Characterization of inflammatory factor-induced changes in mesenchymal stem cell exosomes and sequencing analysis of exosomal microRNAs
2019-10-31ChenHuangWenFengLuoYuFengYeLiLinZheWangMingHuaLuoQiDeSongXuePingHeHanWeiChenYiKongYuKuanTang
Chen Huang, Wen-Feng Luo, Yu-Feng Ye, Li Lin, Zhe Wang, Ming-Hua Luo, Qi-De Song, Xue-Ping He,Han-Wei Chen, Yi Kong, Yu-Kuan Tang
Chen Huang, Wen-Feng Luo, Yu-Feng Ye, Qi-De Song, Xue-Ping He, Han-Wei Chen, Yu-Kuan Tang, Department of Minimally Invasive Interventional Radiology, Guangzhou Panyu Central Hospital, Guangzhou 511400, Guangdong Province, China
Chen Huang, Han-Wei Chen, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China
Chen Huang, Wen-Feng Luo, Yu-Feng Ye, Han-Wei Chen, Medical Imaging Institute of Panyu,Guangzhou 511400, Guangdong Province, China
Li Lin, Jinan University Biomedical Translational Research Institute, Jinan University,Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China
Zhe Wang, Yi Kong, Department of Pharmacy, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
Ming-Hua Luo, Department of Radiology, Shiyan People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518108,Guangdong Province, China
Abstract
Key words: Mesenchymal stem cells; Exosomes; MiRNA; Inflammatory cytokines;Angiogenesis
INTRODUCTION
Stem cell transplantation has been developing rapidly and has resulted in breakthroughs for the treatment of various diseases.There is especially an interest in the transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are tissue-derived cells with self-renewal abilities.Their exosomes (MSCs-exo) not only contain the unique active components of all stem cells, but also are relatively more safe, are more chemically stable, and have the capacity for targeted delivery to biological pathways of interest[1-4].
分筋错骨手以巧著称,利用撬杠原理,以小力扼制大力;或者利用转轴原理,以旋臂扼制轴心,一般需是双手并用,也可以双手与双脚并用,目的是让敌方关节脱臼,或者断筋伤骨,失去抵抗能力,只要肯下工夫,女子也可练成。龙爪手就不同了,这项功夫仅有身高、臂长、手大、力大的男人才有资格练。为什么?龙爪手,全凭一双手甚至一只手擒拿对方,身材不高、臂展不长者,在对手挥舞兵器的情况下,无法抢得先机,根本没有机会触碰对方关节,更不用说将对手擒获。手掌小、手指短,则无法抓握对方脖颈、肩膀、肘关节、膝关节和踝关节。龙爪手的基础功夫也很难练就,意志不坚韧的,筋腱不强健的,无法坚持下去。其基础功夫有两项:上缶功和擒缶功。
Exosomes were first foundin vitroin cultured sheep erythrocyte supernatant[5].They are membranous vesicles with a diameter of 30-150 nm and a density of 1.10-1.18 g/mL.They are able to affect gene regulation by carrying and releasing various bioactive molecules such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and proteins, both of which can then function as paracrine signaling mediators impacting biological pathways relevant to disease processes[6].MiRNAs are non-coding RNAs 22-25 nucleotides in length[7-10].Exosomes are especially important in producing miRNAs that impact angiogenesis[11].
There is promising research on using MSCs-exo to encourage wound healing and to treat inflammatory arthritis and ischemic diseases.However, in treating these diseases, MSCs are exposed to microenvironments filled with numerous inflammatory cytokines, such as vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α, and interleukin (IL) 6.The effects of these inflammatory cytokines on the morphology and quantity of MSCs-exo and how these effects impact the production of miRNAs and downstream regulatory mechanisms are largely unknown.In this study, we analyzed the effects of VCAM-1, TNFα, and IL6 on the morphology and quantity of MSCs-exo, how these effects enhance differential expression of miRNAs, and how the target genes of these miRNAs and their associated regulatory mechanisms are regulated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture
Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells were obtained from the Polywin Corporation (Guangzhou, China).The phenotypes of the MSCs were characterized by flow cytometric analysis of cell surface antigens, including tests for the cluster of differentiation (CD)29, CD34, CD44, CD73, and CD105.The MSCs were divided into four groups: Control group: MSCs (1.0 × 105cells/mL) were cultured in a serum-free DMEM/F12 (Sigma-Aldrich, United States) medium for 48 h; VCAM-1 group: MSCs(1.0 × 105cells/mL) were cultured in a serum-free DMEM/F12 (Sigma-Aldrich)medium, and VCAM-1 reagent (ADP5, R&D Systems, United States) was added to the medium at a concentration of 20 ng/mL for 48 h; TNFα group: MSCs (1.0 × 105cells/mL) were cultured in a serum-free DMEM/F12 (Sigma-Aldrich) medium, and TNFα reagent (T6674, Sigma-Aldrich) was added to the medium at a concentration of 20 ng/mL for 48 h; and IL6 group: MSCs (1.0 × 105cells/mL) were cultured in a serum-free DMEM/F12 (Sigma-Aldrich) medium, and IL6 reagent (200-06-20,PeproTech, United States) was added to the medium at a concentration 20 ng/mL for 48 h.The number, distribution, and morphology of cells in each group were observed under a microscope at 100× or 200× magnification for 48 h.
