Effects of Medicated Bamboo Cupping Therapy of Zhuang Nationality Medicine on Long-term Efficacy and Quality of Life in the Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia with Stagnation of Liver Qi and Spleen Deficiency Syndrome
2020-12-31ZHANGYunbo张云波
ZHANG Yun-bo (张云波)
Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Rongshui Miao Nationality Autonomous County, Rongshui 545300, China
ABSTRACT Objective:To investigate the effect of medicated bamboo cupping therapy of Zhuang nationality medicine on long-term efficacy and quality of life in the treatment of functional dyspepsia with stagnation of liver Qi and spleen deficiency syndrome, and to provide a new, effective and easy to promote treatment method for functional dyspepsia. Methods:A total of 150 cases of functional dyspepsia treated in our hospital from March 2014 to October 2015 were selected as research subjects, and they were divided into the treatment group (medicated bamboo cupping therapy), the control A group (Omeprazole Enteric-coated Tablets + Domperidone Tablets) and the control B group (acupuncture), 50 cases in each group. The clinical efficacy, the gastric electrical index, the recurrence rate and the quality of life were observed and compared. Results:The total effective rate in the treatment group was higher than that in the control A group and the control B group (P<0.05).Compared with before treatment, the main frequency and electrical amplitude in each group was significantly improved, and the rhythm disorder coefficient was significantly reduced (P<0.05). After treatment, compared with the control A group and the control B group, the difference of rhythm disturbance coefficient in the treatment group was statistically significant (P<0.05). The recurrence rate in the treatment group was lower than that in the control A group and the control B group at 1 month,3 months and 6 months after drug discontinuance, with no significant difference (P>0.05). Compared with before treatment, scores of each physiological function after treatment had no significant change(P>0.05), and the scores of physiological function, body pain, general health, vitality, social function,emotional function and mental health were significantly improved (P<0.05). The comparison of scores in each group had no significant difference (P>0.05). Conclusion:The medicated bamboo cupping therapy of Zhuang nationality medicine on functional dyspepsia with stagnation of liver Qi and spleen deficiency syndrome can significantly improve clinical efficiency, and reduce the coefficient of rhythm.The long-term recurrence rate is low, and the quality of life is significantly improved. It is a convenient and effective treatment, which is worthy of promotion.
KEYWORDS Dyspepsia; Zhuang nationality medicine; Bamboo cupping therapy; Efficacy; Quality of life
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a common and frequently-occurring clinical gastroenterology disease, which occupies a relatively high proportion of patients in daily outpatient clinics. FD not only reduces the quality of life of patients, but also brings a greater economic burden to patients,so it has gradually become an important issue in modern society. This project intends to observe the efficacy of medicated bamboo cupping therapy of Zhuang nationality medicine on FD based on a large number of clinical practices in the early stage, through a large sample of expanded cases, randomized clinical trials, to perform a comprehensive evaluation and analysis of the improvement of the patient's symptom score and its gastrograph, to evaluate the clinical efficacy of this therapy on FD, and to explore its related mechanisms in the treatment of FD.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
General Information
The subjects of this study were 150 patients with functional dyspepsia admitted to the hospital from March 2014 to October 2015. All patients were diagnosed by electronic gastroscopy, and the diagnosis and screening of cases were performed in strict accordance with the FD diagnostic criteria in Rome II. Among them, there were 87 males and 63 females, aged 21-65 years old, with an average age of (45.68±12.52) years, the course of disease of 12-45 months, and the average course of(25.62±10.89) months. All patients gave informed consent and signed an informed consent form. By using randomized single-blind method, they were divided into the treatment group (medicated bamboo cupping therapy), the control A group (Omeprazole Enteric-coated Tablets + Domperidone Tablets) and the control B group (acupuncture), with 50 cases in each group. There was no statistically significant difference in gender, age, course of disease and other conditions between groups (P>0.05), and were comparable.
Diagnostic criteria of traditional Chinese and Western medicine[1]:Standards for Diagnosis and Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia in Traditional Chinese Medicine and Standards for Diagnosis and Efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Diseases and Syndromeis referred for diagnosis and syndrome differentiation of traditional Chinese medicine;Rome III Diagnostic Criteria of Functional Gastrointestinal Diseasesis referred for western medicine diagnosis and classification.
