,34 staff nurses and nine administrators working in acute care.In this study, the perception of indicators and barriers to successful nurse practitioners' role implementation was investigated among a multidisciplinary team working with nurse practitioners.The physicians, staff nurses and administrators found that the lack of clarity and understanding of nurse practitioners'role was the most vital barrier to efficacious implementation in acute care settings.The lack of role clarity leads to the absence of administrative support and from nursing leadership.Cummings et al.'s 2003 [11] case study examined the effects of the implementation of nurse practitioners'role in acute care with a sample of 17 individuals from a multidisciplinary team, two administrators, one nurse manager, three acute care nurse practitioners, two physicians, one clinical specialty nurse, two clinical supervisors and six registered nurses,revealing that the misunderstanding and lack of clarity regarding nurse practitioners' role was the most significant barrier to implementation.Some of the participants thought nurse practitioners' role was similar to that of nurse staff and the nurse practitioners have to assist the nurses.Other participants said nurse practitioners'role was an extension of physicians' role.Staff nurses in this study said the nurse practitioners' role was physicians' extension role.A lack of clarity regarding nurse practitioners' role can impact on practice the independency and flexibility of their role.
Sullivan-Bentz,et al.2010 [23], performed a qualitative study in primary healthcare among 23 nurse practitioners and 21 coparticipants including family physicians, nurse practitioners and managers.They explored the influences that delay the successful transition and implementation of nurse practitioners'role into primary healthcare.Family physicians and managers were unfamiliar with the nurse practitioners'role and needs.They did not knowledge the scope of practice of nurse practitioners in primary healthcare and what they expected from the nurse practitioners.Furthermore, in their qualitative studies, Thrasher and Pure-Stephenson 2007 [17] and Poghosyan et al.2013[22] identified the barriers associated with the implementation of nurse practitioners' role.Thrasher and Pure-Stephenson's 2007 [17] study was conducted in an emergency department, and the sample size was 24; Poghosyan et al.'s 2013 [22] study was conducted in primary health centres with a sample of 23,and they found that the lack of nurse practitioners'role clarity in the organization and among healthcare professionals impacted the implementation of nurse practitioners'role and their relationship with team members in healthcare settings.
The two cross-sectional studies[18,20]conducted in hospitals and community health centres Poghoysan et al.'s 2015 [18] study included 569 nurse practitioners,and Zwijnenberg and Bours's 2001 [20] study had 62 nurse practitioners and physicians assistants, found that the lack of nurse practitioners' role clarity in the organization was a problem related to the organizational and system levels, as there were no clear job description and policy obtainable by the administration, which was a barrier to implementing their role.Similarly, the case study conducted in three primary healthcare by Sangster-Gormley et al.2013[21] (n=16) found that defining the role of nurse practitioners among the team members required time and effort and misunderstanding the nurse practitioners' role delay the implementation of nurse practitioners' role and the functions with other team members.The last descriptive study by Guzman et al.,2010 [19] conducted in Ontario public health units for 29 nurse practitioners found 42.8% of physicians misunderstood the nurse practitioners'role, which was the most significant barrier to implementation and impacted other services applied by nurse practitioners in health settings, such as referrals to other health professionals.The lack of a standard job description,lack of physicians and nurses'understanding of nurse practitioners' role and no clear vision for the role are barriers[11,15,17,18].
Fee for service physician remuneration
In three qualitative studies [16, 17, 23] the fees for service physician remuneration were examined.They were conducted in primary healthcare and emergency departments;the sample size of Gould et al.'s 2007[16]study was seven nurse practitioners.These three studies found the physicians feel threaten by nurse practitioners as they practice in health settings.As the fee for service model was applied, the physicians felt their income would be affected because they thought the nurse practitioners could accomplish the physicians' job.The fee for service payment method create a barrier to implement the nurse practitioners'role and prevented them from working within their full scope of practice in the emergency department as the physicians would not provide the nurse practitioners the opportunity to practice their role.Only physicians who are working under salary or within alternate funding accepted the nurse practitioners' role to be implemented, as it did not impact their outcome [16,17,23].