Exosome isolation
Exosomes were isolated from the culture supernatant by ultracentrifugation according to methods described previously[12,13].Briefly, the culture medium of each group was collected and centrifuged at 2000× gfor 10 min at 4 °C.The supernatant was then centrifuged at 10000× gfor 10 min at 4 °C.Next, the supernatant was passed through a 0.2-μm filter (Steradisc; Kurabo, Bio-Medical Department, Tokyo, Japan).The filtrate was ultracentrifuged at 100000 ×gfor 70 min at 4 °C (Type 70Ti ultracentrifuge;Beckman Coulter, Inc., Brea, CA, United States).The precipitate was next rinsed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and ultracentrifuged at 100000 ×gfor 70 min at 4 °C.The exosome-enriched fraction was next reconstituted in PBS for further studies.
Characteristics and distributions of exosomes in each group were observed.The particle size and concentration of exosomes in each group were measured by nanoparticle tracking analysis.
Differential miRNA analysis and target gene and regulatory signal pathway prediction
The miRNAs of MSCs-exo were sequenced by BGISEQ-500 technology in each group.Sequenced data were compared with miRBase and other non-coding databases.Bioinformatics analysis pipeline steps for miRNA sequencing were: (1) Filtering small RNAs: 18-30 nt RNA segments were separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis(PAGE); (2) 3’ adaptor ligation: A 5-adenylated, 3-blocked single-stranded DNA adapter was linked to the 3’ end of selected small RNAs from step 1; (3) Reverse primer annealing: the RT primer was added to the solution from step 2 and crosslinked to the 3’ adapter of the RNAs and to excess free 3’ adapter; (4) 5’ adaptor ligation: a 5’ adaptor was linked to the 5' end of the product from step 3.The adaptor was attached to the end only, not to the 3’ adaptor or RT primer hybrid chain, thus greatly reducing self-ligation; (5) cDNA synthesis: The RT primers in step 3 were reverse extended to synthesize cDNA strands; (6) PCR amplification: High-fidelity polymerase was used to amplify cDNA, and cDNA with both 3’ and 5’ adaptors was enriched; (7) Library fragment selection: The PCR products of 100-120 bp were separated by PAGE to eliminate primer dimers and other byproducts; (8) Library quantitative and pooling cyclization; (9) Eliminating the low-quality reads, adaptors and other contaminants to obtain clean reads; (10) Summarizing the length distribution of the clean tags, common, and specific sequences between samples; (11)Assigning the clean tags to different categories; (12) Predicting novel miRNAs; (13)Function annotation of known miRNAs; and (14) Comparing clean reads to the reference base group and other small RNA databases using AASRA software[14],except that Rfam was compared with cmsearch[15].We used TPM[16]to standardize miRNA expression levels and predicted target genes using RNAhybrid[17], miRanda[18],and TargetScan[19].
Hierarchical clustering analysis showed differentially expressed miRNAs by functional pheatmap.TheP-values obtained from the differential gene expression tests were corrected by controlling the false discovery rate (FDR)[20]as more stringent criteria with smaller FDRs and bigger fold-change values can be used to identify differentially expressed miRNAs.
Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis was performed to identify all GO terms that are significantly enriched in a list of target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs, as well as the genes that correspond to specific biological functions.
The hypergeometric test was then used to find significantly enriched GO terms based on this database (http://www.geneontology.org/).Pathway-based analyses were used to discover the biological functions of target genes using KEGG[21](the major public pathway-related database).
