Pathogenesis of Photoaging in Human Dermal Fibroblasts
2020-04-03LingYiLeeandShengXiuLiu
Ling-Yi Lee and Sheng-Xiu Liu∗
Department of Dermatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui 230022, China.
Introduction
Photoaging is well known as the major effect of extrinsic skin aging evoked by cumulative exposure to ultraviolet light(UV).Solar UV is ubiquitous,and it is subdivided into three zones based on wavelength: UVA (315-400nm),UVB(280-315nm),and UVC(100-280nm).1UVB affects the epidermis and the upper layer of the dermis,while UVA penetrates into the lower dermis. However, UVC is predominately absorbed and reflected by the ozone layer.2As UVC is not a main source of skin-damaging radiation,it will not be discussed in this article. In addition to UV,visible light (VIS) (380-780nm) and near-infrared radiation (IRA) (750-1400nm) may also lead to photoaging,although this requires confirmation in clinical research.Similar to UVA,IRA reaches the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin.Thus,modern sun protection approaches are required to protect the skin against UV,VIS,and IRA(Fig. 1).3
Photoaging causes premature skin senescence, skin inflammation,and diverse cancerous diseases.Photoaging is classified as either hypertrophic or atrophic. Hypertrophic photoaging is characterized by deep, coarse, and abundant wrinkles, homogeneous skin color, thickened skin,sallowness,and a high global photoaging score with a low risk of erythema and cancer development.Atrophic photoaging is characterized by fine wrinkling, a shiny appearance, erythema, telangiectasia, dyspigmentation,and a tendency to develop actinic keratoses, seborrheic keratoses, and skin cancers.1
Photoaged skin is identified by degradation of the dermal extracellular matrix (ECM), including reduced collagen synthesis,enhanced collagen degradation,loss of hyaluronic acid (HA), and disorganized elastin.4Photoaged human skin has elevated levels of pH and sebum and reduced elasticity, hydration, and tonicity; furthermore,the serum concentration of fibronectin is decreased,while the serum concentrations of neutrophil elastase 2,elastin,and carbonylated protein are increased.5The alteration of the ECM and the changes that occur with the progression of photoaging are influenced by cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, which is a structural component of cartilage.6Granzyme B is a serine protease that cleaves ECM proteins and induces proteinases,which degrades the ECM.7A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study showed that the application of a low-molecularweight collagen peptide significantly improves skin hydration, wrinkling, and elasticity in humans.8Thus,restoration of the collagen deficiency and promotion of the synthesis of collagen, HA, and elastin may prevent and treat wrinkles. This article discusses photoaging mechanisms on human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) (Fig. 1).
DNA photodamage
UVA is subdivided into UVA2(315-340nm)and UVA1(340-400nm). UVA1 is the most common type of UVA,accounting for 75% of the total solar UV. Chronically,UVA1-irradiated HDFs induce residual CPD in the papillary dermis and reduce the capacity of fibroblasts to produce collagen I and III, suggesting that chronic UVA1 exposure causes DNA damage. Furthermore,UVA1 upregulates matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 expression, downregulates versican expression, and decreases elastin gene expression, all of which cause skin photoaging.10
Wavelengths of less than 290nm are absorbed and reflected by the ozone layer.HDFs exposed to chronic lowdose UVB (>290nm) radiation induce residual CPDs,which are believed to decrease the genomic stability and are constantly present in DNA and attenuated via semiconservative replication. Those residual CPDs are overexcited in the heterochromatin and at the TT dipyrimidine sites (where T is thymine).9
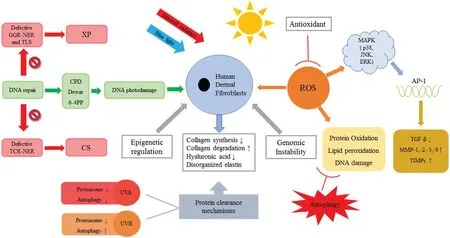
Figure 1. Photoaging mechanisms on human dermal fibroblasts.The solar ultraviolet light,infrared light and blue light act on human skin that result in DNA photodamage and redox reaction, respectively, and in turn lead to photoaging. Biomolecule oxidation not only alters cellular communication but also causes protein,lipid,and DNA oxidation.To maintain cellular homeostasis,antioxidants inhibit the formation of reactive oxygen species.Protein clearance mechanisms that contain ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy-lysosome protect against oxidative damage,including lipid oxidation,protein oxidative carbonylation,and DNA damage.Epigenetic regulation and genomic instability are also involved in the pathogenesis of photoaging.