Resistance from other health professionals
Resistance from other health professionals is a barrier to implementing nurse practitioners' role in health settings.This barrier was examined in seven studies[11, 16, 18-21, 23].Lack of nurse practitioners' role clarity leads to resistance from other health professionals.Physicians did not collaborate with nurse practitioners and did not seek input from nurse practitioners in patients' care [18,23].Referrals to other healthcare professionals or specialities by nurse practitioners were not accepted and refused by physicians, which is an important barrier that nurse practitioners revealed [11,16,18,19,20,21,23].The pharmacists refused prescriptions written by nurse practitioners to patients and the medical speciality did not accept the referrals from nurse practitioners because they did lacked awareness of the nurse practitioners'role[21].Lack or/and misunderstanding the nurse practitioners'role in health settings cause the physicians and other healthcare providers,such as staff nurses and pharmacists, to be unsupportive and resistant [11, 16, 18-21, 23].The resistance from staff nurses and residents occurs because they felt threatened by the nurse practitioners and the residents try to manage all patients on the unit so the nurse practitioners will manage only the chronic and stable cases [11].Physicians have not accepted the nurse practitioners' role, as they fear they will take the physicians'role[16].
Discussion
The findings of the 10 studies in this review illustrate the barriers to implementing nurse practitioners'role in different health settings, such as primary healthcare,hospitals, acute care departments and emergency departments.All health settings have similar barriers,as discussed earlier in the results section,which are the lack of clarity regarding nurse practitioners'role, fees for service physician remuneration and resistance from other health professionals.
Nurse practitioners are becoming increasingly popular around the world [25].Nurse practitioners are becoming more common and the successful implementation of their role depends on a number of factors.Implementation can be defined as the transmission time occurring after decisions are made to adopt innovations.Different influences on implementation can be barriers or facilitators [21].Therefore, health settings must prepare the environment and the culture before establishing and implementing a new role, such as the nurse practitioners' role.Implementing new role into the organization is not straightforward multiple influences can affect the implementation such as barriers [26].In some countries introduced and implement nurse practitioner role in primary care was difficult and was a challenge in primary health care.Understanding the involvement of nurse practitioners'role in primary care have to be visible and clear and the change that may occur as a result of implementing the role need to be identified to ensure the successful implementation[27].
The lack of clarity of nurse practitioners'role in the organization is the most significant barrier in implementation that nurse practitioners found in the studies included in this review [11, 28, 29].Further issues could be developed as a result of the unclear role of the nurse practitioners in the organization, such as ‘role conflict”, “role overload” and the acceptance of the nurse practitioners'role can also be changed by the stakeholders [12].Physicians commonly misunderstand nurse practitioners' role and scope of practice, which is associated with difficulty in collaboration with them.Lack of physicians'knowledge of nurse practitioners' role involve the relationship between them which influence on accepting the nurse practitioner practice [17, 22, 26].Absence of clarity of nurse practitioners' role can cause a difficulty to fulfil the nurse practitioner role expectation in the organizations [21].Also, lack of clarity of nurse practitioners' role by physicians can lead to interprofessional conflict or misunderstanding such as understanding the prescribing authority and limitation for nurse practitioners in practice [20, 23,30].In primary healthcare,the nurse practitioners have similar responsibilities as primary care physicians to provide care to their patient population.The ability of nurse practitioners to fulfil their role in the organizations can be affected by the lack of understanding by the physicians and the administration stakeholders [22, 23].However, both studies were conducted with a limited sample and the participants practicing nurse practitioner role in different status and regulation which may experience different barriers and organizational realities.