In vitro Matrigel tube formation assay
HUVECs (4.0 × 104, serum-starved overnight) were seeded in a 96-well plate, cultured in 5% CO2overnight, and then treated with PBS (control), control scrambled MSCsexo, MSCs-exoTNFα(5 × 109, stimulated with TNFα), or MSCs-exoIL6(5 × 109, stimulated with IL6).The plates were previously coated with 150 μL of growth factor-reduced Matrigel (356234, Corning, United States) in serum-free medium.Tube formation ability of control or MSCs-exo-treated HUVECs was examined by determining the total number of tubes formed and branching points in 4 to 6 h.Each condition in each experiment was assessed at least in duplicate.
系统使用的无线传输模块是nRF24L01。nRF24L01是NORDIC公司设计的新型单片2.4GHz射频收发器件[9]。它包括频率发生器、功率放大器、晶体振荡器、调制器和解调器。输出功率、频道选择和协议的设置可以通过SPI接口进行设置。该模块具有极低的电流消耗:当工作在发射模式下,发射功率为-6dBm时电流消耗为9.0mA;在接收模式时为12.3mA;掉电模式和待机模式下电流消耗更低。
Western blot analysis
HUVECs (4.0 × 104) were treated with PBS (control), control scrambled MSCs-exo,MSCs-exoTNFα(5 × 109, stimulated with TNFα), or MSCs-exoIL6(5 × 109, stimulated with IL6).The effect of MSCs-exo treatment on PI3K-AKT and MAPK, which are related to angiogenic signaling, was examined by measuring the expression of AKT (1:1000 dilution, 4691S, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, United States), phospho-AKT (1:1000 dilution, 13038S, Cell Signaling Technology), phospho-p44/42 MAPK(Erk1/2) (1:2000 dilution, 4370S, Cell Signaling Technology), and p44/42 MAPK(Erk1/2) (1:1000 dilution, 4695S, Cell Signaling Technology) in endothelial cells by Western blot.Each condition in each experiment was assessed at least in triplicate.
Statistical analysis
The data from each group were collected and analyzed using SPSS 11.5 software (IBM SPSS China, Shanghai, china).Numerical data are presented as the mean ± SE;comparisons between groups were evaluated by Student’st-test or ANOVA, withP<0.05 considered significant.
RESULTS
Phenotypic characterization of MSCs
Cell purity (85% to 95%) was determinedviaflow cytometry.The cells were positive for mesenchymal cell markers such as CD29, CD44, CD73, and CD105 and negative for hematopoietic cell markers such as CD34 and HLA-DR (Figure 1).
Effect of inflammatory cytokines on MSCs-exo
The VCAM-1 group had small regularly shaped MSCs-exo.The TNFα group had large irregularly shaped MSCs-exo.The IL6 group had medium regularly shaped MSCs-exo (Figure 2)
The density of MSCs-exo was 7.42 × 108/mL in the control group, 1.10 × 109/mL in the VCAM-1 group, 7.37 × 108/mL in the TNFα group, and 3.01 × 108/mL in the IL6 group (Figure 3).
Effect of differential miRNA expression, secondary to inflammatory cytokine exposure, on biological function
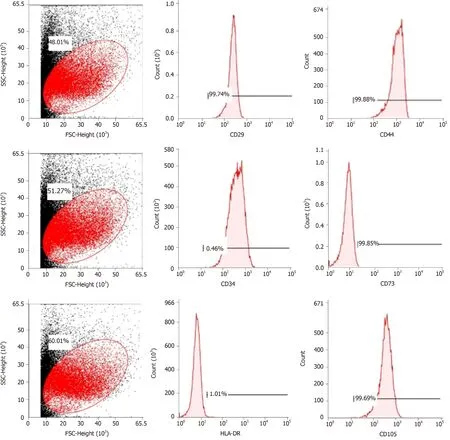
Figure 1 Flow cytometric analysis of mesenchymal stem cell-related cell surface markers.
Correlation analyses showed that the miRNA expression profiles in the IL6 group(0.583) and TNFα group (0.697) were more different from that of the control group than that in the VCAM1 group (0.985) (Figures 4 and 5).The top 10 miRNAs in each group are shown in Table 1.Many miRNAs, particularly some important angiogenesis-related miRNAs, were downregulated in the TNFα group and IL6 group compared to the control group (Tables 2-4 and Figure 6).Hierarchical clustering indicated that the expression levels of the majority of miRNAs in the IL6 group were downregulated compared with those of the control group (Figure 7).According to GO enrichment analysis, miRNAs in exosomes exposed to inflammatory cytokines,compared to controls, had a different regulatory effect on cellular components,molecular function, and biological processes (Figure 8).More specifically, pathway enrichment analysis showed that the target genes of the differentially expressed miRNAs, including those related to angiogenesis, differed among the four groups(Figures 9 and 10).The following angiogenesis-related pathways were more downregulated in the TNFα and IL6 groups than in the control group: The PI3K-AKT signaling pathway (Q= 0.0978197212 and 0.0581120875 in the TNFα group and IL6 group, respectively), the MAPK signaling pathway (Q= 0.5775485 and 0.9837761532 in the TNFα group and IL6 group, respectively), and the VEGF signaling pathway (Q= 0.4082212190 and 0.1711566 in the TNFα group and IL6 group, respectively)(Figures 10-13).

