High flux hemodialysis in elderly patients with chronic kidney failure
2020-06-17HaiYanXueBinDuanZhenJiangLiPengDu
Hai-Yan Xue, Bin Duan, Zhen-Jiang Li, Peng Du
Hai-Yan Xue, Dialysis Center, The Fourth People’s Hospital of Shaanxi, Xi’an 710043, Shaanxi Province, China
Bin Duan, Zhen-Jiang Li, Peng Du, Department of Kidney Diseases, Dialysis Center, Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China
Abstract
Key words: Elderly patients; Chronic kidney failure; High flux; Hemodialysis
INTRODUCTION
The main symptoms in chronic kidney failure (CKF) include kidney dysfunction, and even metabolic disorder. In patients with advanced kidney failure, uremia is another major symptom which disrupts patients’ daily routine and throws their life into confusion[1-3]. Hemodialysis, an advanced blood purification technique, helps improve symptoms and prolong the life of patients whose kidneys do not work normally by effectively removing waste products such as toxins from the blood.
However, conventional hemodialysis cannot remove toxins clearly, which may induce complications, and then lead to rising medical expense accordingly.Furthermore, over the prolonged dialysis duration, the increased and accumulated toxins obviously may pose a deadly threat to patients[4]. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the efficacy of high flux hemodialysis in elderly patients with CKF.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data collection
Sixty-six patients with CKF who received treatment at our hospital were selected between October 2017 and October 2018. They were divided into a study group and a control group according to the treatment they received, with 33 patients in each group. The inclusion and exclusion criteria for the study were as follows: Patients who were diagnosed with stable CKF and who were willing to participate in the study were included in the study. However, patients with complications, active autoimmune disease, or malignant tumors as well as patients with incomplete clinical medical record were excluded. For the study group, there were 16 female patients and 17 male patients. The age of the patients in the study group ranged from 60 to 76 years with an average age of 66.45 ± 4.11 years. For the control group, there were 15 female patients and 18 male patients. They were aged between 60 to 76 years with an average age of 66.26 ± 4.05 years. There was no significant difference in the basic data between the two groups (P> 0.05).
Research methods
In the study group, the patients received high flux hemodialysis with a coefficient of ultrafiltration (KUF) of 56 mL/h per mmHg and blood flow rate of 220 to 250 mL/min(3 times a week, 4 h per session). In the control group, the patients underwent hemodialysis using a 4008B dialysis machine with a KUFof 10 mL/h per mmHg and blood flow rate of 220 to 250 mL/min (3 times a week, 4 h per session). Kidney dialysis was performed using hydrogencarbonate based dialyzate solution. Low molecular weight heparins were used as anticoagulants.
Measurements
Kidney function and serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen concentrations were recorded before and after the treatment[5].
Toxin levels in serum and the incidence of complications were observed. The overall incidence of complications was calculated as No. of cases with fatigue +muscle spasms + itchy skin + arthralgia/total No. of cases × 100%[6].
Statistical analysis
SPSS19.0 was used to analyze the data in the study.P< 0.05 indicated that there was a significant difference.
RESULTS
Kidney function before and after treatment
The study showed that there was no significant difference in kidney function between the two groups before the treatment (P> 0.05). After the treatment, kidney function was better in the study group than in the control group (P< 0.05, Table 1).
Serotoxin levels in the two groups
According to Table 2, there was no significant difference in β2-microglobulin and blood urea nitrogen between the two groups (P> 0.05). Parathyroid hormone and serum cystatin C levels were significantly lower in the study group than in the control group (P< 0.05).
Complications in the two groups
The incidence of complications is presented in Table 3. The incidence of complications was 8.57% in the study group, which was significantly lower than that of the control group (20.00%;P< 0.05).
DISCUSSION
Patients with CKF are troubled by kidney disease, which is an irreversible disease,and may lead to kidney dysfunction. Loss of kidney function may be accompanied by multiple organ failure or metabolic disorder, which would endanger patients’ lives[7].In addition, decreased kidney function, metabolic disorders, and the associated toxins at the advanced stage will affect quality of life and living conditions of patients.However, management of kidney disease including the use of hemodialysis can help to promote metabolism[8]. Hemodialysis as an advanced blood purification technique to manage kidney failure can cleanse toxins from the blood, prolong kidney function,and improve patients’ quality of life. However, for conventional hemodialysis, the high prevalence of dyslipidemia may cause cardiovascular diseases and an increase in mortality. Moreover, toxins accumulating in the body over time may induce some complications[9].
The present study researched high flux hemodialysis in elderly patients with CKF.The results revealed that there was no significant difference in the main functions of the kidney between patients receiving high flux hemodialysis and those receiving conventional hemodialysis before the treatment (P> 0.05). There was also no significant difference in the levels of β2-microglobulin and blood urea nitrogen between the two groups (P >0.05). However, after the treatment, the main function parameters of the kidney were better in the study group than in the control group (P<0.05). What’s more, the levels of parathyroid hormone and serum cystatin C were lower in the study group than in the control group (P <0.05). The incidence of complications was significantly lower in the study group than in the control group (P< 0.05).