The acceptance of nurse practitioners as a team member in the organization could occur if the standard and certification of their role are known, which can improve the confusion that occurs among other health professions [15].However, this study was conducted with a small sample size from one Canadian region and a possible lack of consistency among the participants in the study due to an absence of standard of practice and accreditation for the nurse practitioner role in the organization.Role ambiguity is a significant barrier to implementing nurse practitioners' role in health settings.It occurs as a result of confusion among stakeholders and team members regarding the scope of practice, the objective, responsibility and the expected outcome of the role [31, 32].The beginning of the nurse practitioners'role ambiguity occurs in the early development of the role and continued as it was presented into different health settings especially where other health professionals or administrations had not been previously exposed to nurse practitioners [31,32].Role overlap and role confusion may occur due to a lack of clarity of nurse practitioners'role, which can impact the performance and outcomes of care[12,31].According to Lowe et al.2013[33],the lack of support and acceptance among other healthcare providers occur because of the lack of clarity regarding their role.Nurse practitioners may feel isolated due to the misunderstanding of their role by colleagues and staff nurses and may other nurses may feel professionally jealous due to such an unclear new role in the organization.Few studies found lack of clarity of the nurse practitioners' role in health settings cause confusion.So,this confusion of the nurse practitioners'role in the healthcare can delays progression of the role and impacts the potential involvement that nurse practitioner can make to administer care [11, 21, 33].Nurse practitioners'role impacts healthcare provision;therefore, role clarity regarding their practice is essential[34].Overlap the role of nurse practitioners in the organization can create misunderstanding amongst the staff nurses regarding what is required from nurse practitioners to administer or practice in health settings,such as nurses believing that the nurse practitioner is responsible for imparting his/her own treatments [17].However,this study was conducted with a sample from one Canadian region so the results may or may not be generalizable to other authority.
The lack of role clarity by managers and/or administration could lead to limit the ability to create a productive environment for nurse practitioners in the organizations to practice their role [18].Though, this study collects the data with mixed mode which may have impacted the study finding and nurse practitioner practice have different environment in different state was not captured in the survey.Nurse practitioners'role overlap can also impact their role implementation in emergency departments, as found in previous studies [17, 28].Role overlap occurs when staff believes there is overlap between nurses and nurse practitioners about the assessment and monitoring of the patients in health settings.Furthermore, overlap could occur between nurse practitioners and physiotherapists in activities related to lung auscultation and chest assessment [8].Role overlap, as healthcare providers state, occurs in prescriptive rights between nurse practitioners, physicians and pharmacists.Additionally, overlap occurs in work share associated to patients discharge plan and family meeting.Role overlap that occurs in such organizations is mainly because of the lack of role clarity between nurse practitioners and physicians in patients' history records and prescriptive rights [8].Most of the physicians and healthcare providers such as staff nurses in the health settings believed nurse practitioners' role is equal to the new residents' role and nurse practitioners' role is a combination of nursing and medical roles, while other physicians argued the nurse practitioners'role is not combination of nursing and medical role.These arguments and misunderstandings occur because the role of nurse practitioners remains unclear in these organizations [8,12].
Fee-for-service physician remuneration is the second barrier impacting the implementation of nurse practitioners' role.This is a model of payment to physicians according to each service provided to the patients, such as physical examination, immunization and prescription [35, 36].This model of payment has been applied in Canada since 1966 the inception of Medicare.The majority of Canadian family physicians receive fee-for-service payment.This approach is applied to ensure high-quality care to patients [35,36].Most physicians want to perform care to the most patients possible and work more hours to get paid depending on the number of services they provide to their patients [35].Most countries approach fee-for-service model in primary care and community centres for general practitioners [27].Therefore,physicians feel threatened by nurse practitioners regarding their income.As nurse practitioners can administer care to patients via physical examination,referral,requesting a test and prescribing medication,it can impact physicians'remuneration.All physicians in organizations obtaining their payment by the fee-for-service model are affected by hiring nurse practitioners [16, 17].Several studies found nurse practitioners can administer care similar to physicians and the payment for the nurse practitioners is lower than that for physicians in fee-for-service methods.Further,nurse practitioners spend more time with their patients than physicians and give more in-depth care[37, 38].The fee-for-service model pays more to healthcare providers who examine more patients and spend less time and do not care about the quality of care, which may impact patients' satisfaction.Physicians performed a quick patient's examination,and the outcome of the quick examination is more test request and more prescribed medication as a result of efficient clinical diagnosis and examination [37, 38].Nurse practitioners have reported that as fee-for-service remuneration for physicians is applied,they cannot practice their complete scope of practice[23].In Australia, funding absence is a barrier to implementing nurse practitioners' role in health settings because nurse practitioners can access the fee for the service they performed before they gain access to funding through the Medicare benefits schedule[33].However, the fee-for-service model is not preferred by nurse practitioners to practice their full scope of practice and role in health settings, and physicians feel threatened in their outcome by nurse practitioners practicing in an organization[16,17,23,27].