Figure 2 Morphology of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes (magnification, ×65000).
MSCs-exo promote endothelial cell angiogenesis
The ability of MSCs-exo to enhance tube formation was assessed using a Matrigel assay.MSCs-exo, on average, caused an increase in tube formation and branching (P<0.05; Figure 14) compared to the untreated control group.The angiogenesis effect of MSCs-exo stimulated with TNFα and IL6 was lower than that cultured without TNFα or IL6.This finding confirmed that MSCs-exo can promote angiogenesis (Figure 14).
MSCs-exo stimulated with IL6 inhibit PI3K-AKT signaling pathway activation in endothelial cells
We observed a decline in the expression of phosphorylated AKT (pAKT) in endothelial cells after MSCs-exo were stimulated with IL6, although MSC-EV treatment had no effect on the expression of their unphosphorylated forms (Figure 15).
DISCUSSION
MSCs have been used to treat cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and represent a promising cell-based therapy for regenerative medicine and the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases[22].Their treatment efficacy hinges on their ability to alter disease-specific pathwaysviasecreted miRNAs, so it is imperative to understand how disease environments, which often are inflammatory, can impact secreted miRNAs and thus potentially their treatment efficacy.MSCs-exosomes are used for treating CVDs such as acute myocardial infarction, stroke, pulmonary hypertension, and septic cardiomyopathy[23].Biological properties of MSCs-exo have rendered them as a new strategy for wound regeneration and ischemic disease[24-26].MSCs-exo exert an anti-inflammatory effect on T and B lymphocytes independently of MSCs priming.The potential therapeutic effects also were demonstrated in inflammatory arthritis[27].
Ischemic diseases, trauma, and immunological diseases are all accompanied by inflammatory reactions, and a large number of inflammatory cytokines including VCAM-1, TNFα, and IL6 are involved in the progression of these diseases.T cells are activated dependent on VCAM-1 interactions[28].VCAM-1 plays a “backup” role in hASC contact-dependent immune suppression[29].TNFα is a multifunctional cytokinethat acts as a central biological mediator for critical immune functions, including inflammation, infection, and antitumor responses[30].IL6 plays an important role in the inflammatory response following hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[31].Therefore, the biological properties of MSCs-exos and their therapeutic effects need to be studied together with the inflammatory factors.A large amount of evidence suggests that the effect of MSCs-exo therapeutics will be affected by the inflammatory environment with regard to most of CVDs and ischemic diseases[32-40].

