基于MF-DFA特征和LS-SVM算法的刀具磨损状态识别
2018-08-10庞弘阳宋伟杰康振兴
关 山,庞弘阳,宋伟杰,康振兴
基于MF-DFA特征和LS-SVM算法的刀具磨损状态识别
关 山,庞弘阳,宋伟杰,康振兴
(东北电力大学机械工程学院,吉林 132012)

切削刀具;刀具磨损;声发射;状态识别;多重分形;去趋势波动分析;支持向量机
0 引 言
切削是机械加工中的重要工序,为提高机械加工的自动化和智能化水平,提高生产效率和质量,迫切要求对刀具磨损状态进行可靠监测,磨损状态特征提取是实现刀具磨损状态监测的关键[1]。近年来学者运用时频谱、功率谱、小波变换等手段对切削力信号、振动信号和声发射信号等对刀具磨损状态进行监测[2-4]。刀具磨损过程中发出的声发射(acoustic emission,AE)信号受到刀具磨损,材料晶格滑移,刀具与工件摩擦以及刀具破损影响,呈现出随机性、非线性和耗散性的特点,传统线性信号处理方法难以精确提取磨损阶段特征[5]。
笔者近几年的研究中运用非线性手段分析了刀具磨损AE信号的混沌特性和云特性,提高了识别准确率[6-7],然而这些特性不能表征刀具磨损的内在动力学特性。分形理论描述了自然界大量存在的偶然性和不规则,近年来随着研究的深入,在故障诊断领域得到了一定的应 用[8-13]。文献[9-13]以振动信号、AE信号以及刀口形貌图像等为研究对象,利用广义分形维数作为特征量,实现了对机械设备故障特征的提取,在整体反映非线性信号的分形特性上取得了一定效果,然而仅采用单分形方法很难准确反映刀具磨损过程中复杂的内在动力学特性。Kantelhardt等[14]在单分形的基础上,提出了多重分形去趋势波动分析(multifractal detrended fluctuations analysis,MF-DFA)方法,既可以反映非线性信号的整体分形特性,也具有较强的局部分析能力,能够准确描述信号的局部动特性。目前MF-DFA方法在信号处理领域取得了一定的进展[15-17]。文献[15]应用MF-DFA方法于液化泵退化特征提取中,分析了分形谱参数对液化泵不同退化状态的反映能力。文献[16]利用MF-DFA方法估计分形谱参数作为齿轮箱故障特征量,为齿轮箱故障特征提取提供了一种新方法。文献[17]采用MF-DFA方法分析了风电场风速时间序列波动,实现了风速变化趋势的预测。
针对刀具磨损AE信号通常具有随机性强和易埋没于噪声的特点,笔者提出一种基于MF-DFA和最小二乘支持向量机(least square support vector machine, LS-SVM)算法的刀具磨损状态特征识别方法。首先,用MF-DFA方法处理去噪后的刀具磨损AE信号,讨论其长程相关性和分形特性;然后,分析对比了不同磨损阶段下多重分形谱参数的变化,筛选出能灵敏表征刀具磨损状态的多重分形谱参数作为特征量;最后,利用LS-SVM算法实现不同刀具与材料组合切削的刀具磨损状态识别,验证本文所提方法的有效性,以期提高磨损监测准确性。
1 基于MF-DFA的多重分形谱分析
1.1 MF-DFA理论简介
1)计算序列x偏离均值的累计离差()


2)将()划分为互不重叠的长度(尺度)为的N(N= int(/))个等长子序列。为保证序列信息不丢失,则再从()尾端向前划分一次共得到2N个子序列。
3)利用最小二乘法拟合等长子序列的局部趋势函数y()

式中a为拟合多项式的系数,=0, 1,…,,为多项式拟合最高阶数。
4)计算均方误差函数2(,)
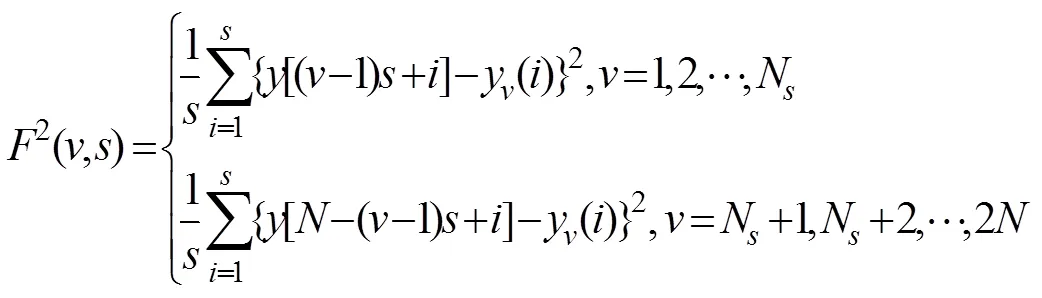
5)确定对于2N个子序列全序列的阶波动函数F()

式中阶数的取值范围为非零实数,当=2时则为经典的DFA法,即表示尺度下波动的均方误差2()。此外,当<0时,F()依赖于2(,)的小波动,当>0时,F()依赖于2(,)的大波动。
当=0时,波动函数由式(5)确定。

