UFLC-PDA-MS/MS Profiling of Seven Uncaria Species Integrated with Melatonin/5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptors Agonistic Assay
2020-03-02JianGangZhangXiaoYanHuangYunBaoMaJiJunChenChangAnGeng
Jian-Gang Zhang ·Xiao-Yan Huang ·Yun-Bao Ma ·Ji-Jun Chen ,2·Chang-An Geng
Abstract
Keywords Uncariae Ramulus Cum Uncis·Uncaria plants·LCMS-IT-TOF analyses·Melatonin and 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors
1 Introduction
Uncariae Ramulus Cum Uncis (Gou-Teng),the dried hookbearing stems ofUncariaplants (Rubiaceae),is a wellknown traditional Chinese medicine (TCM),which has long been used for the treatment of hypertension,fever,headache,dizziness,stroke,and bilious disorders in China [1-4].In addition to monotherapies,Gou-Teng is also prescribed in many formulae,such as Diao-Teng San (Cho-Deung-San in Korean and Choto-san in Japanese) and Yi-Gan San (Yokukansan in Japanese) [2].Indole alkaloids as the characteristic constituents ofUncariaplants are responsible for the hypotensive effects,e.g.rhynchophylline and hirsutine showing antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic effects [5,6].According to the latest Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2015 edition),fiveUncariaplants,namelyUncaria rhynchophylla(U.r),Uncaria macrophylla(U.m),Uncaria sinensis(U.si),Uncaria hirsuta(U.h),andUncaria sessilifructus(U.se),are documented as the official resource of Gou-Teng [7].Furthermore,severalUncariaplants,e.g.Uncaria scandens(U.sc),Uncaria laevigata(U.l),andUncaria yunnanensis(U.y),are also used as the substitutes of Gou-Teng in prescriptions [8,9].Although recent studies have manifested the antidepressant-like effects ofU.rhynchophyllaandU.lanosa,and locomotor decreasing effects ofU.rhynchophylla,U.macrophylla,andU.sinensis[10-12],few reports can discern the difference regarding the chemical profiles and biological activities between differentUncariaspecies.Thus,the clinical application of Gou-Teng is bewildered for the morphological and chemical similarity between differentUncariaplants.Different from the cardiovascular effect,the psychiatric property and active constituents of Gou-Teng are still disputed.Melatonin (MT) and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptors are two types of neurotransmitter receptors closely related to mental diseases [13-16],and thus are used to evaluate the psychiatric effects of differentUncariaplants.The present study applied an ultra-fast liquid chromatography equipped with ion trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UFLC-IT/TOF-MS) and combined with melatonin and 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors agonistic assay to discern sevenUncariaspecies regarding their chemical profiles and psychiatric properties.
2 Resultsand Discussions
2.1 LCMS-PDA Analyses
SevenUncariaplants were analyzed by UFLC-PDA-MS/MS to provide their respective base peak chromatograms (BPCs) in both positive and negative modes (Fig.1).In total,57 compounds including 35 indole alkaloids,ten flavonoids,five triterpenoids,five chlorogenic acids,and two other compounds were characterized according to their UV absorptions,MS/MS fragmentations,retention time,and comparing with the reported compounds (Table 1).
2.1.1 Indole Alkaloids
Indole alkaloids are the characteristic constituents inUncariaplants with high response in positive mode MS.In this investigation,a number of 35 indole alkaloids were described and divided into six subclasses including cadambine-type (19,21,23,26,47),vinsosamide-type (15),D-seco-type (18,25,33,38,44,50),corynoxine-type (11,20,22,24,27,28,31,32,34,35,36,37,42),corynantheintype (40,43,45,48,51,53,55,57),and ajmalicine-type (39,54).In accordance with the previous investigation [17],D-secoalkaloids commonly generated the characteristic fragmentation ions ascribed to the loss of 17 Da (NH3) in the MS2experiment;the indole and oxindole alkaloids could be differentiated from their respective maximal UV absorptions around 280 nm (indole) or 240 nm (oxindole);the numbers and types of glycosyl moieties were determined by the mass defects between the parent and fragment ions.