Inclusion criteria[2]: ① Patients suffer from persisted or recurred pain and discomfort in the middle of the upper abdomen (such as early full,abdominal distension, nausea, belching, etc.).② The above symptoms occurred at least within the past year or lasted for 12 weeks without continuous occurrence. ③ Symptoms has nothing to do with defecation. ④ Digestive endoscopy and other examinations confirmed no organic diseases.⑤ Inclusion criteria: Those who meet the diagnostic criteria of Western medicine are 18 and 65 years old.
Exclusion criteria[3]: (1) Those who do not meet the diagnostic criteria and inclusion criteria;(2) Although they meet the diagnostic criteria,patients have one of the following conditions: ①Pregnancy and patients with achalasia, pyloric obstruction, sliding esophagus hiatal hernia are excluded. ② Patients with severe cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, liver and kidney failure, and hematopoietic system diseases are excluded. ③ Patients who have been treated or whose recurrence may affect the results of the experiment are excluded. ④ Patients with a history of severe mental illness, alcoholism, etc. are excluded. ⑤ Patients with gastroparesis or irritable bowel syndrome are excluded. ⑥ Patients with poor compliance and incomplete data are excluded.
Methods
The treatment group was treated by medicated bamboo cupping therapy. Self-made prescription ofRadix Aucklandiae(木香) 20 g,Radix Codonopsis(党参) 20 g,Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis(厚朴)20 g,Radix Astragali seu Hedysari(黄芪) 30 g,Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae(白术) 20 g,Radix Bupleuri(柴胡) 15 g,Rhizoma Zingiberis(干姜) 20 g, andRadix Angelicae Sinensis(当归) 10 g was taken. The above herbs were put into the cloth bag and tighten. The herbs were decocted with soft fire. After boiling, the cloth bag and decoction were put into a bamboo pot and boiled for 2 minutes, with the mouth of the pot facing down.When the decoction and water vapor boil, tweezers were used to quickly take out the bamboo pot and a dry towel was used to absorb the boiling water droplets. Then the bamboo pots were tightly on Zhongwan (RN12), Zusanli (ST36), Pishu (BL20),Weishu (BL21), Zhangmen (LR13), and Sanyinjiao(SP6). Due to the negative pressure in the jar, the medicine jar is tightly attached to the acupoints on the body surface. If the bamboo pot becomes loose due to unskilled or make a mistake, it needs to be performed again. The sheet is covered to keep it warm, and leave the pot for about 10 minutes, three times a week and 2 weeks as a course of treatment. Precautions during treatment:Generally, it is recommended with little intake and low-fat diets, and avoid starchy foods such as soy products and potatoes.
The control A group was treated with omeprazole enteric-coated tablets and domperidone.Both drugs were purchased from our hospital's pharmacy: among them, omeprazole entericcoated tablets were produced by Shandong Lu, nan Pharmaceutical Factory, 10 mg/tablet, 28 tablets/box; domperidone tablets were produced by Xi'an Janssen Company, 10 mg/tablet, 30 tablets/box.Medication method: for omeprazole enteric-coated tablets, 2 tablets each time, 2 times a day, taking every other 12 hours in the morning and evening,and for domperidone tablets, 1 tablet each time, 3 times a day, taking 15 minutes before meals. The course of treatment and precautions were the same as the treatment group.
The control B group was given conventional 0.30 mm50 mm needle acupuncture. Acupoint selection: Zhongwan (RN12), Zusanli (ST36),Pishu (BL20), Weishu (BL21), Zhangmen(LR13), and Sanyinjiao (SP6), once a day,30 minutes retention of each time. The course of treatment and precautions were the same as the treatment group.
Observation Indicators
(1) Safety observation[4]: Physical examination items: routine tests of blood, urine, and feces,chest X-ray and ECG, liver, gallbladder, spleen and pancreas B-ultrasound and liver and kidney function are observed. (2) Efficacy observation[5]:symptoms score and electrogastrograph test(main frequency, main power, normal slow wave, bradycardia, tachycardia) are observed.(3) Follow-up for 6 months, the recurrence rate of each group is observed. (4) At 1 month after treatment, the SF-36 Scale is used to evaluate the quality of life of each group.