Xeroderma pigmentosum(XP)is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes a high incidence of tumors in skin that is exposed to sunlight.Therefore,patients with XP need to be strictly shielded from sunlight at all times. The main cause of tumor development in patients with XP is oxidative DNA damage. The manifestations of XP are photosensitivity, abnormal pigmentation, skin cancers,intractable neurological lesions,and other dermatological disease. XP is a serious disease caused by DNA repair defects. Patients with XP have deficiencies in the nucleotide-excision repair pathway and the translesion synthesis pathway; responsible genes of XPA, XPB(ERCC3), XPC, XPD (ERCC2), XPE (DDB2), XPF(ERCC4), and XPG (ERCC5) are related to nucleotideexcision repair deficiencies, whereas XPV (POLH) is related to translesion synthesis deficiency. (ERCC3,ERCC2, ERCC4, ERCC5, and POLH are DNA repair genes that are responsible for XP.)11Translesion synthesis polymerases are divided into different enzymes:Rev1,Pol η, Pol ι, Pol κ, Polθ , Pol ζ, and other polymerases.12
Photoaging can be prevented by the administration of various plant compounds. Caffeic acid is a major dietary phenolic acid that prevents UVB-induced photodamage by suppressing the formation of single UVB-induced CPDs in HDFs.13Silibinin promotes DNA repair during UVB radiation by activating the p53-dependent nucleotideexcision repair pathway, including the expression of XP complementation group A,XP complementation group B,XP complementation group C, and XP complementation group G in HDFs.14Arthrospira platensis extracts relieve UVB-induced senescence by inhibiting DNA damage to prevent CPD formation in HDFs.15
Cockayne syndrome (CS) is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes defects in the ERCC excision repair 8 and CSA ubiquitin ligase complex subunit and ERCC excision repair 6 and chromatin remodeling factor.ERCC6-mutant mesenchymal stem cells and neural stem cells are highly susceptible to UV radiation. Transcriptional blockage is rescued in gene-corrected CS mesenchymal cells exposed to UV irradiation.16
Imbalance of proteostasis
Various types of protein are compromised by UV irradiation, which leads to homeostatic dysfunction in the cells. Proteostasis is necessary for cell viability, and it includes both molecular chaperone and protein clearance mechanisms.Protein clearance mechanisms are involved in the ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy-lysosome systems.17The ubiquitin-proteasome system is composed of a cascade of the ubiquitin-activating enzyme, ubiquitinconjugating enzyme, ubiquitin ligase, proteasome, and protein. Autophagy is the lysosomal degradation of damaged organelles and damaged macromolecules. The three main types of autophagy are macroautophagy,microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy.18Autophagy removes the damaged lipids, proteins, and DNA, which protects against oxidative damage such as lipid oxidation, protein oxidative carbonylation, and DNA damage.19,20Previous in vitro research shows that basal levels of intracellular autophagy increase with cellular aging, while basal levels of autophagy remain unchanged in aging skin. Upregulation of autophagy is very important in aging HDFs.21Cavinato et al.22treated diploid HDFs derived from newborn foreskins with repeated mild doses of UVB and discovered that UVB induced the senescence of HDFs, inhibited proteasome production,and enhanced autophagic activity.Moreover,UVB enhanced the production of reactive oxygen species(ROS)prior to the autophagy activation.22However,some studies report that increased autophagy activity mitigates photoaging in HDFs.15,23Autophagy is assumed to act in a context-dependent manner based on the amount of UV radiation.20Future studies should focus on the inconsistencies in the results of previous studies.
The enhancement of autophagy reduces the HDF damage caused by UV exposure. One study administered a synthetic silent information regulator T1 activator(Aquatide) to cultured HDFs isolated from neonatal foreskins that were exposed to a high dose of UVB for 16 hours15;Aquatide inhibited the photodamage in HDFs exposed to UVB by directly activating silent information regulator T1 and increasing autophagy induction via deacetylation of forkhead box class O.15Another study reported that cyanidin-3-o-glucoside suppresses UVAinduced HDF injury by enhancing autophagy.23
Catalgol et al.24found that UVA induced singlet oxygen formation, which not only caused protein oxidation but also inhibited the proteasome activity in HDFs. Reduced lysosomal cathepsin (Cat) D expression and activity damage the degradation of intracellular advanced glycation end-products in HDFs after repetitive UVA irradiation, which may accelerate advanced glycation endproduct deposition in photoaged skin.25Upregulation of Cat G and suppression of serpin B6c(which is considered a potential inhibitor of Cat G) are linked to UVB-induced wrinkle formation.26Chronic UVA irradiation inhibits the transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling via the inhibition of MMPs, and Cat G is reduced in HDFs.27UVA increases Cat K production in HDFs by activating the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway and the expression of activator protein-1 (AP-1).28UVA exposure increases Cat L expression and activity in HDFs, probably by activating c-Jun N-terminal kinase(JNK) and downregulating AP-1.29