High flux hemodialysis is a highly effective technique to purify the blood. It works smoothly in the process of convection-diffusion and adsorption. It utilizes dialyzer membranes of high energy and high biocompatibility to purify the blood.Comparatively, high flux hemodialysis has larger pore sizes which promote improvement in the activity of lipoprotein and lipid metabolism[10]. It can effectively remove toxins from the blood and improve lipids in the blood which play an essential role in the formation of complications with high diffusion and filtration[11].
Large middle molecules such as serum phosphate were risky for the complications in patients receiving continuous hemodialysis. In terms of removing toxins, low flux hemodialysis’ performance is not so good, although it has good therapeutic efficacy.By using membranes of high biocompatibility, high flux hemodialysis can help reducethe incidence of dialysis membrane reactions and inflammatory stress. It removes smaller-sized middle molecules from the blood by creating dispersion and removes larger middle molecules by creating adsorption. It can effectively reduce the incidence of complications and treatment duration and improve the survival. Furthermore, it does not require specialist equipment and the cost is comparatively low[12].
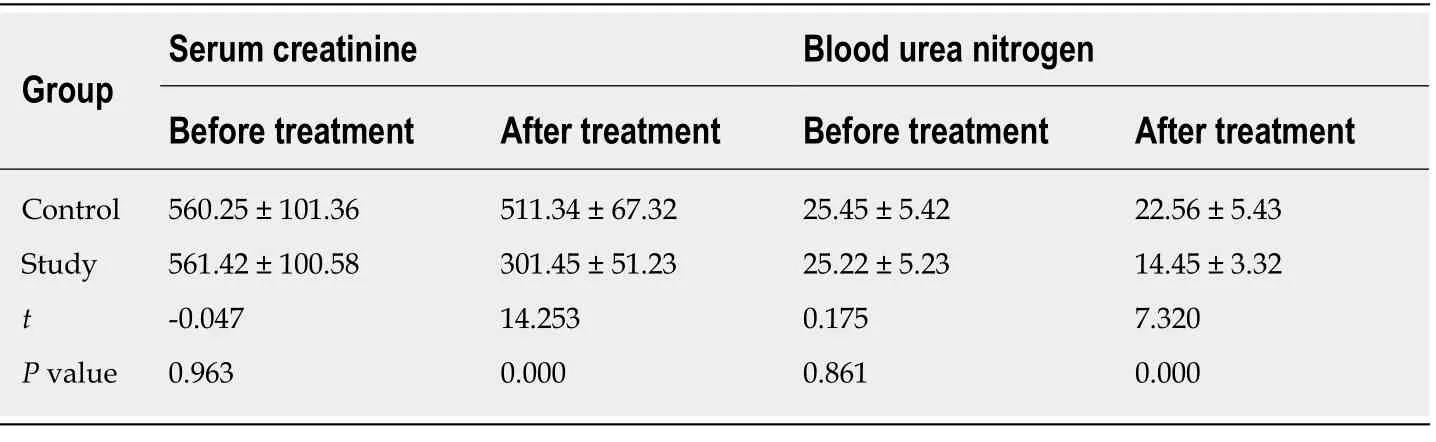
Table 1 Kidney function before and after treatment (mmol/L)
In the past, most patients received conventional hemodialysis + hemodiafiltration(HDF)[13]. Presently, nevertheless, they use HDF more frequently. However, HDF requires a large amount of replacement fluids, which increase the cost of health care,and accordingly the use of HDF is restricted. In China, many patients who need hemodialysis cannot get enough benefits from the long-term treatment of hemodialysis because of the financial burden. Some patients can only afford a single dose, which hinders the achievement of the targeted treatment efficacy. High flux hemodialysis can save the treatment expense for the population as well as reduce the length of hospital stay and mortality rate, improve quality of life, and prolong the survival of patients[13-15].
A study by Zhang[16]showed that after high flux hemodialysis, creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels were lower and the overall efficacy was well-improved,indicating that high flux hemodialysis can effectively improve disease indexes and clinical symptoms.
In conclusion, in the present study, high flux hemodialysis improves kidney function and reduces the incidence of complications and serum toxins in elderly patients with CKF.