2.1.1.1 Cadambine-Type AlkaloidsPeak 21 was identified as cadambine from the [M+H]+ion atm/z545.2129 with the diagnostic MS2ions atm/z383.1612 (C21H22N2O5) and 351.1245 (C20H18N2O4),corresponding to the sequential loss of glycosyl and MeOH moieties [18].Peak 19 showed the loss of 17 Da from 565 to 548,and the loss of 162 Da from 548 to 386,which was characteristic for the hydrated derivative of cadambine [18].Peaks 23,26,and 47 possessed the same molecular formula of C27H34N2O 10with two more hydrogens than 21.In the MS 2 spectra,the identical fragmentation atm/z385 (C21H24N2O5) and 367 (C21H22N2O4) suggested closely related structures.In accordance with the previous reports,3α-dihydrocadambine,3β-dihydrocadambine,and 3β-isodihydrocadambine were reasonably suggested [19].
2.1.1.2 Vincosamide-Type Alkaloids Peak 15showing a molecular formula of C38H50N2O19was deduced from the [M+H]+ion atm/z839.3054.In the positive MS2experiment,the sequential losses of three glycosyl moieties (C6H10O5,162 Da) suggested the presence of three glucosyl in the structure.Finally,this compound was isolated under the guidance of LCMS analysis,and identified to be 2′-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]-11-hydroxyvincosamide based on rigid 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic data [20].
2.1.1.3 D-seco Indole AlkaloidsD-secoindole alkaloids can be well recognized from the diagnostic MS2ions attributed to the neutral loss of 17 Da (NH3) from the precursor ions.Peaks 33 and 38 were assigned with the same molecular formula of C27H34N2O 9 from the [M+H]+ion atm/z531.Their similar MS 2 fragmentations atm/z514 (C27H31NO9) and 352 (C21H21NO4) indicated a pair of isomers,which were generated from the cleavage of 3-epi-strictosidine and strictosidine [21].Peak 18 with a molecular weight of 516 was deduced to be the demethylated derivative of 38,owing to a CH2(14 Da) less in the molecular formula.The MS2fragmentation ion atm/z338.1568 implied the successive loss of 17 Da (NH3) and 162 Da (C6H10O5),by which this compound was assigned as strictosidinic acid [22].The molecular formula of 25 was determined as C28H30N2O11by the protonated ion ([M+H]+) atm/zat 571.1896 and deprotonated ion ([M-H]-) atm/z569.1780.In the MS2experiment,the sequential losses of 162 Da (C6H10O5),18 Da (H2O),and 14 Da (CH2) was consistent with the presence of glucosyl,hydroxyl,and methoxyl groups.From the above analyses,peak 25 was tentatively assigned as desoxycordifoline that had been isolated fromChimarrhis turbinate[23].Peaks 44 and 50 shared the molecular weight ofm/z930 and 902,respectively,corresponding to the chemical composition of C44H54N2O20and C44H58N2O18.The sequential losses of two 162 Da (C6H10O5) indicated the presence of two glucosyls.Taking its UV absorption at 219 nm into consideration,peak 44 was tentatively deduced to be neonaucleoside C [24].Similarly,peak 50 was attributed to be bahienoside B from the fragments atm/z341.1434 (C19H20N2O4) and 323.1406 (C19H18N2O3),by retrieving the compounds isolated from the same genus [25].
2.1.1.4 Corynoxine-Type AlkaloidsThe spirocyclic corynoxine-type alkaloids account for the largest number of indole alkaloids withinUncariagenus.Generally,this type of alkaloids can be well recognized by their UV maximum absorption at about 240 nm [17].Peaks 34,37,and 42 were isomers with the equal molecular formula of C22H28N2O 4,which were determined by the [M+H]+ion atm/z385.The MS2fragments atm/z353 and 321 were attributed to the consecutive losses of methoxyl groups.The ion atm/z267 indicated the loss of the C5-side chain.By comparing their relative retention time on octadecylsilyl (ODS) column,they were deduced as is or hynchophylline,corynoxine,and rhynchophylline [26].Peaks 27 and 31 occupied the same molecular weight of 384,corresponding to the molecular formula of C21H24N2O5.Their MS2fragments atm/z367,351,and 335 accounting for the lost H2O and two additional oxygen atoms indicated an oxygenated derivative of rhynchophyllic acid.Likewise,peaks 24 and 35 were deduced as dehydro-derivatives of rhychophylline,and peak 11 was proposed as the demethylated derivative of rhychophylline [27].