Furthermore, resistance from other health professionals is another major barrier influencing the implementation of nurse practitioners' role in health settings.It was found in the literature reviews that resistance from other health professionals towards nurse practitioners presented as not accepting referrals from them and not collaborating.The most important barrier to implementing nurse practitioners' role was the unwillingness of specialists to accept referrals from nurse practitioners.In addition, there was a lack of respect and trust from physicians and other health professionals towards nurse practitioners [19, 23].However, Guzman et al., 2010 [19] study was conducted with a small sample size which may have lack of the ability to reveal important relationships among health professionals.The relationship between the nurse practitioners and physicians is the main facilitator to implementing nurse practitioners'role in health settings and ensuring successful implementation if they have a good relationship [11, 21, 27].In most the literature reviewed, collaborative practice between different health professionals such as nurse practitioners, physicians, pharmacists, and staff nurses was found to positively influence patient care and successful implementations of new roles in the organizations[11,21,27].However,Sangster-Gormley et al., 2013 [21], study was conducted within the primary health care only and it focuses in primary health care settings which may not reflects organizational realities.Nurse practitioners experience resistance from other healthcare providers in the practice, which negatively impacts their performance and implementation their full scope of practice[18,39].Further,nurse practitioners suffer from resistance from healthcare providers outside the organization, which occurs, for example, in rural areas when refusing a referral or prescription and more resistance occurs in hospital settings.All this resistance from other health professionals occurs because nurse practitioners' role is new in their organization and they are not acknowledged with the nurse practitioners' role and scope of practice [18, 39].Additionally, other health professionals feel they are threatened by the nurse practitioners'role because some policy and regulation were changed occur in the health setting after implement the nurse practitioners' role.The lack of role clarity and misunderstanding the nursed practitioners' role in the organization contributes to resistance from other health professionals [18, 39].This resistance to nurse practitioners in health settings means poor acceptance of nurse practitioner by other health professionals in the organization.Resistance to nurse practitioners in the organizations by other healthcare providers is a barrier that influences the implementation of their role[11,18,21,27,39].
Unsuccessful collaboration among nurse practitioners and physicians can be a barrier to practice,and it occurs because physicians view a certain amount of incompetence, thereby having a more negative attitude towards nurse practitioners [16, 20, 26].Resistance to nurse practitioners' scope of practice in the health setting occurs as a refused for a referral from the nurse practitioners to the physicians, as the physicians believe nurse practitioners increase their workload and burden to them [38].Many medical professions who are members of the Australian Medical Association believe nurse practitioners, after they are authorized to practice their role, will be a threat to the physicians' role in the organization, and are thus resistant to support nurse practitioners [30].Moreover, other health professionals, such as staff nurse and clinical nurse specialists, have fears related to the nurse practitioners'practice, as they worry they will lose autonomy and control, creating resistance.The absence of clarity of nurse practitioners'role has the potential to negatively affect team communication,support,acceptance and professional confidence[31].
Limitations
This integrative review discussed and explained the barriers that influence the implementation of the nurse practitioners' role in health settings.The main limitation was the limited numbers of studies included,resulting in a small number of barriers discussed in this review.More were barriers found, but they did not meet the inclusion criteria such as not primary studies and non-English language studies.