Standards for Judging the Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine
(1) Symptom score and statistics: According to the clinical symptoms of abdominal pain, bloating,early full, belching, nausea, regurgitation, vomiting,and loss of appetite, 8 symptoms were divided into four levels respectively: none, mild, moderate and severe. Among them, the none was patients with no obvious symptoms. The mild was that the symptoms exist but not obvious; after reminding,patients can realize that. The moderate is that the patient clearly felt the symptoms, but did not affect life. The severe is that the patient's symptoms have a greater impact on life. The 4 levels were respectively recorded as 0, 1, 2, 3 points. The symptom total score was added to each symptom score, and the total symptom score was added to the symptom total score.The results were calculated after 2 weeks. The data was input into the computer for analysis and statistics.The efficacy of various symptoms was determined according to the following formula: Symptom score decreased rate = (Symptom score before treatment-Symptom score after treatment)÷(Symptom score before treatment)×100%. Clinical cured: all symptoms disappeared; clinically markedly effective: symptom score was decreased more than 2/3; clinically effective: symptom score was decreased more than 1/3 but not reached 2/3; ineffective: symptom score was decreased less than 1/3, and symptoms did not change significantly. Total effective rate =(clinical cured cases + clinically markedly effective cases + clinically effective cases)/total number of cases×100%.
Statistical Methods
SPSS 17.0 statistical software was used for data analysis. Count data such as total effective rate and recurrence rate were expressed in percentage(%), and measurement data such as gastric electrical index and SF-36 score were expressed as (). Pairwise comparisons of data between groups were performed byttest and LSD test, and comparison of count data between groups was performed by chi-square test. Only whenP<0.05,the difference was statistically significant.
RESULTS
Comparison of Overall Efficacy in Each Group
In the treatment group, 12 cases were clinically cured, 18 cases were markedly effective,17 cases were effective, 3 cases were ineffective,and the total effective rate was 94.00%. In the control A group, 5 cases were clinically cured, 12 cases were markedly effective, 19 cases were effective, 14 cases were ineffective, and the total effective rate was 72.00%. In the control B group,8 cases were clinically cured, 18 cases weremarkedly effective, 14 cases were effective, 10 cases were ineffective, and the total effective rate was 80.00%. The total effective rate of clinical treatment in the treatment group was highest than that in the control A group and the control B group(P<0.05) (Table 1).
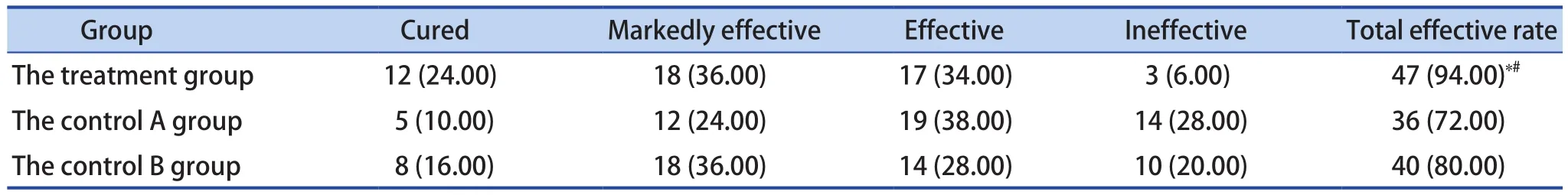
Table 1. Comparison of the Overall Efficacy of Each Group [n (%), n=50]
Table 2. Comparison of Gastric Electrical Indexes Before and After Treatment (, n=50)

Table 2. Comparison of Gastric Electrical Indexes Before and After Treatment (, n=50)
Notes: Compared with before treatment, P<0.05; compared with the control A group and the control B group, #P>0.05; compared with the control A group and the control B group, ⊙P<0.05
Group Time Main frequency/times·min-1 Electric amplitude/μV Rhythm disturbance coefficient The treatment group Before treatment 1.75±0.26 110.85±10.36 45.82±4.93 After treatment 3.25±0.29# 198.28±15.88# 24.56±4.16⊙The control A group Before treatment 1.82±0.25 109.58±11.26 46.29±5.03 After treatment 3.46±0.30 202.35±12.32 30.24±4.59 The control B group Before treatment 1.79±0.25 108.98±11.26 47.29±4.39 After treatment 3.52±0.28 209.29±12.35 31.29±5.72
Comparison of Gastric Electrical Indexes Before and After Treatment
Compared with before treatment, the main frequency and electrical amplitude in each group were significantly improved, and the rhythm disorder was coefficient decreased significantly (P<0.05).Before treatment, compared with the control A group and the control B group, there was no significant difference in the main frequency, electrical amplitude, and rhythm disorder coefficient in the treatment group (P>0.05). After treatment, compared with the control A group and the control B group,there was no significant difference in the main frequency and electrical amplitude in the treatment group (P>0.05), and the rhythm disorder coefficient was significantly different, which was statistically significant (P<0.05) (Table 2).