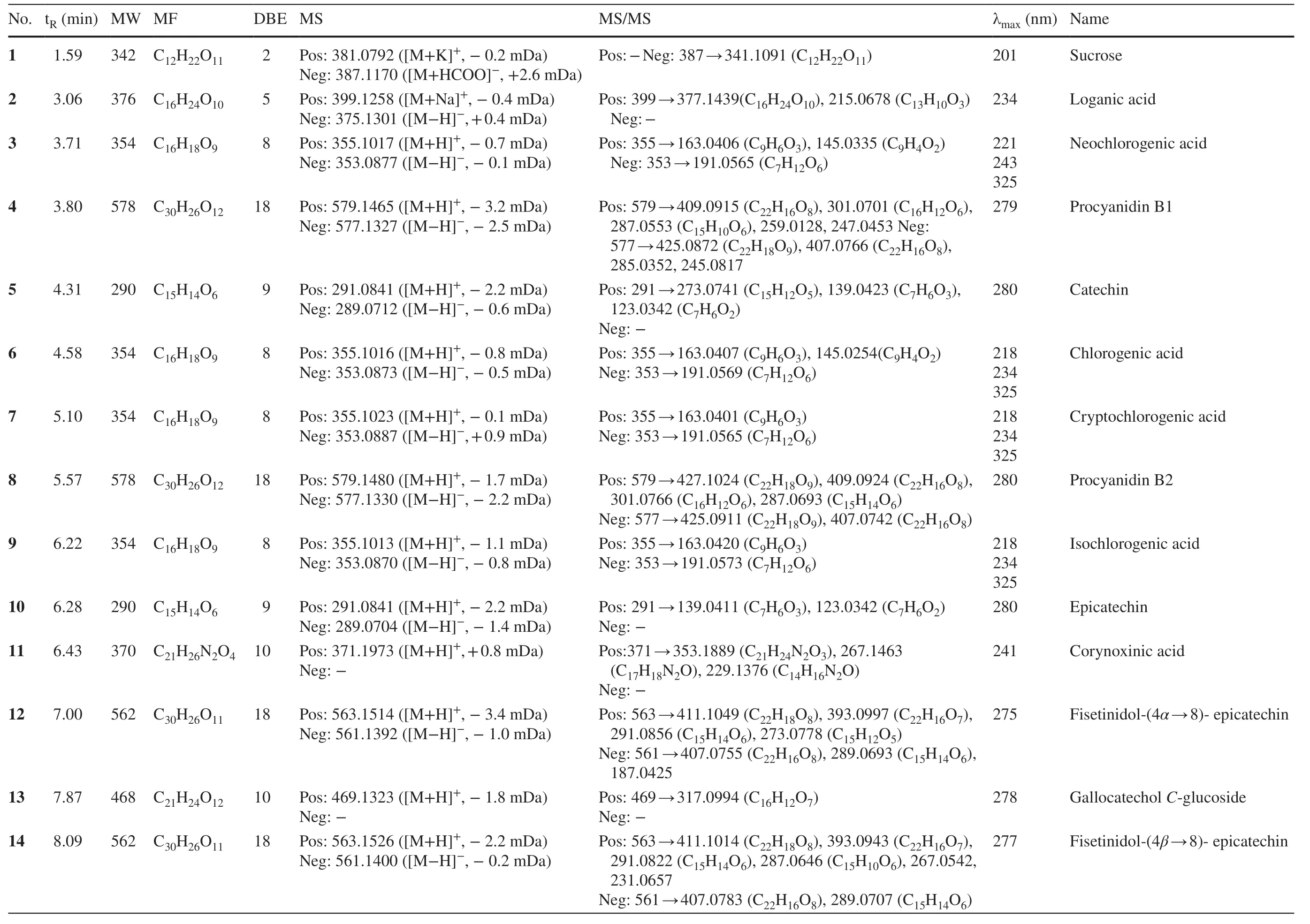
Table 1 Characterization of peaks in seven Uncaria plants by UFLC-DAD-MS/MS analyses
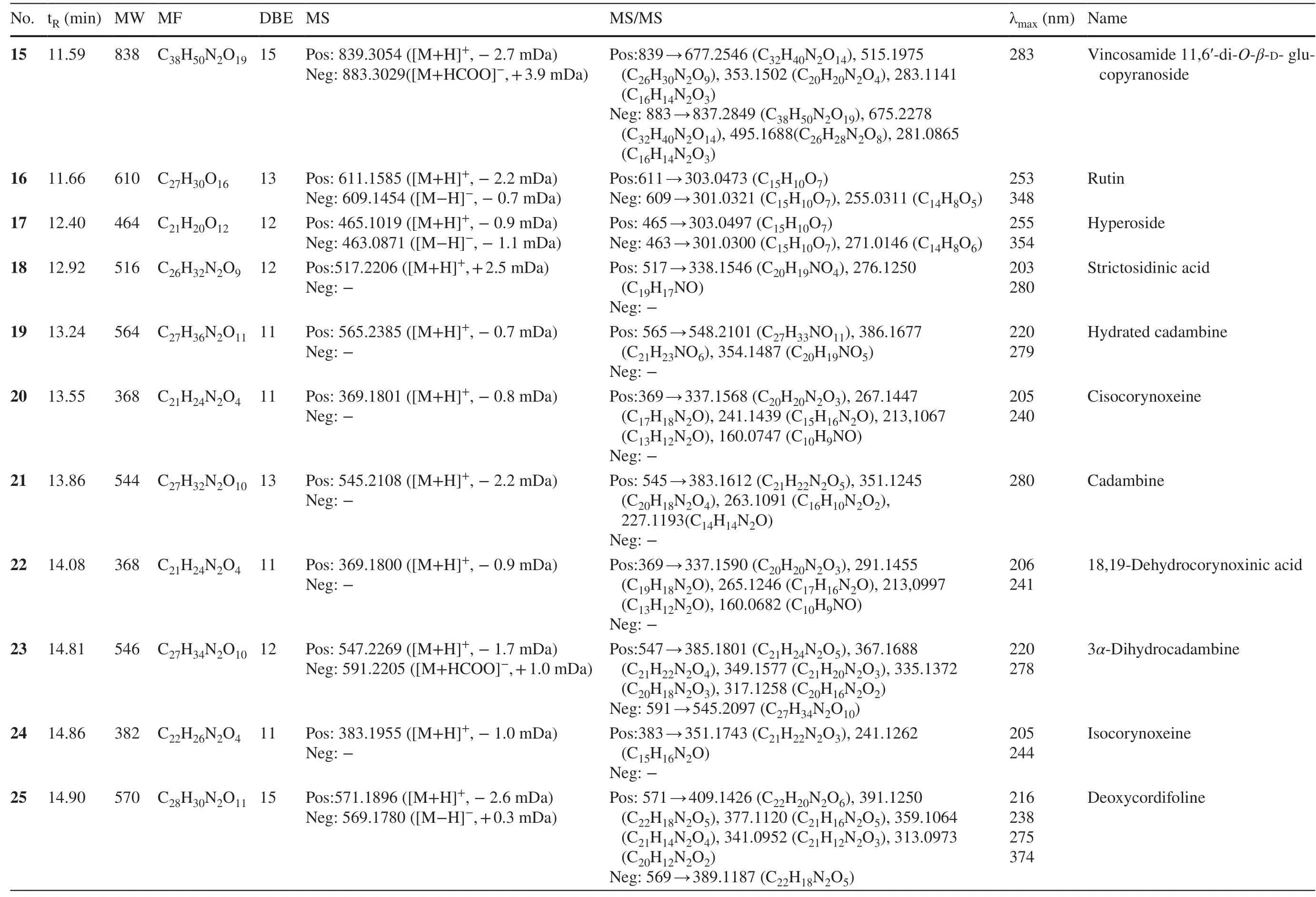
Table 1 (continued)

Table 1 (continued)

Table 1 (continued)

Table 1 (continued)
Peaks 20,22,28,32,and 36 had the same molecular formula of C21H24N2O4,with a CH2less than corynoxeine.The MS 2 fragmentation fromm/z369 to 337 verified the presence of an OMe group.The abovementioned features pointed to the demethyl corynoxeine or its isomer.The decarbonylation and decarboxylation neutral losses of 28 Da and 46 Da were proved by the ions atm/z 309 and 291.By retrieving the corynoxine-type alkaloids isolated from this genus,the de-methyl derivates of corynoxeine,cisocorynoxeine (20),18,19-dehydrocorynoxinic acid (22),18,19-dehydrocorynoxinic acid B (28),demethylcorynoxeine (32),and demethylisocorynoxeine (36) were proposed [28].
2.1.1.5 Corynanthein-Type AlkaloidsPeak 40 showed the protonated ion atm/z355.1994,indicating the molecular formula of C21H26N2O3.The MS2profiles atm/z224.1340 (C12H17NO3),212.1241 (C11H17NO3),and 144.0792 (C10H9N) were indicative for sitsirikine [29].Peaks 55 and 57 were assigned as hirsuteine and hirsutine,respectively,by reason of their molecular formula (C22H26N2O3and C22H28N2O3) and MS 2 fragments.Peaks 48 and 53 with the same formula of C22H26N2O3were determined to be corynantheine and geissoschizine methyl ether following their MS 2 fragments [30].Similarly,peaks 45 and 51 were tentatively deduced to be the dihydroxy and dihydro derivatives of corynantheine [17].
