薄荷复合精油吸嗅对轻度认知功能障碍患者乙酰胆碱酯酶影响的研究
2019-07-01孙凡石敏徐守宇梁康向伟华
孙凡 石敏 徐守宇 梁康 向伟华
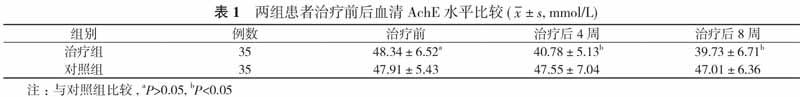
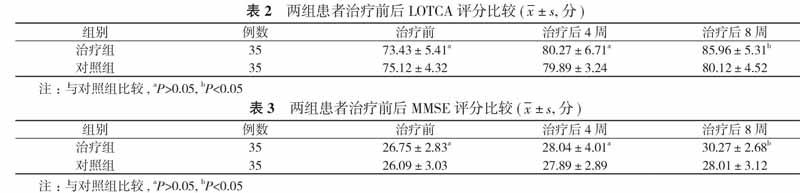
【摘要】 目的 觀察芳香药物吸嗅对轻度认知功能障碍(MCI)患者乙酰胆碱酯酶(AchE)的影响, 通过洛文斯顿作业疗法认知评定量表(LOTCA)评分、简易智能精神状态检查量表(MMSE)评分综合评价, 探讨薄荷复合精油吸嗅对轻度认知功能障碍患者认知功能的影响。方法 70例轻度认知功能障碍患者, 按照随机、双盲、对照的原则分为治疗组和对照组, 每组35例。两组患者均给予认知训练, 治疗组在认知训练的基础上给予薄荷复合精油芳香疗法, 对照组在认知训练的基础上给予生理盐水雾化吸入。比较两组患者治疗前后血清AchE水平、MMSE及LOTCA评分。结果 两组患者治疗前血清AchE水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗后4、8周, 治疗组患者的血清AchE水平分别为(40.78±5.13)、(39.73±6.71)mmol/L, 均明显低于对照组的(47.55±7.04)、(47.01±6.36)mmol/L, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组患者治疗前、治疗后4周LOTCA、MMSE评分比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗后8周, 治疗组患者的LOTCA、MMSE评分分别为(85.96±5.31)、(30.27±2.68)分, 均明显高于对照组的(80.12±4.52)、(28.01±3.12)分, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 薄荷复合精油吸嗅治疗可通过降低患者血清AchE含量, 改善轻度认知功能障碍患者的认知功能, 值得临床推广。
【关键词】 薄荷复合精油;芳香疗法;轻度认知功能障碍;乙酰胆碱酯酶
【Abstract】 Objective To observe the effect of aromatic drug sniffing on acetylcholinesterase (AchE) in patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). To explore the effect of mint complex essential oil sniffing on cognitive function of mild cognitive impairment patients by Lovingston occupational therapy cognitive assessment scale (LOTCA) and mini-mental state examination (MMSE) score. Methods A total of 70 patients with mild cognitive dysfunction were divided by principles of randomization, double blindness and control into treatment group and control group, with 35 cases in each group. Both groups were given cognitive training. The treatment group received mint complex essential oil aromatherapy on the basis of cognitive training, and the control group received saline atomization inhalation on the basis of cognitive training. Serum AchE level, MMSE and LOTCA scores were compared before and after treatment in two groups. Results Both groups had no statistically significant difference in serum AchE level before treatment (P>0.05). After 4 and 8 weeks of treatment, the treatment group had obviously lower serum AchE level respectively as (40.78±5.13) and (39.73± 6.71)mmol/L than (47.55±7.04) and (47.01±6.36) mmol/L in the control group. Their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Both groups had no statistically significant difference in LOTCA and MMSE score before treatment and after 4 weeks of treatment (P>0.05). After 8 weeks of treatment, the treatment group had LOTCA and MMSE score respectively as (85.96±5.31) and (30.27±2.68) points, which were obviously higher than (80.12±4.52) and (28.01±3.12) points in the control group. Their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Mint compound essential oil may improve the cognitive function of patients with mild cognitive impairment by reducing the serum AchE content, and it is worthy of clinical promotion.
