逐水饮治疗恶性胸腔积液大鼠的效果及对其胸膜组织TGF-β1、AQP-1表达的影响
2020-09-02刘晓芳王晓婷赵楠
刘晓芳 王晓婷 赵楠
[摘要] 目的 研究逐水飲对大鼠恶性胸腔积液的治疗作用及对大鼠胸膜组织转化生长因子-β1(TGF-β1)和水通道蛋白-1(AQP-1)表达的影响。方法 建立恶性胸腔积液大鼠模型,将建模成功的大鼠按随机数字表法分为5组,分别为模型组(MC)、阳性对照组(PC)、逐水饮高剂量组(HD)、逐水饮中剂量组(MD)、逐水饮低剂量组(LD),每组10只。另取10只正常大鼠记为正常组(NC)。建模后第1天,PC腹腔注射2 mg/kg顺铂注射液,1次/2 d;HD、MD和LD分别灌胃66.0、33.0、16.5 g/kg的逐水饮药液,1次/d;NC和MC灌胃等体积的生理盐水,1次/d,共7 d。比较各组胸腔积液量和癌细胞含量;苏木精-伊红染色观察胸膜组织病变;比较各组TGF-β1和AQP-1表达。 结果 MC、PC、HD、MD和LD第4、8天大鼠胸腔积液量、癌细胞数均高于第1天,第8天均高于第4天;第1天MC大鼠胸腔积液量高于NC,第4、8天MC大鼠胸腔积液量、癌细胞数均高于NC,PC、HD、MD、LD均低于MC,HD低于PC,LD高于PC,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。NC大鼠胸膜组织结构正常。MC大鼠胸膜增厚严重,癌细胞、淋巴细胞浸润严重。HD、MD、LD胸膜层厚减轻,癌细胞浸润较少。与NC比较,MC TGF-β1和AQP-1表达水平升高(P < 0.05);与MC比较PC、HD、MD和LD TGF-β1和AQP-1表达水平均降低(P < 0.05);与PC比较,HD TGF-β1和AQP-1表达水平降低,LD TGF-β1和AQP-1表达水平升高,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。 结论 逐水饮对大鼠恶性胸腔积液疗效良好,可能与下调TGF-β1、AQP-1表达有关。
[关键词] 逐水饮;恶性胸腔积液;转化生长因子-β1;水通道蛋白-1
[中图分类号] R737.11 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)07(c)-0017-05
Effect of Zhushui Yin on rats with malignant pleural effusion and its effect on expression of TGF-β1 and AQP-1 in rat pleural tissues
LIU Xiaofang1 WANG Xiaoting2 ZHAO Nan1▲
1.College of Acupuncture and Massage, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150040, China; 2.Department of Oncology, Harbin Chinese Medicine Hospital, Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150900, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the therapeutic effect of Zhushui Yin on malignant pleural effusion in rats and its effect on expression of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and aquaporin-1 (AQP-1) in rat pleural tissues. Methods The rat model of malignant pleural effusion was established, and the successfully modeled rats were divided into five groups according to the random number table method, namely, the model group (MC), the positive control group (PC), the high-dose group (HD), the middle-dose group (MD), and the low-dose group (LD), with ten rats in each group. Another ten normal rats were recorded as normal group (NC). On the first day after modeling, PC was intraperitoneally injected with 2 mg/kg Cisplatin Injection once every two days. HD, MD and LD were respectively given 66.0, 33.0 g/kg and 16.5 g/kg of Zhushui Yin Liquid once a day. NC and MC were given the same volume of normal saline, once a day, for seven days in total. The amount of pleural effusion and the content of cancer cells in each group were compared. Pleural lesions were observed by hematoxylin-Eosin staining. The TGF-β1 and AQP-1 expression were compared in each group. Results The amount of pleural effusion and the number of cancer cells of MC, PC, HD, MD and LD on the fourth day and the eighth day were all higher than those on the first day, and the eighth day was higher than the fourth day. On the first day, the pleural effusion amount of MC rats was higher than NC, on the fourth day and the eighth day, the pleural effusion amount and cancer cell number of MC rats were higher than those of NC, while PC, HD, MD and LD were lower than MC, HD was lower than PC, LD was higher than PC, and the differences were statistically significant (all P < 0.05). The pleural structure of NC rats was normal. The pleural thickening and infiltration of cancer cells and lymphocytes were serious in MC rats. The pleural thickness in HD, MD, LD was reduced and the infiltration of cancer cells was less. Compared with NC, the expressions of TGF-β1 and AQP-1 in MC were increased (P < 0.05). Compared with MC, the expression levels of TGF-β1 and AQP-1 in PC, HD, MD and LD were all decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with PC, the expression levels of TGF-β1 and AQP-1 in HD were decreased, while the expression levels of TGF-β1 and AQP-1 in LD were increased, with statistically significant differences (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Zhuishui Yin has a good effect on malignant pleural effusion in rats, which may be related to down-regulation of TGF-β1 and AQP-1 expression.
