济南冬季泉水水系中趋磁细菌的多样性
2020-07-04王浩然张连越刘沛余
王浩然 张连越 刘沛余
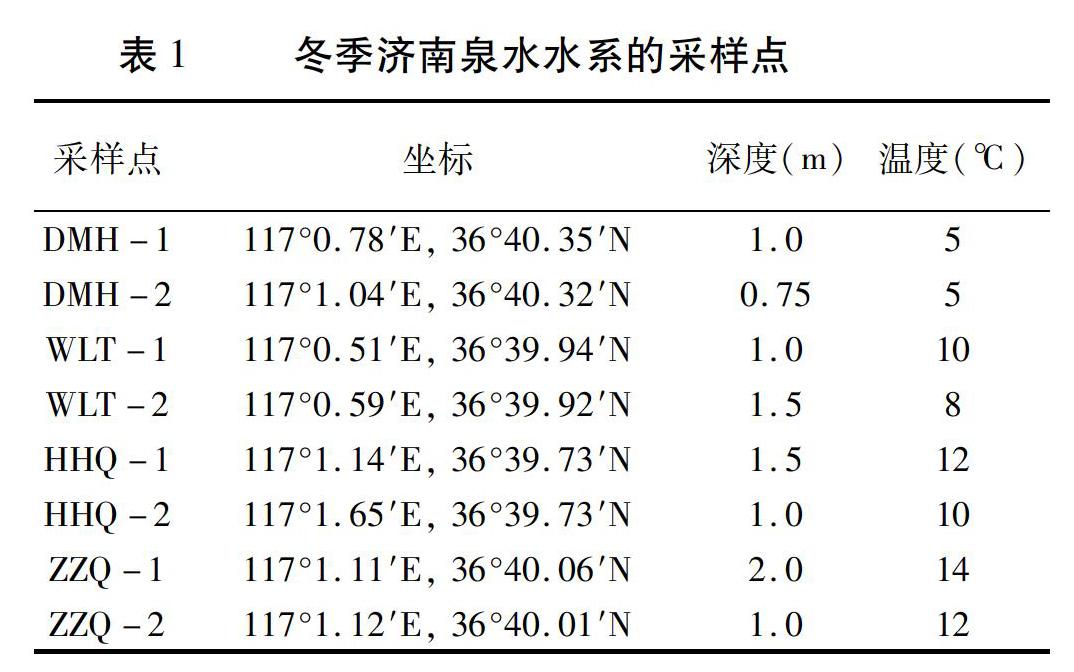
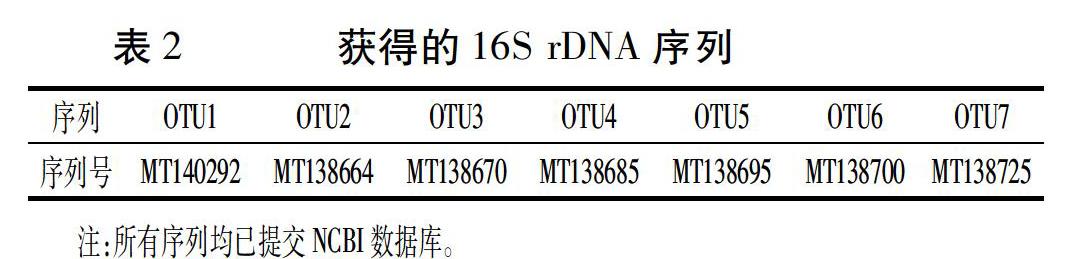
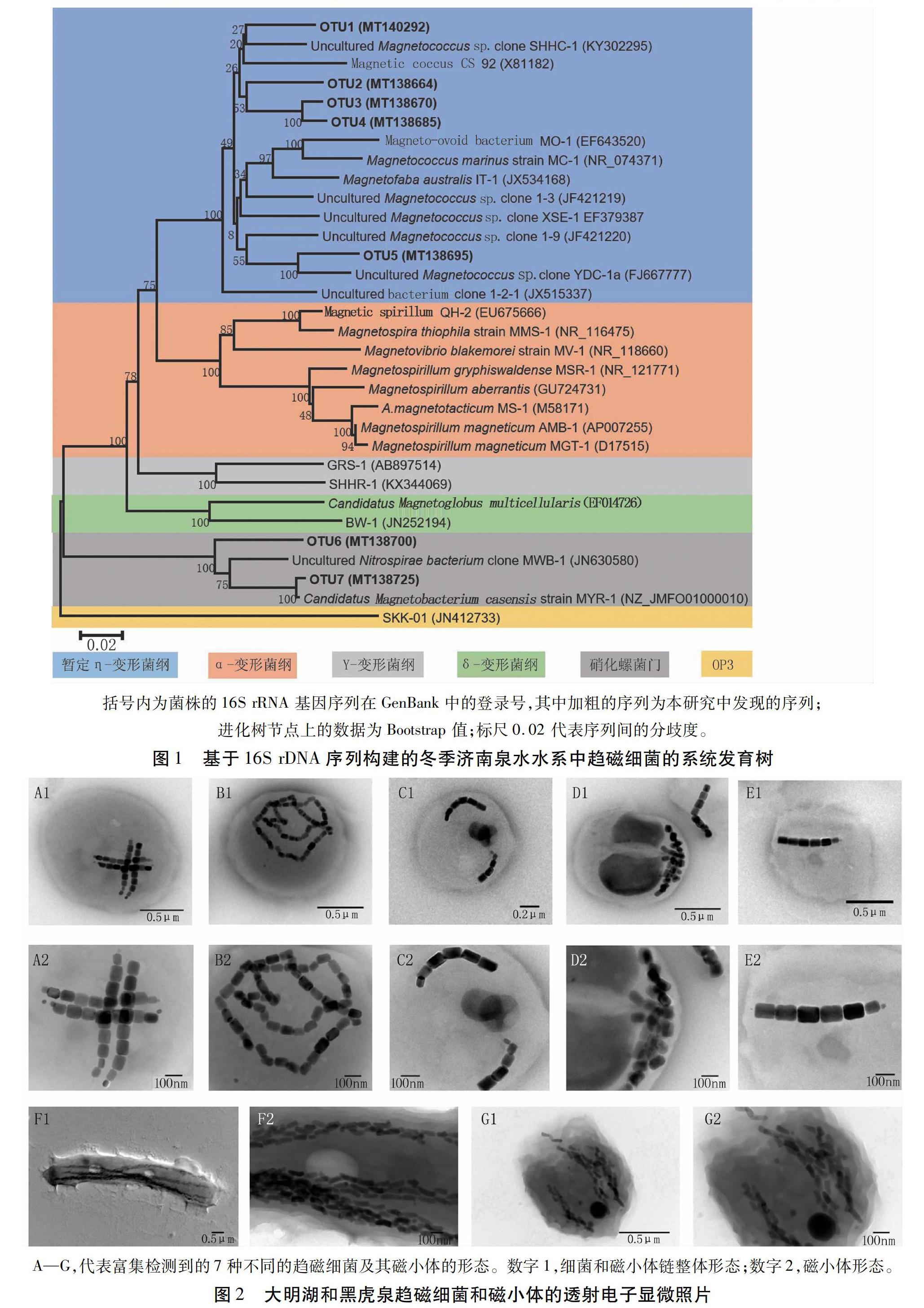
摘要:为探究济南冬季泉水水系中细菌的生态分布、未培养趋磁细菌及其磁小体形态的多样性,选择济南市泉水源头、护城河及泉水汇集的大明湖等8处不同位点,于2018年1月13日收集水底表层泥样,富集环境中趋磁细菌,提取样品总DNA,进行16S rDNA高通量测序及生物信息学分析,并利用透射电子显微镜观察和统计趋磁细菌及磁小体的形态,揭示济南泉水水系中趋磁细菌的分布特征。结果表明,济南冬季泉水水系中趋磁细菌分布明显不均,泉水源头处未检测到趋磁细菌;黑虎泉下游护城河中发现了少量单链趋磁球菌,基因序列表明为新种,暂定为η-变形菌纲(Candidatus Etaproteobacteria)的一个菌株;众泉汇集的大明湖中趋磁细菌种类最多,且细菌和磁小体形态多样性复杂。微生物多样性分析发现,冬季泉水水系中细菌种类主要是变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、蓝细菌门(Cyanobacteria)和绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi),三者总丰度均占细菌总量的65%以上,具有磁细菌生长所需的群落环境。本研究可为深入研究未培养趋磁细菌的全基因组及可培养条件等提供素材与线索。
關键词:济南泉水;冬季;趋磁细菌;磁小体;暂定η-变形菌纲;16S rRNA;微生物多样性
中图分类号:S273:Q938.8文献标识号:A文章编号:1001-4942(2020)04-0079-07
Abstract In order to explore the ecological distribution of bacteria, the diversity of uncultured magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) and