A-D: Density of exosomes of different sizes in (A) the control group, (B) the vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 group, (C)the tumor necrosis factor α group, and (D) the interleukin 6 group.
Some previous reports showed[41]the effect of stimulation with cytokines interferon γ and TNFα on adipose MSCs (AMSCs).Pro-inflammatory stimuli could enhance the immunosuppressive functions of AMSC-derived exosomes.There was an increase in the expression of miRNAs (miR-34a-5p, miR21, and miR146a-5p) in exosomes produced by pre-activated AMSCs compared to those released by untreated cells.
The present study also found that the inflammatory cytokines VCAM-1, TNFα, and IL6 impact the size and morphology of MSCs-exo as well as the diversity of miRNAs they can produce, especially miRNAs impacting angiogenesis.According to GO enrichment analysis, miRNAs in exosomes exposed to inflammatory cytokines,compared to controls, had a different regulatory effect on cellular proliferation and differentiation, molecular signal transduction, immunosuppressive functions,angiogenesis and so on.
Some observed effects suggested that inflammatory cytokines impaired the ability of MSCs-exo to promote angiogenesis.For example, the TNFα and IL6 groups exhibited decreased numbers of angiogenesis-related miRNAs, such as miR-196a-5p,miR-17-5p, miR-146b-5p, miR-21-3p, and miR-320.The same groups also had downregulated angiogenesis-related signaling pathways, such as PI3K-AKT, MAPK,and VEGF.However, other effects suggested that inflammatory cytokines may promote the ability of MSCs-exo to encourage angiogenesis.Exosomes contained hsamir-4488, hsa-mir-671-5p, and hsa-mir-4446-3p after VCAM-1 stimulation, hsa-mir-4488, hsa-mir-671-5p, and hsa-miR-497-5p after TNFα stimulation, and hsa-mir-4488,hsa-miR-145-5p, and hsa-miR-1260a after IL6 stimulation, all of which promote angiogenesis.More specifically, hsa-miR-671-5p encourages NM_006500.2 to produce the downstream product VEGFb, which activates the VEGF pathway and therebypromotes angiogenesis.Hsa-miR-671-5p also encourages NM_001773.2 to produce CD34, which in turn activates the PI3K-AKT pathway, this promoting cell proliferation and angiogenesis.It is unclear what the ultimate results of these competing effects on angiogenesis would be.
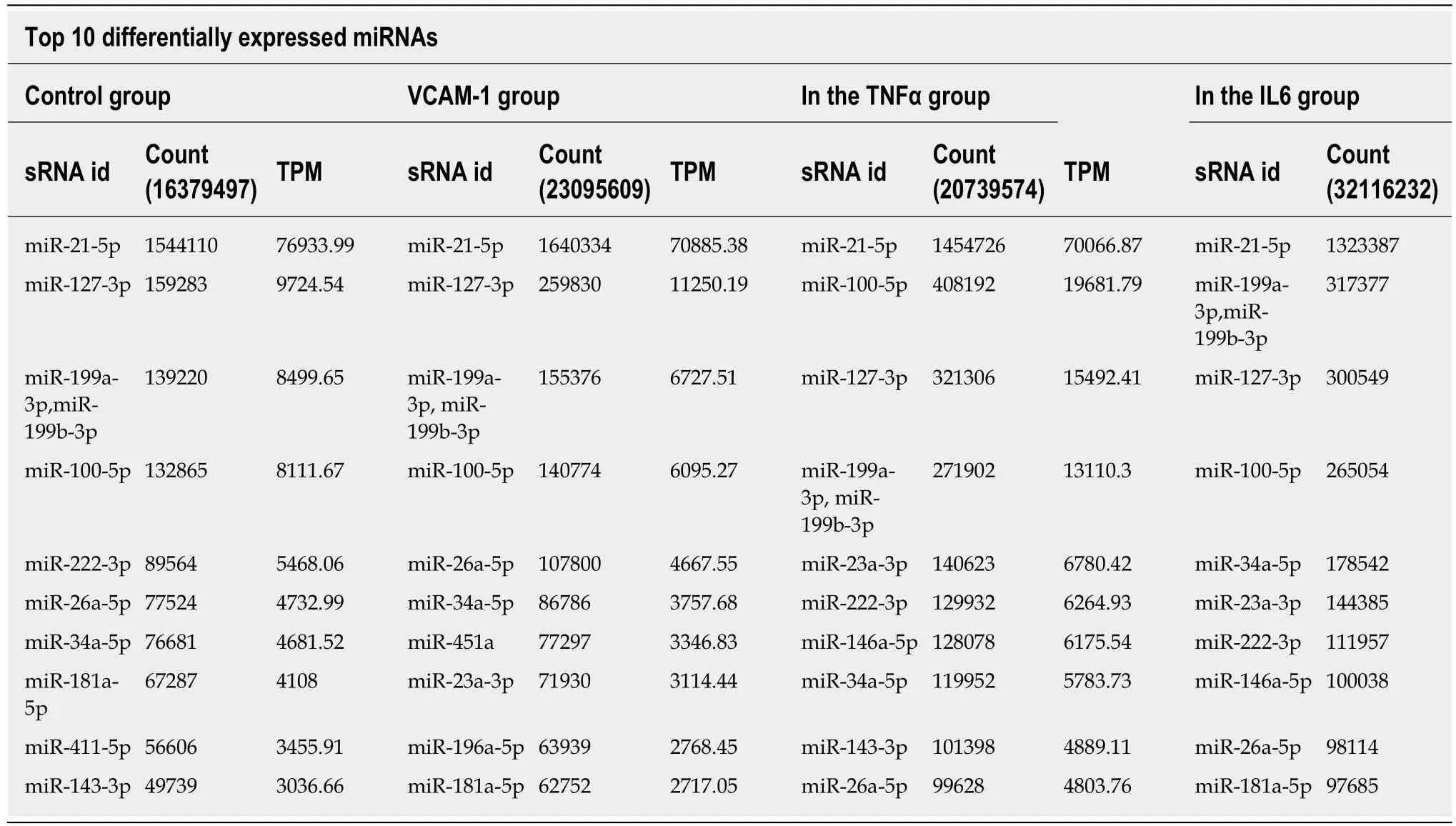
Table 1 Differentially expressed miRNAs