[Key words] Zhushui Yin; Malignant pleural effusion; Transforming growth factor-β1; Aquaporin-1
恶性胸腔积液是由恶性肿瘤引起的常见并发症,多发于癌症晚期[1]。肺癌导致的恶性胸腔积液在临床较多见,占50%~60%[2]。恶性胸腔积液目前常用方法是通过胸腔给予化疗药物,但此类药物具有对人体毒副作用大、恶性胸腔积液易反复等缺陷[3-4]。逐水饮具有清肺利水、益气散毒等作用[5]。有研究显示[6],逐水饮联合香菇多糖可有效控制恶性胸腔积液,但对于逐水饮单独的作用效果及其作用机制相关报道较少。因此本研究使用逐水饮治疗恶性胸腔积液并探索其作用机制,现报道如下:
1 材料与方法
1.1材料
64只2月龄SPF级别Wistar大鼠,雌雄各半,体重230~260 g,购自浙江维通利华实验动物技术有限公司[许可证号:SCXK(浙)2019-0001];艾氏腹水瘤细胞购自上海雅吉生物科技有限公司;逐水饮:黄芪20 g、葶苈子20 g、瓜蒌皮20 g、苦参20 g、白花蛇舌草20 g、人参15 g、大枣15 g、桑白皮15 g、百部15 g、莪术15 g、甘草15 g,夏枯草10 g均购自同仁堂大药房(逐水饮由医院药剂科制备成流浸膏,含生药1 g/mL);順铂购自成都利尔药业有限公司(批号:A2018070508);苏木精-伊红染色(HE)试剂盒、反转录试剂盒、RNA提取试剂盒、PCR(RT-qPCR)荧光染料预混试剂盒、Western blot试剂盒均购自上海李记生物科技有限公司(批号:17052210、17081207、2015052305、Y145831-012、09114 0125);引物设计委托广州伯信生物科技有限公司;转化生长因子-β1(TGF-β1)鼠单克隆抗体(批号:2010050233),水通道蛋白-1(AQP-1)鼠单克隆抗体(批号:2016040412)和β-actin鼠单克隆抗体(批号:2008112010)及兔抗鼠IgG二抗(批号:2012052428)均购自美国abcam公司。
DMS-854光学显微镜购自深圳市奥凯视科技有限公司;TG16KR高速冷冻离心机购自上海继谱电子科技有限公司;DYCZ-24DN垂直电泳设备购自北京六一仪器厂;JM1966-018500 RT-qPCR仪器购自美国罗氏公司;HF100HA动物X光机购自日本Ltd公司。
1.2 建模、分组和干预方法
Wistar大鼠饲养在23℃恒温,湿度50%,12 h明暗交替的无菌动物饲养房中。雌雄分笼饲养。本研究通过黑龙江中医药大学实验动物伦理委员会伦理审查,伦理审查受理号:2019040502。