Comparison of Recurrence Rates in Each Group
The recurrence rates in the treatment group after withdrawal for 1 month, 3 months and 6 months were 4.00%, 10.00% and 16.00%, respectively,which were lowest than those in the control A group and the control B group, but there was no significant difference (P>0.05) (Table 3).
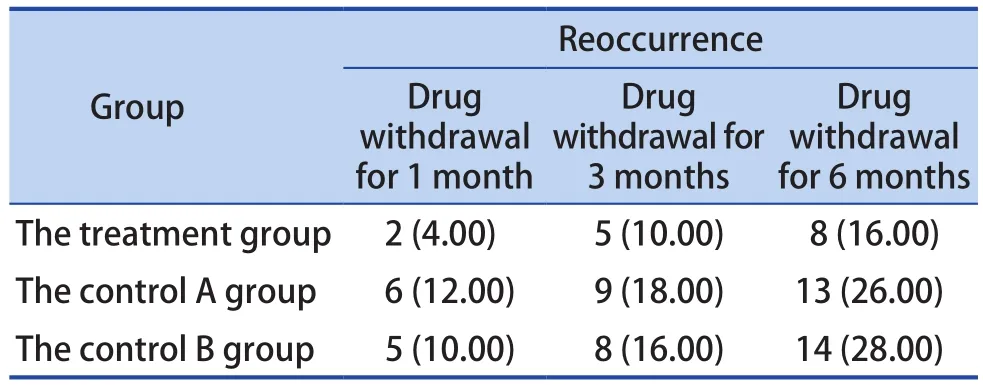
Table 3. Comparison of Recurrence Rate in Each Group [n (%), n=50]
Comparison of Quality of Life After Treatment in Each Group
Compared with before treatment, there was no significant change of the physiological function scores in each group after treatment (P>0.05), and the scores of physiological function, physical pain,general health, vitality, social function, emotional function, and mental health were significantly improved (P>0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the scores among each group after treatment (P>0.05) (Table 4).
DISCUSSION
Functional dyspepsia is a clinically very common gastrointestinal dysfunction disease. It refers to persistent or recurrent pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen. Other symptoms include nausea, post-sternal burning and early full, belching,and abdominal distension, etc.. After examination,organic diseases are excluded, that is, there is no abnormality in the structure, morphology and biochemical of the gastrointestinal system. The incidence of this disease in the population is high.Statistics in Europe and the United States indicate that the proportion of patients complaining of dyspepsia is as high as 40%-70% in outpatients for digestive diseases, of which about 40%-55%are FD, accounting for the total outpatients 5%of the amount. The medical statistics show that the incidence of patients with FD can reach 10%-30% in China, accounting for about 40%internal medical visits[6]. With the development of society and economy, people's dietary structure has been adjusted, and the increase in life pressure and psychological pressure has led to a significant increase in the incidence of FD. At present, it is recognized that FD is a gastrointestinal dysfunction disease caused by various factors such as gastric acid secretion disorder, gastrointestinal motility dysfunction, Hp-related chronic gastritis[7], and it is difficult for western medicine to treat FD with satisfactory results. The effect of a drug is not accurate, and the efficacy of the drug has not been proven[8], so it is of great significance to actively explore its effective methods.