2.1.1.6 Ajmalicine-Type AlkaloidsAjmalicine-type alkaloids maintain a pentacyclic heteroyohimbines framework showing similar UV absorption with corynanthein-type alkaloids.Peaks 39 and 54 were attributed with C21H24N2O3and C22H26N2O4with 11 double bond equivalents.The mass losses fromm/z352 to 321.1647 (C20H20N2O2),222.1198 (C12H15NO3),210.1126 (C11H15NO3),and 144.0798 (C10H9N) were in agree with ajmalicine [31].Similarly,peak 54 was reasonably deduced to be pubescin from the MS2fragments atm/z223.1304 (C15H14N2) and 184.0878 (C12H9NO) [32].
2.1.2 Flavonoids
Flavonoids display characteristic UV absorptions at 220-280 (band II) and 300-400 (band I) nm,by which they can be easily characterized [33].Peaks 4 and 8 with UV maximum absorption at 280 nm were designated with the molecular formula of C30H26O12with 18 unsaturation degrees.Consequent MS 2 experiment on [M+H]+ion generated fragments atm/z409 (C22H16O8),301 (C16H12O6),and 287 (C15H10O6) indicating flavonoids dimers.Their relative retention time on ODS column were in accordance with procyanidin b1 (4) and procyanidin b2 (8) [34].Peaks 5 and 10 were a pair of isomers with identical molecular formula of C15H14O6.The MS2ion atm/z139 (C7H6O3) was ascribed to the A1,3retrocyclization fragment on ring C.Taking their UV