建模、分组及给药:在5%CO2,37℃恒温细胞培养箱中培养艾氏腹水瘤细胞,接种于4只大鼠腹腔内,7 d后,将腹水中的肿瘤细胞吹散成单个悬浮状态。随机挑选50只大鼠进行建模。将1×108个/mL浓度细胞悬液从大鼠右侧腋后线处第11~12肋骨间隙注射入胸腔,每只大鼠注射0.3 mL,余下10只记作正常组(NC),同样操作胸腔注射0.3 mL生理盐水。建模24 h后通过X线片对建模大鼠进行病理评价[7]。将建模成功的大鼠将按照自然数编号并利用SAS 9.0计算机软件建立随机数字表将其分为5组,分别为模型组(MC)、阳性对照组(PC)、逐水饮高剂量组(HD)、逐水饮中剂量组(MD)、逐水饮低剂量组(LD),每组10只。PC腹腔注射2 mg/kg的顺铂注射液,1次/2 d,HD、MD、LD分别灌胃66、33、16.5 g/kg逐水饮药液,1次/d。MC和NC灌胃等体积生理盐水,1次/d。连续7 d。在建模后第8天,颈椎脱臼法处死大鼠。
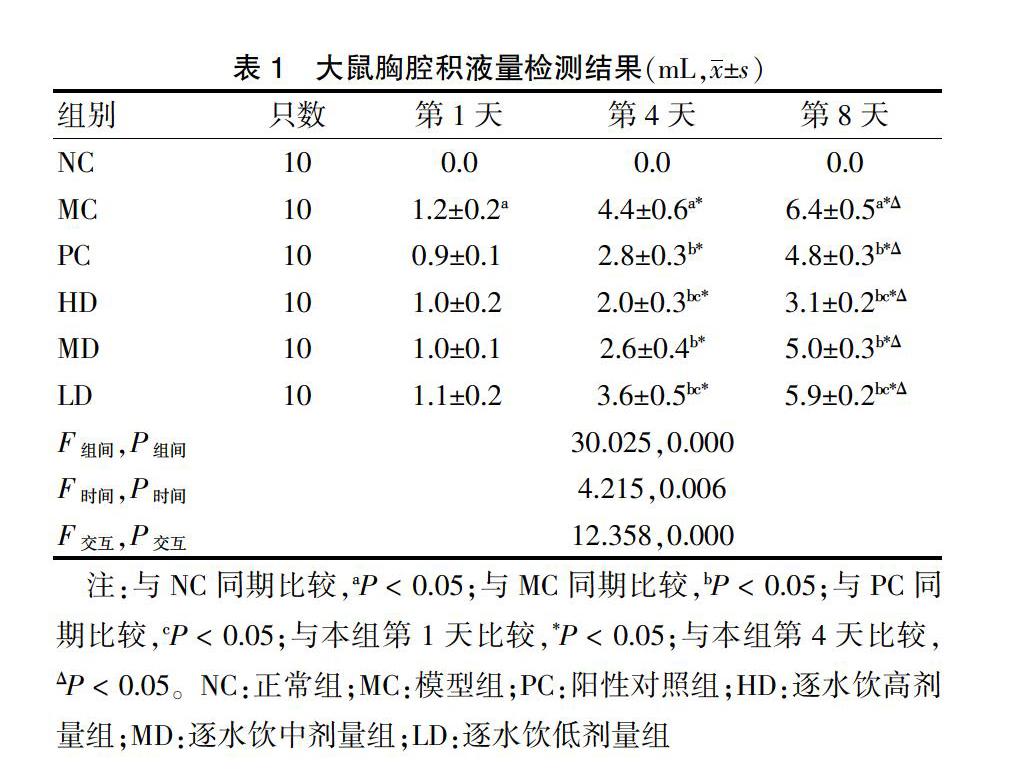
大鼠胸腔积液量检测:分别在建模后第1、4、8天,使用10 mL注射器从大鼠膈肌腹面向胸腔内进针并抽取胸腔内积液,记录抽取胸腔积液量。
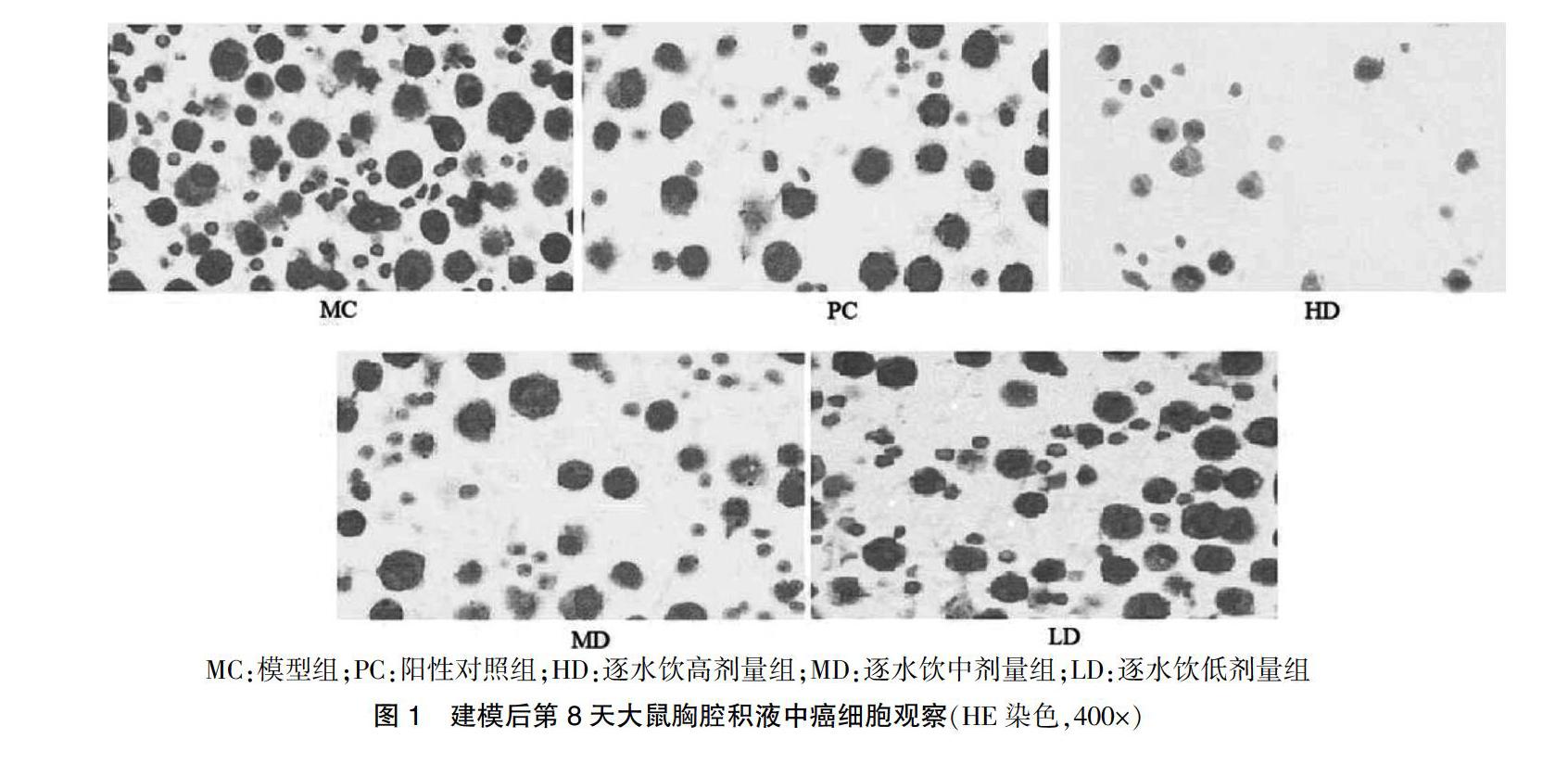
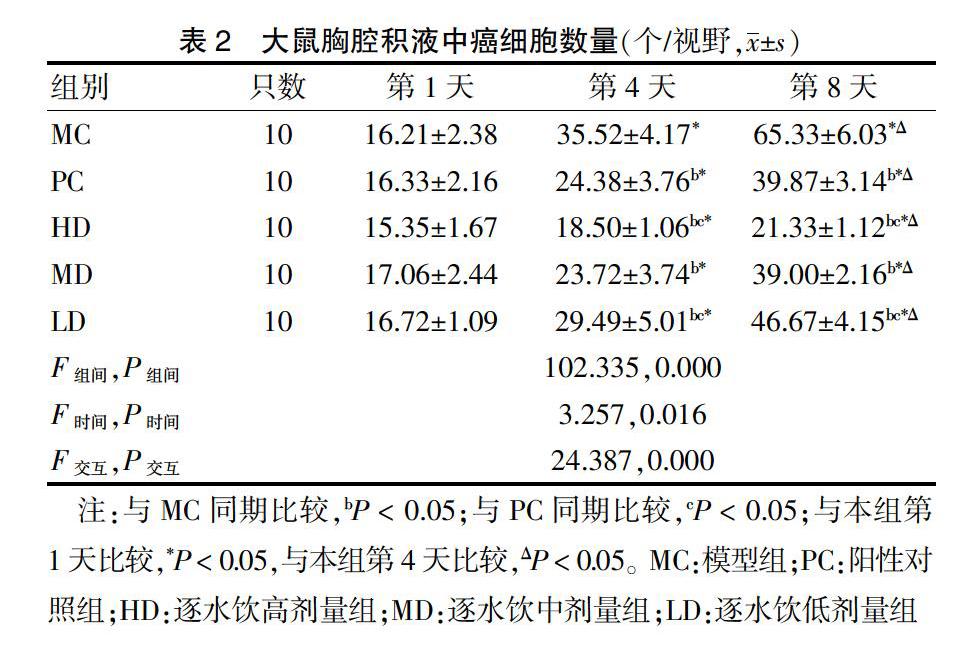
观察大鼠胸腔积液沉渣中癌细胞量:分别在建模后第1、4、8天,每只大鼠取2 mL胸腔积液,4℃,3000 r/min,离心半径6.3 cm,离心10 min。取沉淀涂片并使用HE染色试剂盒对图片染色后封片并在显微镜200×视野下观察。
观察大鼠胸膜组织病理变化:剪开大鼠胸腔,取胸膜组织于10%福尔马林溶液中进行固定,石蜡包埋后切片,按照HE染色说明书和染色,封片,光镜下观察。
胸膜组织中TGF-β1、AQP-1 mRNA检测:取2 mg胸膜组织,提取组织中总RNA,反转录为cDNA。设计上下游引物。反应体系:cDNA 0.5 μL,dNTP 1 μL,荧光染料预混试剂1 μL,上下游引物分别1 μL,ddH2O 5.5 μL,总体积10 μL。95℃ 10 min,35个循环95℃ 30 s,56℃ 15 s,72℃ 30 s。对溶解曲线进行分析,并以β-actin为对照。
胸膜组织中TGF-β1、AQP-1蛋白检测:取2 mg胸膜组织提取总蛋白,按照Western blot试剂盒说明书操作。显色后使用扫描仪扫描成像并分析条带灰度值,以β-actin为对照。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 23.0统计学软件进行数据分析,计量资料用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间两两比较采用SNK-q和LSD-t检验;重复测量数据采用重复测量方差分析。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 大鼠胸腔积液量检测