Table 4. Comparison of SF-36 Scores in Each Group (, Point)
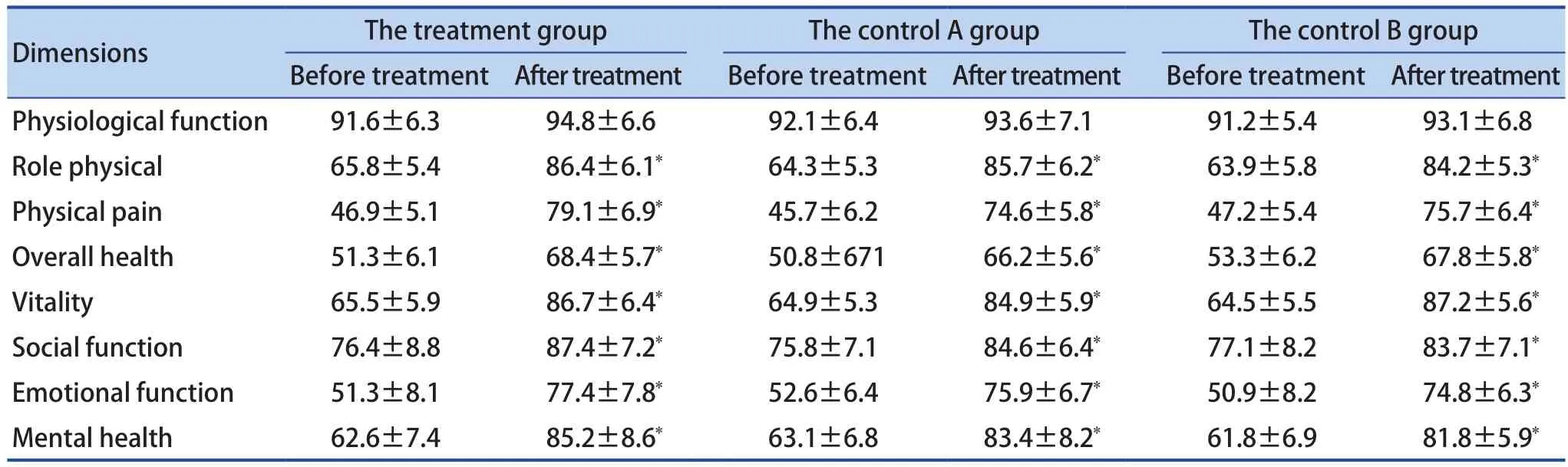
Table 4. Comparison of SF-36 Scores in Each Group (, Point)
Notes: Compared with before treatment, P<0.05
Dimensions The treatment group The control A group The control B group Before treatmentAfter treatment Before treatmentAfter treatment Before treatmentAfter treatment Physiological function 91.6±6.3 94.8±6.6 92.1±6.4 93.6±7.1 91.2±5.4 93.1±6.8 Role physical 65.8±5.4 86.4±6.1 64.3±5.3 85.7±6.2 63.9±5.8 84.2±5.3 Physical pain 46.9±5.1 79.1±6.9 45.7±6.2 74.6±5.8 47.2±5.4 75.7±6.4 Overall health 51.3±6.1 68.4±5.7 50.8±671 66.2±5.6 53.3±6.2 67.8±5.8 Vitality 65.5±5.9 86.7±6.4 64.9±5.3 84.9±5.9 64.5±5.5 87.2±5.6 Social function 76.4±8.8 87.4±7.2 75.8±7.1 84.6±6.4 77.1±8.2 83.7±7.1 Emotional function 51.3±8.1 77.4±7.8 52.6±6.4 75.9±6.7 50.9±8.2 74.8±6.3 Mental health 62.6±7.4 85.2±8.6 63.1±6.8 83.4±8.2 61.8±6.9 81.8±5.9
Modern studies have shown that electrogastrogram detection and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy have important guiding significance for the diagnosis and treatment of FD. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is the main means to exclude organic diseases,and electrogastrograph can provide a reference for diagnosis, and its positive predictive value is estimated to be between 60% and 69%[9]. At present, acid suppression, anti-Hp and prokinetic therapy are still the main methods of western medicine for the treatment of functional dyspepsia,but acid suppression therapy has limitations. It has significant effects on symptoms such as heartburn and epigastric pain, but the effect is uncertain for other types of dyspepsia. Moreover, the treatment course of western medicine is long (2 to 4 weeks of medication is required), and the condition is prone to relapse, which causes a greater economic burden on patients. Studies have shown that the effective rate of acid suppression therapy is 35%-80%, while the effective rate of placebo is 32%-80%[10], which brings confusion to clinical treatment.