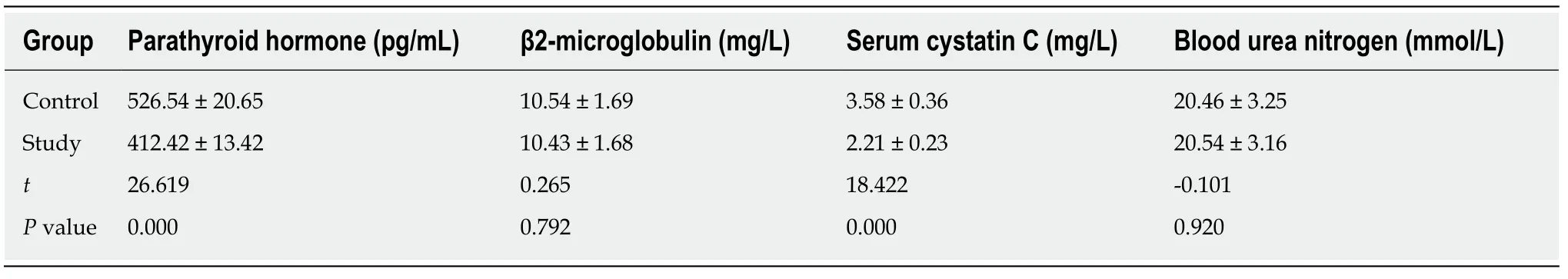
Table 2 Serotoxin levels in the two groups
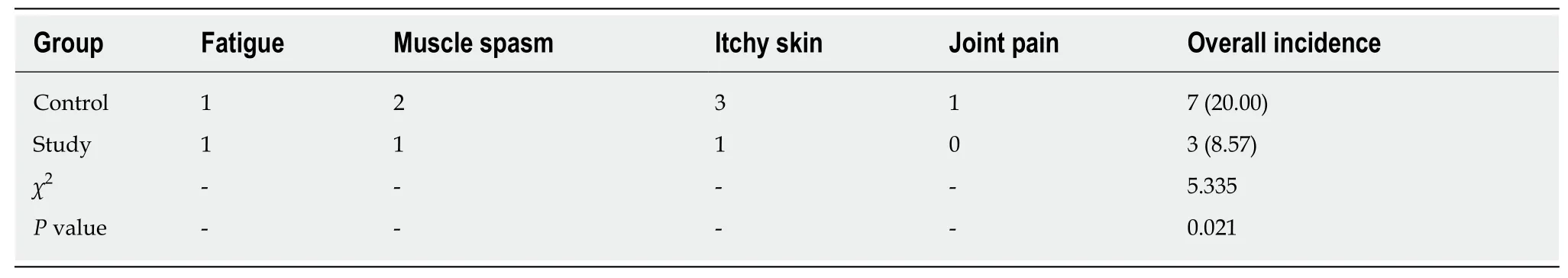
Table 3 Complications in the two groups, n (%)
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Hemodialysis is an advanced blood purification technique to manage kidney failure. However,conventional hemodialysis may cause cardiovascular diseases and an increase mortality because of the high prevalence of dyslipidemia. Moreover, toxins accumulating in the body over time may induce some complications. High flux hemodialysis has been reported to effectively improve disease indexes and clinical symptoms. Little data is available on the effectiveness of high flux hemodialysis in the real clinical world. The present study researched the effect of high flux hemodialysis on kidney function, incidence of complications, and serum toxins in elderly patients with chronic kidney failure (CKF).
Research motivation
This study explored the effectiveness of high flux hemodialysis in the real clinical world to find ways to improve kidney function and reduce the incidence of complications in patients with CKF.
Research objectives
The study aimed to identify the efficacy of high flux hemodialysis in elderly patients with CKF.
Research methods
Sixty-six patients with CKF who received treatment at our hospital were enrolled and observed between October 2017 and October 2018. They were divided into a study group and a control group according to the treatment they received. Patients in the study group received high flux hemodialysis with a coefficient of ultrafiltration of 56 mL/h per mmHg and blood flow rate of 220 to 250 mL/min (3 times a week, 4 h per session). Patients in the control group underwent hemodialysis using a 4008B dialysis machine with a KUF of 10 mL/h per mmHg and blood flow rate of 220 to 250 mL/min (3 times a week, 4 h per session). Kidney function, serum creatinine,blood urea nitrogen concentration, toxin levels, and overall incidence of complications were compared between the two groups.
Research results
Before the treatment, there was no significant difference in kidney function, β2-microglobulin, or blood urea nitrogen between the two groups. In contrast, kidney function was better in the study group than in the control group after the treatment. In addition, the study group had significantly lower parathyroid hormone and serum cystatin C than the control group. The incidence of complications was 8.57% in the study group, which was lower than that of the control group (20.00%).
Research conclusions
After the treatment, kidney function was improved in patients receiving high flux hemodialysis compared with patients receiving conventional hemodialysis. High flux hemodialysis can effectively remove toxins from the blood and regulate lipids in the blood. It also helps reduce dialysis membrane reactions, inflammatory stress, and the incidence of compilations. What’s more, the healthcare expense is comparatively low for high flux hemodialysis.
Research perspectives
High flux hemodialysis is worthy of clinical promotion in elderly patients with CKF.
杂志排行
World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Tumor circulome in the liquid biopsies for digestive tract cancer diagnosis and prognosis
- Isoflavones and inflammatory bowel disease
- Cytapheresis for pyoderma gangrenosum associated with inflammatory bowel disease: A review of current status
- Altered physiology of mesenchymal stem cells in the pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
- Association between liver targeted antiviral therapy in colorectal cancer and survival benefits: An appraisal
- Peroral endoscopic myotomy for management of gastrointestinal motility disorder