建模及干预期间均未出现大鼠死亡,且50只建模大鼠均建模成功,MC、PC、HD、MD、LD各10只。大鼠胸腔积液量组间比较、时间点比较及交互作用差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05),提示大鼠胸腔积液量与时间和给药剂量有关。进一步两两比较,组内比较:MC、PC、HD、MD和LD第4、8天大鼠胸腔积液量均高于第1天,第8天均高于第4天;组间比较:第1天MC高于NC,第4、8天MC均高于NC,PC、HD、MD、LD均低于MC,HD低于PC,LD高于PC,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。见表1。
[8] 李慧,嚴时,刘岩,等.晚期NSCLC患者恶性胸腔积液中上清和细胞沉淀EGFR基因突变状态的比较[J].国际肿瘤学杂志,2018,45(1):10-15.
[9] Ferreiro L,Toubes ME,San José ME,et al. Advances in pleural effusion diagnostics [J]. Expert Rev Respir Med,2020,14(1):51-66.
[10] 李枋霏,王维,张仲妍,等.葶苈大枣泻肺汤辅助化疗治疗肺癌恶性胸腔积液临床研究[J].国际中医中药杂志,2018,40(3):214-217.
[11] Congcong Q,Hengting Z,Shuhui L,et al. Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety for Lentinan in the Control of the Malignant Pleural Effusions via Intrapleural Injection [J]. Am J Med Sci,2019,358(6):400-411.
[12] 毕兰青,朱凡,张勤英,等.紫杉醇腹腔灌注和静脉滴注双途径给药模式二线治疗胃癌伴恶性腹腔积液的效果[J].中国医药,2018,13(1):92-95.
[13] 李俊娇,葛信国.葛信国教授运用扶正逐饮法治疗肺癌恶性胸腔积液经验[J].中国中医急症,2018,27(1):159-161.
[14] 李政,王巍,李康.葶苈甘遂逐水饮联合胸腔内灌注化疗治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌伴恶性胸水临床疗效分析[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2016,18(1):198-200.