absorptions at 280 nm and retention time into consideration,peaks 5 and 10 were reasonably determined as catechin (5) and epicatechin (10) [12].Peaks 12 and 14 were isomers with the same molecular formula of C30H26O11,suggesting flavonoids dimers.The MS2fragments atm/z291.0856 (C15H14O6) and 273.0778 (C15H12O5) were attributed to fisetinidol and catechin moieties.From the above analyses,they were tentatively deduced to be fisetinidol-(4α→ 8)-epicatechin and fisetinidol-(4β→ 8)-epicatechin [35].Peak 13 with a formula of C21H24O12showed MS2information atm/z317.0994 (C16H12O7),corresponding to the loss of a C5part from theC-glycosyl moiety.From the above analyses,this peak was defined as gallocatecholC-glucoside [36,37].Peak 16 was designed with the molecular formula of C27H30O16with an additional C6H10O4part than 17 (C21H20O12).In the MS2experiment,the same fragments atm/z303 in positive mode and 301 in negative mode suggested the same aglycone in 16 and 17.By retrieving the database,they were deduced as rutin (16) and hyperoside (17) [17].Peak 29 gave [M+H]+ion atm/z449.1068 and [M-H]-ion atm/z447.0939,corresponding to the molecular formula of C21H20O11.In the MS2experiment,the diagnostic MS2ions atm/z301.0358 (C15H10O7) and 271.0288 (C14H8O6) in negative mode were indicative for the sequential loss of rhamnosyl and formaldehyde moieties.From the above analyses,this peak was deduced as quercetin 3-rhamnoside [38].