最近几年,社会中钢结构桥梁工程数量不断增加,桥梁事业的发展同样走向繁荣。随着社会对桥梁工程要求的出新,钢结构桥梁工程的施工复杂程度水平提升,施工专业水平也越来越高。钢结构式桥梁的跨度不断负担大,无疑在无形中提高了钢结构式桥梁工程的施工风险。减小钢结构桥梁工程施工过程中的风险,是做好桥梁工程施工管制工作的重中之重。
Altered cellular communication and free radical theory
Generally, UVB radiation at a low irradiance is more photocarcinogenic than that at a high irradiance.A study that evaluated sunscreen use reported that UVA with a low irradiance aggravates photoaging in comparison to high irradiance UVA, as low UVA radiation produces higher levels of ROS, more MMP-1, JNK phosphorylation, and less type I collagen expression in cultured fibroblasts.30These results suggest that sunscreen use actually has a harmful effect with longer sun exposure.30
A therapeutic study in which HDFs were treated with a single dose of UVA(7.5J/cm2)reported higher expression of MMPs and Toll-like receptor pathway genes in senescent HDFs compared with non-senescent HDFs.31Furthermore, the non-senescent HDFs showed downregulation of collagen gene expression.31
An increasing number of new useful ingredients for cosmetic and pharmaceutical products are being developed. Antioxidants that scavenge ROS may prevent and relieve photodamage. Evaluating how these new ingredients protect the cells and skin functions from UV exposure will provide more information about the altered cellular communication and free radical theory of photoaging.
Extracellular vesicles derived from human adiposederived stem cells promote the rescue of HDFs with UVBinduced injury by inhibiting the overexpression of MMPs(MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, and MMP-9) and increasing the expression of collagens (type I-V), elastin, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1,and transforming growth factor-β1.32
Pueraria montana var. lobata ethanol extract upregulates collagen and preserves appropriate HA levels in HDFs with UVB-induced injury,which increases the total collagen and the expression of type I collagen,and inhibits ROS production.UVB irradiation has no significant effect on the generation of HA in HDFs treated with P.montana var. lobata ethanol extract.33
Vicenin-2 significantly suppresses UVB-induced cytotoxicity,ROS formation,mitochondrial membrane potential loss, apoptotic morphological changes, and DNA damage in HDFs. In addition, vicenin-2 prevents the activation of MAPKs, MMPs, and AP-1 to alleviate photoaging in HDFs.34
Hydrangenol is extracted from the leaves of Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser., and it enhances cell viability and inhibits the degradation of pro-collagen type I in UVBirradiated HDFs. Hydrangenol induces HA production and reduces mRNA expression levels of MMP-1,MMP-3,ROS, hyaluronidase-1, hyaluronidase-2, cyclooxygenase-2, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, and IL-1 in UVB-irradiated HDFs. Hydrangenol also suppresses AP-1 and the activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 by downregulating the phosphorylation of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. MAPKs (including p38,JNK,and extracellular signal-regulated kinase)have been recognized as targets for the chemoprevention of skin disease.35
Blue light (BL) and VIS are emitted from electronic devices and light-emitting diode lighting.BL induces longlasting hyperpigmentation through the activation of Opsin-3 receptors on the surface of melanocytes.However, there is no current evidence to suggest that VIS causes skin cancer.The biological effects of BL(400-500nm)are similar to those of UVA radiation;as the wavelength of BL is closely related to the UVA spectrum, BL can reach the subcutaneous layer and may have similar photoaging effects to UVA. Olive fruits protect fibroblasts from the harm caused by light-emitting diode BL by inhibiting ROS production, reducing the expressions of MMP-1 and MMP-12, maintaining the generation of collagen type I,decreasing the production of 8-dihydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine, and preserving the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen without influencing cell viability.36
IRA upregulates the production of matrix-degrading enzymes, which is mediated by ROS.3Acute exposure to IRA upregulates the expression of MMP-1 and induces DNA damage, cytotoxicity, and oxidative stress. IRA exposure of HDFs weakens the endogenous antioxidant enzymatic defense and causes dysfunction of DNA repair by reducing the concentration of growth arrest DNA damage 45 alpha protein.37Polypodium leucotomos(Fernblock®) prevents the photoaging caused by VIS and IRA by reducing the levels of MMP-1 and Cat K and inhibiting alterations in the expressions of fibrillin 1,fibrillin 2, and elastin in HDFs.38A vehicle-controlled,double-blind, randomized study reported that topically applied sunscreen has protective effects against IRA.39
Epigenetic regulation
Epigenetics consists of three regulatory mechanisms,including DNA methylation, histone modification, and noncoding RNA (ncRNA) regulation. ncRNAs are classified as long ncRNAs, microRNAs, and circular RNAs (circRNAs).