[15] Dai B,Xiao Z,Mao B,et al. lncRNA AWPPH promotes the migration and invasion of glioma cells by activating the TGF-β pathway [J]. Oncol Lett,2019,18(6):5923-5929.
[16] 吕大伦,徐姝娟,陈雷,等.人促红细胞生成素对大鼠急性创面转化生长因子β1/Smad3信号转导通路的影响[J].中华烧伤杂志,2018,34(10):719-726.
[17] Wu DW,Chang WA,Liu KT,et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and protein level in pleural effusion for differentiating malignant from benign pleural effusion [J]. Oncol Lett,2017,14(3):3657-3662.
[18] Hojski A,Leitgeb M,Crnjac A. Release of growth factors after mechanical and chemical pleurodesis for treatment of malignant pleural effusion: a randomized control study [J]. Radiol Oncol,2015,49(4):386-394.
[19] Liu M,Liu Q,Pei Y,et al. Aqp-1 Gene Knockout Attenuates Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension of Mice [J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2019,39(1):48-62.
[20] 杨格强,祝艳妮.沉默AQP-1对PDGF诱导的视网膜色素上皮细胞增殖迁移的影响研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2018,17(20):2169-2173.
[21] Zhang JX,Xie CM,Zhu ZW,et al. Potential role of AQP1 and VEGF in the development of malignant pleural effusion in mice [J]. Med Oncol,2012,29(2):656-662.
(收稿日期:2020-01-10)