2.1.3 Chlorogenic Acids
Chlorogenic acid analogues are a type of caffeoyl quinic acids widely present in plants.In the UV spectrum,the maximum absorption at around 325 nm was due to the presence of caffeoyl group.In the MS 2 experiment,the product ions atm/z163 (C9H6O3) in positive mode and 191 (C7H12O6) in negative mode were indicative for caffeic acid and quinic acid moieties.In this study,four isomers,namely,neochlorogenic acid (3),chlorogenic acid (6),cryptochlorogenic acid (7),and isochlorogenic acid (9) with identical formula of C16H18O9were detected and tentatively characterized by their retention time on ODS column [39].Peak 30 was assigned with the molecular formula of C25H24O12with an additional quinoyl moiety compared to chlorogenic acid.This deduction was verified by the MS2ions atm/z353.0882 (C16H18O9) and 173.0401 (C7H10O5) in negative mode.Thus,peak 30 was delineated as dicaffeoylquinic acid [40].
2.1.4 Triterpenoids
Peak 56 showing terminal absorption in UV spectrum was revealed with the molecular formula of C30H46O5.The abovementioned features were indicative for a triterpenoid.The MS2fragments atm/z469 (C30H44O4),451 (C30H42O3),and 423 (C29H42O2) were in accordance with quinovic acid [41].Peaks 49 and 52 were deduced to be diglycoside and triglycoside derivatives of quinovic acid by the additional two and three glycosyls which were verified by the sequential loss of C6H10O5parts in the MS2experiments.Thus,quinovic acid diglycoside and quinovic acid triglycoside were respectively determined [42].
2.1.5 Other Compounds.
Peak 1 was assigned as sucrose which was widely present in plants by the characteristic [M+K]+ion atm/z381.0792.Peak 2 had a molecular formula of C16H24O 10 showing [M+Na]+ion atm/z399.1258 and [M-H]-ion atm/z375.1301.In the MS 2 experiment,the loss of glycosyl was verified by the ion atm/z215.0678 (C13H10O3).Thus,this peak was illustrated as loganic acid,the biosynthetic precursor of indole alkaloids [43].
2.2 Chemical Comparison
As shown in Figs.2 and 3,a temporal and spatial distribution of chemical constituents in sevenUncariaplants provided a visual overview of their difference.The chemical profiles ofU.rhynchophyllaandU.scandenswere similar in terms of either indole alkaloids or other types of compounds.Indole alkaloids as the characteristic constituents were more prolific inU.rhynchophyllaandU.scandenswhen comparing to otherUncariaplants.Cadambine-type and corynanthein-type alkaloids were the characteristic constituents inU.rhynchophyllaandU.scandens,whereascorynoxine-type alkaloidswere widely distributed in all the sevenUncariaplants.Besides alkaloids,flavonoids were another type of constituent inUncariaplants,which were mainly distributed inU.rhynchophylla,U.macrophylla,andU.yunnanensis.For the triterpenoids,U.hirsutaandU.laevigatashowed more prolific than other plants.