Our study demonstrated that MSCs-exo perhaps induced HUVECs to form capillary-like structuresin vitro.The effect of MSCs-exo in promoting angiogenesis would be reduced when the stem cells were subjected to TNFα and IL6 stimulation.Besides endothelial cell angiogenesis-related molecular expression, functional characteristics such as the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway may be down-regulated in MSCs-exo that were stimulated with IL6.
The major limitation of this study is that it was conductedin vitro.Further research needs to be conductedin vivousing an animal model that more closely mirrors the inflammatory environment to which MSCs are exposed when administered for treatment in humans.
In conclusion, inflammatory cytokines may lead to changes in exosomal miRNAs that abnormally impact cellular components, molecular function, and biological processes.Furtherin vivoresearch needs to be conducted to explore how the treatment efficacy of MSCs is impacted by these inflammatory-induced changes in exosomes and their miRNAs.
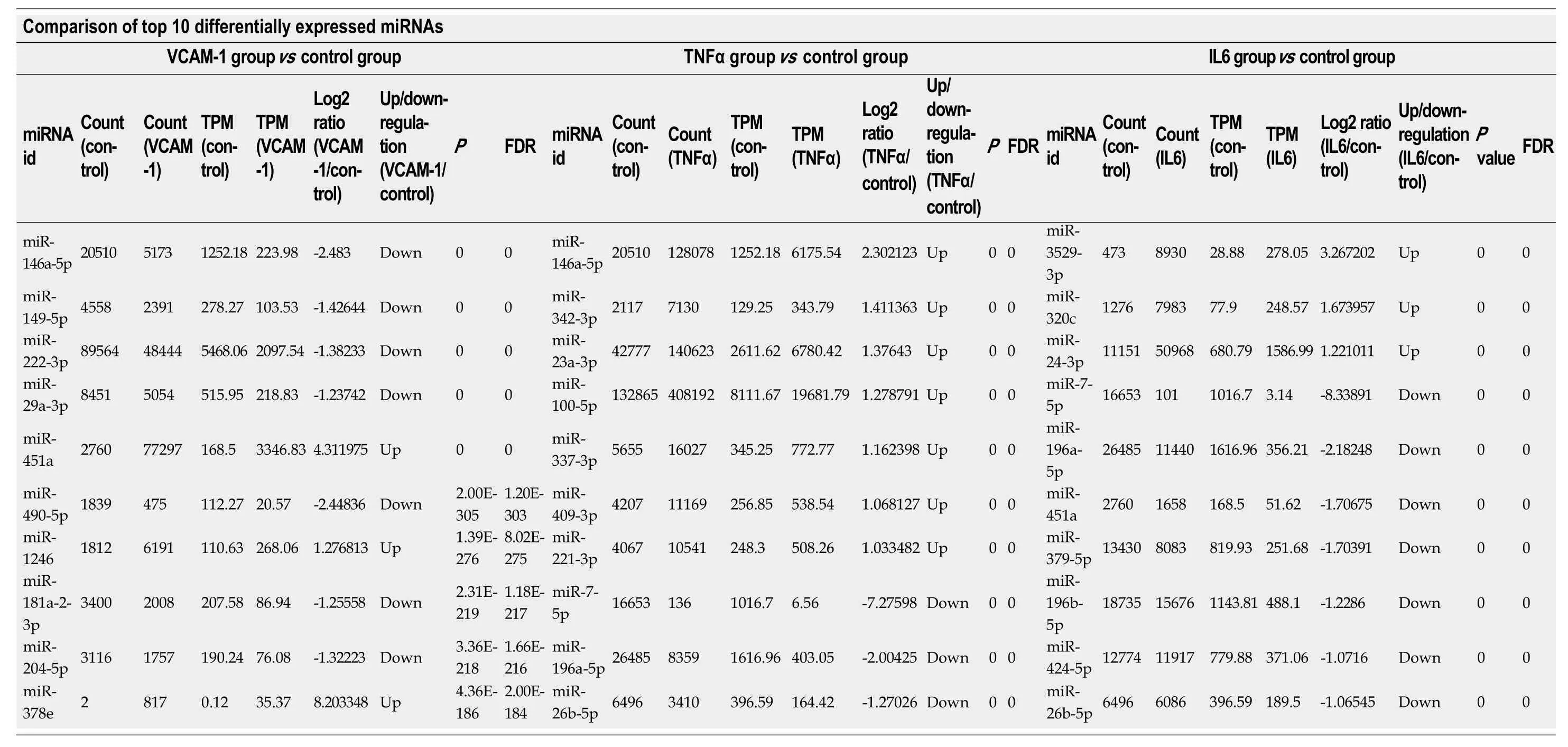
Table 2 Top 10 differentially expressedmiRNAs in each group (Poisson distribution screening)