There is no systematic and complete record in traditional Chinese medicine. According to its main clinical manifestations, the disease should be classified into categories such as "fullness","stomach pain", "poor appetite" and "noisy"[11]. The mechanism is that the chest and abdomen are stuffy and full of discomfort caused by invagination of exogenous pathogens, inadequate diet, emotional disorder, weak spleen and stomach, etc., which lead to unfavorable Qi (气) movement in the middle Jiao (焦) and malfunction of descending and ascending[12]. In Zhuang nationality medicine,this disease belongs to the category of "Donglang(东郎)", and it is believed that the etiology and pathogenesis of the disease are valley tract diseases caused by weak valleys, improper diet or infestation of insects, which leads to stagnation of food, and Qi stagnation[13]. Although internal administration of traditional Chinese medicine has its advantages in the treatment of functional dyspepsia, it is only a clinical observation of single and proven prescriptions for the treatment of FD, and there are still certain limitations: ① Most reports are still based on the summary of clinical experience, and the efficacy standards are not uniform[14]; functional dyspepsia cannot be evaluated objectively and quantitatively[15]. ② Herb decoction is inconvenient, and the patient's taste and compliance is poor. Therefore, clinicians and researchers from all over the world are exploring other treatment approaches. On the basis of inheriting the bamboo cupping therapy of Zhuang nationality medicine,our department creatively applies this therapy to treat spleen and stomach diseases. This therapy is based on the main role of acupoints, combined with the warm nature of the bamboo pot, the principle of negative pressure and the osmotic therapeutic effect of Chinese materia medica decoction, the balance of visceral functions is regulated through the skin,meridians and viscera. After administering this therapy to some FD patients, it was initially observed that it has a significant effect on relieving clinical symptoms. In order to further objectively evaluate its curative effect, it is planned to conduct gastrograph test while changing the observation symptoms. The purpose is to seek a new, accurate and economical and simple external treatment method for FD patients, and to promote the treatment techniques to grassroots and community hospitals as a practical external treatment method of traditional Chinese medicine, which is the purpose and significance of this project. The results of this study show that the treatment of functional dyspepsia with stagnation of liver Qi and spleen deficiency syndrome by Zhuang nationality Medicine bamboo cupping therapy can significantly improve the clinical effectiveness, reduce the rhythm disorder coefficient, and improve the clinical treatment effect. The long-term recurrence rate is low and the quality of life is significantly improved, which is a convenient and effective method.
In summary, the long-term curative effect of medicated bamboo cupping therapy on functional dyspepsia of stagnation of liver Qi and spleen deficiency syndrome is significant, and the quality of life of patients has been significantly improved.Through the research of this project, we can enrich the methods of treating FD in our hospital, reduce the cost of drug treatment for patients, reduce the economic burden of patients and society, and promote the construction of Zhuang nationality Medical Specialty in our hospital, which can bring great social benefits; moreover, the therapy has no toxic side effects, simple operation, excellent patient compliance, and with good academic and clinical promotion value.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- Clinical Effects of the Qi-acupuncture Therapy of TCM on Portal Hypertension
- Rapid Recovery Strategy of Treating Hemorrhoids in Perioperative Period by Multimodal Analgesia with Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Based on FP-Growth Algorithm to Excavate Medication Rule of Chinese Materia Medica for Radiation Esophagitis
- Application Status of Infrarde Thermography in the Evaluation of Curative Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- A Review on Treating Postoperative Perianal Abscess by the TCM External Therapy
- INSTRUCTION FOR AUTHORS