2.3 Biological Comparison on MT 1/2 and 5-HT 1A/2C Receptors
Gou-Teng as a famous TCM are widely used for treating central nervous system (CNS) diseases in China.Therefore,four neurotransmitter receptors (MT1,MT2,5-HT1A,and 5-HT2C) that are closely related to CNS diseases were used to evaluate the psychiatric-related effects ofUncariaplants.As shown in Fig.4,three plants,U.rhynchophylla,U.macrophylla,andU.yunnanensisshowed obviously agnostic activity on all the four receptors.As a comparison,U.hirsuta,U.sessilifructus,andU.scandenswere moderate,andU.laevigatawas less active.Specifically,U.macrophylladisplayed the most potent activity on MT1receptor with an agonistic rate of 79.0%,then followed withU.rhynchophylla(71.9%),U.yunnanensis(41.5%),andU.scandens(26.1%),whereasU.hirsuta,U.sessilifructus,andU.laevigatawere inactive.For MT 2 receptor,U.yunnanensispossessed the highest agonistic rate of 91.2%,andU.macrophyllaandU.rhynchophyllaexhibited moderate activity with agonistic rates of 54.2% and 44.8%;however,U.scandens,U.sessilifructus,U.hirsuta,and U.laevigatawere weak or inactive.Similar with the MT receptors,U.rhynchophylla,U.macrophylla,andU.yunnanensispossessed significant activity on 5-HT1Aand 5-HT2Creceptors with agonistic rates higher that 60%.Interestingly,U.scandenswas revealed with the highest activity on 5-HT2Creceptor (82.7%),almost threefold higher than 5-HT1A,indicating the subtype selectivity.
3 Conclusion
Gou-Teng has long been recorded in ancient TCM books for the treatment of cardiovascular and mental disorders.According to the latest Chinese Pharmacopoeia,fiveUncariaplants,U.rhynchophylla,U.macrophylla,U.sinensis,U.hirsuta,andU.sessilifructusare documented as the official resources of Gou-Teng.However,their chemical and biological difference as well as the discrepancy with otherUncariaplants are still disputed.Thus,the clinical application of Gou-Teng is confused owing to the prolific resources and morphological similarity between different species.In this investigation,sevenUncariaspecies involving four official,U.rhynchophylla,U.macrophylla,U.hirsuta,andU.sessilifructus,and three local species,U.scandens,U.laevigata,andU.yunnanensiswere extensively compared based on LCMS and bioassay in vitro.In total,57 constituents including 35 indole alkaloids,ten flavonoids,five triterpenoids,five chlorogenic analogues,and two other compounds were characterized based on their MS/MS patterns and UV absorptions.Cadambine-type and corynantheintype alkaloids were exclusively present inU.rhynchophyllaandU.scandens,whereas corynoxine-type alkaloids were commonly detected in all the sevenUncariaplants.ThreeUncariaplants,U.rhynchophylla,U.macrophylla,andU.yunnanensisshowed obviously agnostic activity on four receptors,suggesting their biological similarity regardless of the chemical difference.This investigation supported the synergistic effects of TCMs due to the complicated constituents and their complementarity in taking effects.This study provides valuable information for understanding the chemical and biological difference between differentUncariaplants and the “one-drug multi-source” theory.
4 Experimental
4.1 LCMS Analyses
LCMS analyses were performed on a Shimadzu UFLC/MS-IT-TOF apparatus (Shimadzu,Kyoto,Japan) equipped with a Welch Ultimate XB-C18column (2.1 × 100 mm,i.d.,1.8 μm).The mobile phase for LCMS consisted of water (0.05% formic acid,A) and acetonitrile (0.05% formic acid,B) with the flow rate of 0.2 mL/min.A binary gradient elution was performed as follows: linear gradient (B%) from 10 to 35% in 35 min,and fast increased to 100% in one min and maintained for three min.Re-equilibration duration was five min between individual runs.The injection volume was 2μL for each LCMS analysis.The detailed MS parameters were set as previously reported [44].The PDA profiles were recorded from 190 to 400 nm.The Shimadzu Composition Formula Predictor was used to speculate the molecular formula.