P-values were corrected.TPM: Transcripts per kilobase million; FDR: False discovery rate; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.

Table 4 Comparison of differentially expressed angiogenesis-related miRNAs between the IL6 group and control group

Figure 4 Correlation analyses between groups.

Figure 5 Distribution of differentially expressed miRNAs in different groups.

Figure 6 Volcano plots.

Figure 7 Hierarchical clustering of differentially expressed miRNAs.



Figure 8 Gene ontology enrichment analysis of gene targets of differentially expressed miRNAs.





Figure 9 Pathway enrichment analysis of gene targets of differentially expressed miRNAs.


Figure 10 Gene ontology enrichment analysis of angiogenesis-related genes.
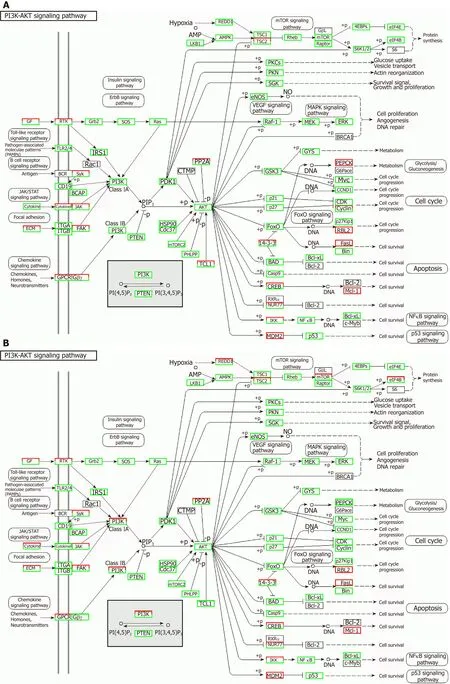

Figure 11 Regulatory mechanism of the PI3K-AKT signal pathway in different groups.

Figure 12 Regulatory mechanism of the MAPK signal pathway in different groups.

Figure 13 Regulatory mechanism of the VEGF signal pathway in different groups.

Figure 14 Tube formation in endothelial cells treated with mesenchymal stem cell exosomes.

Figure 15 Western blot analysis.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Stem cell transplantation has been developing rapidly and has resulted in breakthroughs for the treatment of various diseases.
Research motivation
Treatments utilizing stems cells often require stem cells to be exposed to inflammatory environments, such as vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), and interleukin 6 (IL6).Stem cell-derived exosomes are especially important in producing miRNAs that impact angiogenesis.
Research objectives
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are RNAs 0-20 nucleotides in length, which are derived from hairpin-like precursor miRNAs.They acts as important regulators of mRNA expression.It has been reported that miRNAs play critical roles in some cells and have the potential as diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers.
Research methods
The morphology and quantity of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) exosomes (MSCs-exo) are influenced by different inflammatory cytokine environments.
Research results
The morphology and quantity of each group of MSC exosomes were observed and measured.The miRNAs in MSCs-exo were sequenced.Differential expression of miRNAs and their target genes as well as the related regulatory mechanisms were researched.
Research conclusions
TNFα and IL6 may influence the expression of miRNAs that down-regulate the PI3K-AKT,MAPK, and VEGF signaling pathways; particularly, IL6 significantly down-regulates the PI3KAKT signaling pathway.
Research perspectives
Overall, inflammatory cytokines may lead to changes in exosomal miRNAs that abnormally impact cellular components, molecular function, and biological process, particularly angiogenesis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank all members of the Jinan University Biomedical Translational Research Institute Laboratory who provided us with critical comments and support.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
World Journal of Stem Cells的其它文章
- Effect of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) as natural polymers on mesenchymal stem cells
- Microfluidic three-dimensional cell culture of stem cells for highthroughput analysis
- Neural stem cell transplantation therapy for brain ischemic stroke:Review and perspectives
- Unmodified autologous stem cells at point of care for chronic myocardial infarction
- Stem cell treatment and cerebral palsy: Systemic review and metaanalysis