Any ncRNAs longer than 200 nucleotides are defined as long ncRNAs. UVB-exposed HDFs show increased expression of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 long ncRNA, which leads to photoaging.40Long ncRNA RP11-670E13.6 mitigates the senescence in UVB-exposed HDFs through the p16CDKN2A-phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein pathways. A deficiency in the G1 to S transition may occur by knocking out RP11-670E13.6. Therefore, the p16 protein binds cyclindependent kinase to suppress the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein, which sequesters E2F-transcription factors that regulate the transcription of essential genes for progression into the S phase.31UVB irradiation causes significant increases in the expression levels of lncGKN2-1:1, lnc-CD1D-2:1, lnc-SGCG-5:4, and ROS.HDFs exposed to UVA show changes in lnc-AC010336.2-1, lnc-AHNAK2-7, lnc-AC118344.1-1, and lnc-MAP2K6-4, which probably interact with the MAPK signaling pathway.In HDFs with UVA-induced injury,the expression of lnc-GLI3-4 is increased, while the expression of lnc-LUM-1 is markedly reduced.41
MicroRNAs effectively modulate the autophagic pathway. In addition, reduction in autophagic activity is believed to contribute to the aging phenotype. miR-23a inhibits the AMBRA1 (GenBank accession number:NM_017749)mRNA expression produced by an autophagy-related gene and thus suppresses the autophagy signaling pathway. Therefore, the upregulation of miR-23a leading to decreased autophagic activity is involved in the 8-methoxypsoralen plus UVA irradiation and UVB irradiation stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS) of HDFs.42The epigenetic repressor polycomb group regulates HA synthesis during the UVA-induced fibroblast photoaging process.43
In UVB SIPS, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction shows that the circRNA expression of 228 fibroblasts is upregulated, while the expression of 244 fibroblasts is downregulated. Furthermore, the expression of circRNA_100797 is downregulated in UVB SIPS, while the expression of miR-23a-5p is upregulated. Hsa_circRNA-100797 targets miR 23a 5p,and these two compounds have an antagonistic effect in UVB SIPS.44
Genomic instability
Aging causes altered expressions of genes related to certain processes across the dermis,especially in photoaged skin.45Repeated UVA irradiation of HDFs causes the upregulation of 238 genes and the downregulation of 369 genes.Differentially expressed genes of the pentose phosphate pathway (ENSG00000147224 and ENSG00000169299)and signal pathway (ENSG00000164056) indicate the downregulation of genes encoding ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase and phosphoglucomutase.An elastin-coding gene(ENSG00000049540)is inhibited,whereas collagen-coding genes (ENSG00000160963 and ENSG00000196739) are upregulated.Sprout gene(ENSG00000164056)and Cat K gene (ENSG00000143387) are increased, while MMP genes (ENSG00000262406, ENSG00000166670, and ENSG00000149968),the Cat D gene(ENSG00000117984),and the Cat B gene(ENSG00000164733)are decreased.46
UV-irradiated HDF cells have lower proliferation,more morphological changes, and lower viability compared with nonirradiated HDF cells.Radiation with UV of 320 nm (20J/cm2) causes the upregulation of 2007 kinds of genes, downregulation of 2791 sorts of genes, and upregulation of the expression of genes in the MAPK pathway and also increases necrotic cell death.47
Conclusion
This article illustrates the progress in the study of the pathogenesis of photoaging through five different mechanisms:DNA photodamage,proteostasis imbalance,epigenetic regulation, altered cellular communication, the free radical theory, and genomic instability. These five mechanisms are not entirely independent and are mutually interactive.
The study of the pathogenesis of XP and CS helps us to gain a better understanding of the mechanism and develop possible remedies for photoaging. DNA and conducting functional DNA repair assays will potentially be used to explore the genotype-phenotype correlation. Although several studies have proposed the protein clearance mechanisms, there are still inconsistencies in the results among various research groups.The role of autophagy in UVB and UVA radiation in HDFs is not yet fully clarified.Recent studies have evaluated new ingredients with antioxidant activity, and cosmetics have been developed to minimize photoaging in recent years.
Acknowledgment
The study was supported by the Anhui Province Natural Science Foundation Project (No. 1608085MH194).
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
国际皮肤性病学杂志的其它文章
- Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Pruritus (2018)#
- Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urticaria: 2018 Update#
- Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Psoriasis in China: 2019 Concise Edition#
- Effects of Honokiol on Activation of Transient Receptor Potential Channel V1 and Secretion of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in HaCaT Keratinocytes
- Lipoid Proteinosis Due to Homozygous Deletion Mutation (c.735delTG) in the ECM1 Gene Presents with Seizures and Hoarseness but No Skin Involvement
- Mycobacterium Chelonae/Abscessus Co-infection of the Limbs: A Challenging Case