4.2 Plant Materials
Plants ofUncaria rhynchophylla(Miq.) Miq.ex Havil.(No.2,016,090,001),Uncaria macrophyllaWall.(No.2,016,090,002),Uncaria hirsutaHavil.(No.2,016,090,003),Uncaria sessilifructusRoxb.(No.2,016,090,004),Uncaria scandens(Smith) Hutchins.(No.2,016,090,005),Uncaria laevigataWall.ex G.Don (No.2,016,090,006),andUncaria yunnanensisK.C.Hsia (No.2,016,090,007) were collected from Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture of Yunnan Province in China in September 2016,and authenticated by Dr.Li-Gong Lei (Kunming Institute of Botany,CAS).Voucher specimens (No.2,016,090,001-2,016,090,007) were deposited in the Laboratory of Antivirus and Natural Medicinal Chemistry,Kunming Institute of Botany,CAS.The hook-bearing stems were dried at room temperature and kept in amber glass flasks until extraction.The powder of each sample (2.0 g) was extracted with ethanol-water (7:3,v/v,10 mL) under ultrasonic for 30 min.The extraction was filtered through a PTFE micro-porous filter (0.22 μm,Jiangsu Hanbon Science &Technology Co.,Ltd.) into 2 mL screw cap vials prior to LCMS analyses.
4.3 Agonistic Activities on MT 1/2 and 5-HT 1A/2C Receptors
Bioassay for agonistic activities on melatonin and 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors was performed in accordance with the previous reports [20,45].In brief,HEK293 cells stably expressing human melatonin (MT1and MT2) and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT1Aand 5-HT2C) receptors were maintained in DMEM containing 10% FBS.Cells were seeded at a density of 4 × 104cells/well in pre-matrigel-coated 96-well black wall/clear bottom plates.After overnight incubation at 37 °C with 5% CO2,the cells were dyed with 100 μL of HDB Wash Free Fluo-8 Calcium Assay kit at 37 °C.An hour later,the cells were transferred into FlexStation3 Benchtop Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (Molecular Devices,Sunnyvale,California,United States) for bioassay.The raw data from time sequence recording were normalized as percentage responses to melatonin and 5-hydroxytryptamine as the positive controls,and analyzed to fit the four-parameter logistic equation to assess the agonistic rates.
4.4 Statistical Analyses
All experiments were carried out in triplicate.Data were expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (Mean ± SEM).Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 7 (GraphPad Software Inc.,San Diego,CA) and Origin 2018 (OriginLab Corporation,Wellesley Hills,MA) software.
AcknowledgementsThis work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81573322),the Yunnan Wanren Project (YNWR-QNBJ-2018-061),the Youth Innovation Promotion Association,CAS (2013252),the Program of Yunling Scholarship,the Yunnan Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars (2019FI017),and the Reserve Talents of Young and Middle-aged Academic and Technical Leaders in Yunnan Province.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open AccessThis article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License,which permits use,sharing,adaptation,distribution and reproduction in any medium or format,as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source,provide a link to the Creative Commons licence,and indicate if changes were made.The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence,unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material.If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use,you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.To view a copy of this licence,visit http://creat iveco mmons.org/licen ses/by/4.0/.
杂志排行
Natural Products and Bioprospecting的其它文章
- Dearomatized Isoprenylated Acylphloroglucinol Derivatives with Potential Antitumor Activities from Hypericum henryi
- Triterpenoidsfrom Ainsliaea latifolia and Their Cyclooxyenase-2(COX-2)Inhibitory Activities
- Daphnane Diterpenoids from Trigonostemon lii and Inhibition Activities Against HIV-1
- Alkaloid Constituents of Ficus hispida and Their Antiinflammatory Activity
- A New Epi-neoverrucosane-type Diterpenoid from the Liverwort Pleurozia subinflata in Borneo