their magnetosome morphology in Jinan spring water system in winter, the water sludge samples were collected from 8 sites in the fountainhead, mead stream Hucheng River and downstream Daming Lake on January 13, 2018. The MTB cells were gathered from the sludge samples and used to extract the genome DNA for high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis. The morphology of MTB and magnetosome were observed by transmission electron microscope, and the distribution features of MTB in Jinan spring water in winter were revaled. The results showed that the distribution of MTB in Jinan spring water system was obviously uneven. No MTB was detected at the fountainheads. A small amount of single-stranded magnetococci was found in the downstream of Heihu Spring, which is a strain of Candidatus Etaproteobacteria. Daming Lake had the most diverse types of magnetotactic bacteria, and the morphology of bacteria and magnetosomes was diverse. Microbial diversity analysis showed that the types of bacteria in the spring water system in winter were mainly Proteobacteria,Cyanobacteria and Chloroflexi, whose abundance was more than 65%. The results in this article would provide materials and clues for the further researches of the whole genome and cultured conditions.
Keywords Jinan spring water; Magnetotactic bacteria; Magnetosome; Candidatus Etaproteobacteria; 16S rDNA; Microbial diversity
趋磁细菌是一类可沿地球磁场运动的微生物总称,广泛存在于海洋和湖泊中。其独特之处在于胞内能够合成由生物膜包被的纳米级磁性颗粒——磁小体(magnetosome),目前发现的磁小体主要成分为磁铁矿或胶黄铁矿[1]。相对于人工合成的磁性颗粒,磁小体具有众多优点,如化学组分纯度高、质地均一、热损耗高等,具有广阔的应用前景。然而,趋磁细菌生长条件苛刻,实验室条件下仅有少量趋磁细菌(如AMB-1)能被纯培养[2],这给其深入研究带来较大困难。
快速发展的宏基因组技术为未培养微生物的研究开拓了全新的方法,人们可通过对环境中微生物遗传物质的分析探究趋磁细菌种群的种类、分布以及功能基因簇的起源与系统发育等。由于环境条件可能作为重要的进化压力,在趋磁细菌长期演化过程中扮演重要角色,因此认识不同季节不同天然条件下趋磁细菌的分布就引起人们广泛的兴趣。前人研究揭示,在河流、湖泊、海洋等常见水体及以盐碱湖和热泉为代表的极端环境中趋磁细菌都具有复杂的生物多样性[1,3-6],且种类的分布与环境因子体现出明显相关性[7, 8]。目前还未见有关趋磁细菌在冬季泉水这种寡营养水体环境中的生物多样性研究。本试验即以冬季寡营养的济南天然泉水水系为研究对象,分析趋磁细菌的分布以及细菌和磁小体的形态多样性,揭示不同区域泉水的微生物多样性,为进一步研究趋磁细菌与环境微生物群落之间的关系奠定基础。