Implications of Practice
The implementation of nurse practitioners' role in health settings must be introduced to all healthcare providers and the administration in the organization prior to the implementation.It is fundamental for the administration and policy makers to understand the progression of nurse practitioners'role implementation in the organization so that new roles are organised and supported properly to reflect nurse practitioners'competency and capability.Prepare orientation program in the organization by the administration to introduce the nurse practitioner role performed by the nurse practitioner in the health settings.Successful role implementation in the organization assists nurse practitioners to perform patient care more efficiently.Increasing the community's knowledge about nurse practitioners'role and their ability to deliver care will promote their professional identity.Most literatures mention that administrators play a significant role in the implementation of the nurse practitioners' role in the organizations.Unit mangers support to implement the nurse practitioners'role is required to monitor the implementation and the transition into the role.Further research is needed to identify the need for nurse practitioners in Saudi Arabia and the facilitators to implementing the nurse practitioners' role in health settings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, many countries are considering improving their healthcare systems by increasing the efficiency of healthcare delivery.Healthcare systems can be improved through new or more advanced roles for health professionals.Nurses are one group of clinical professionals who can assist in optimizing healthcare delivery in health settings.Given the growing demands of healthcare systems, nurses can increase the access to care in the face of a shortage or limited doctors.Nurses are the largest profession of healthcare providers in health settings and the primary profession with patient contact.Primary care is a common healthcare approach that is offered in the Middle East.Saudi Arabia is one of the leading countries that has adapted primary healthcare to administer curative and preventative care to the community.Primary healthcare in Saudi Arabia was activated and developed to prevent or minimise diseases and was one of the MOH health strategies.
Nurse practitioners' or acute care nurse practitioners' role can assist the healthcare system by administering care to patients with medical or complex or chronic conditions by providing medical and nursing care via an expanded scope of practice.Implementing nurse practitioners' role can reduce the need for general practitioners in primary care and improve patients' access to care.Nurse practitioners have been effective in the assessment and treatment of chronic disease, which reduces the need for family doctors.Improved teamwork within a practice is another clinical benefit that can be achieved using nurse practitioners.There is an economic advantage to nurse practitioners as well because consultation with a nurse practitioner is more cost efficient than consultation with a general practitioner.However,there are barriers that influence the implementation of nurse practitioners'role in health settings.The lack of understanding the nurse practitioners' role, job description, limited community awareness and resistance from other health professionals can impact the implementation.
This integrative review identified 10 primary studies discussing and explaining the barriers that impact the implementation of the nurse practitioners' role in health settings.All studies included in this integrative review critically explained based on the relevant information categorised into three themes: the lack of clarity regarding nurse practitioners' role, fees for service physician remuneration and resistance from other health professionals.The studies included in this integrative review revealed barriers to nurse practitioners' role implementation in health settings such as acute care, hospitals and primary healthcare.Health settings must prepare the surrounding environment and the culture before establishing a new role, such as the nurse practitioners' role.Implementing a new role into an organization is not straightforward; multiple influences can affect the implementation, such as barriers.The lack of clarity of nurse practitioners'role in the organization is the most significant barrier found in the studies and result in major barriers in implementation.Physicians feel threatened by nurse practitioners regarding their income.Nurse practitioners can administer care to patients via physical examination, referrals, requesting tests and prescribing medications, which can impact physicians' remuneration.Physicians in organizations who obtain their payment by the fee for service model are affected by hiring nurse practitioners.The most important barrier identified was the unwillingness of specialists to accept referrals from nurse practitioners as well as the lack of respect and trust from physicians and other health professionals towards nurse practitioners.The relationship between the nurse practitioners and physicians is the main facilitator to implement the nurse practitioners' role in health settings and ensure successful implementation if they have a good relationship.
杂志排行
Nursing Communications的其它文章
- Bibliometric analysis of qualitative researches in nursing in China from 2013 to 2019
- The effects of Professional Commitment and Patient Safety knowledge-attitude-practice on Undergraduate nursing students'Humanistic Care Ability in clinical practice
- The research status of self-care agency assessment and intervention of enterostomy patients
- A rare condition:Larsen Syndrome