6)对F()的标度行为和长程相关特性的描述体现于()上,若值变化,()不是唯一值,则原始序列是多重分形过程,否则原始序列是一个单分形过程;若原始序列{x}具有相关性,则2()与成幂律关系,即:
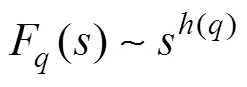
()被称为广义Hurst指数,表征原始序列相关性,可用最小二乘法线性拟合log(2())与log()得到的双对数曲线斜率表示。当=(2)时描述的是序列的长程相关性,被称为长程相关指数,对于平稳时间序列(2)就是Hurst指数。当0.5<≤1,说明序列是持久的长程相关性,即将来会延续过去的递增、递减趋势的性质;<0.5,表明序列是负的、反持久的长程相关性,即将来与过去递增、递减趋势相反;当=0.5,意味着该序列是一独立随机过程,不相关。
1.2 MF-DFA和经典多重分形理论的关系
通过MF-DFA方法得到的()和经典多重分形理论中由标准配分函数得到的()存在式(7)关系[19]:
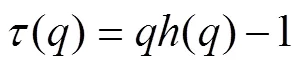
结合Legendre变换[20]对式(7)等号两边对求导得到多重分形谱(),奇异指数和()三者之间的关系为

1.3 估计多重分形谱特征参数
由多重分形谱可得到多重分形的3个重要参数:Δ,0和D。多重分形谱宽度Δ=max-min,反映信号多重分形特性的强弱,多重分形特征越强,D越大。极值点对应的奇异指数0(max=(0)),反映信号的随机性,随机性越大,0越大。多重分形谱维度D=(max)-(min),反映信号最大、最小峰值出现频率的变化,D小于0,表明概率最大子集数目大于概率最小子集数目;反之亦然。
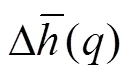
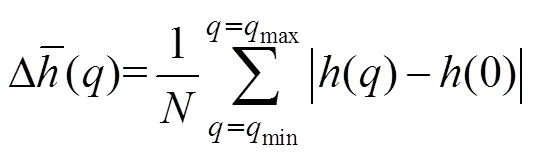
式中(0)为()中值。
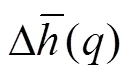
2 刀具磨损状态识别策略
支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)结构简单,泛化能力较好,近几年得到了广泛的研究[21]。当训练集规模很大时,求解标准支持向量机容易出现算法复杂、效率低等问题。因此,文献[22]提出了一种最小二乘支持向量机LS-SVM改变了标准SVM的风险函数和约束问题,用求解线性方程组替代二次规划问题,大大降低了计算的复杂度[23-25]。
支持向量机中的正则化参数和核函数参数对模型的分类性能有很大影响,优化过程中参数之间相互影响,不能使结果最优[26]。本文运用Simplex迭代算法[27]进行参数优化,并结合舍一交叉验证构建最优模型对每组参数组合的性能进行综合判断,来确定正则化参数和核函数参数。

(11)
约束条件为:

利用Lagrange法解式(11)得到:


本文中LS-SVM的输入为特征向量数据,输出为离散数值对应刀具3个磨损阶段。
3 试验与结果分析
3.1 试验数据来源及分析
为检验方法的实用性和有效性,将提出的方法用于刀具磨损状态识别。实测刀具磨损AE信号来源于刀具磨损试验系统,如图1a所示。刀具磨损切削试验在CA6140车床进行,声发射传感器依靠磁力紧紧吸附在刀柄近刀头而不干扰切削的位置。本试验将刀具作为研究对象,一方面通过R15-ALPHA谐振式声发射传感器、PXPAⅡ宽带前置声发射放大器、PXI-6366数据采集卡(采样频率为2 MHz)、计算机等构建了数据采集系统采集AE信号;另一方面使用显微镜测量刀具磨损量的大小(精度为0.01 mm),建立刀具磨损状态信号和磨损量的对应关系。

图1 刀具YT15切削高温合金GH4169信号的采集
试验中采用2两种刀片:YT15硬质合金涂层刀片、KC9125硬质合金涂层刀片;2种试验车削材料为:退火态高碳钢T10、高温合金GH4169。将刀片与试验材料交叉共产生4种组合,切削材料确定后,由于刀具寿命主要由切削三要素决定,因此每种组合考虑切削速度、进给量、切削深度三要素,以刀具磨损量为指标,设计三因素三水平正交试验以确定刀具不同磨损损状态对应的信号采集时间。由于高温合金GH4169对刀具的磨损速率较快,刀具达到进一步磨损的时间较短,因此更换新刀后,在上一次切削时间上延迟切削20 s进行一次数据采集;而退火态高碳钢T10对刀具的磨损速率较低,在上一次切削时间上延迟切削180 s进行一次数据采集,在数据采样完成后同时进行刀具磨损量的测量,以YT15刀具切削退火态高碳钢T10为例制定了图1b所示的信号具体采集过程和表1所示的刀具3种磨损状态界定范围和磨损极限。为了使信号更好地反映刀具当前的磨损状态,所以仅记录每次切削过程最后5 s的数据,减少数据采集量;更换新刀片的目的在于更精准地模拟刀具连续切削的过程。

表1 切削退火态高碳钢T10时刀具磨损阶段定义
本文以切削速度为 520 r/min,切削深度为 0.5 mm,进给量为0.176 mm/r时采集的AE信号为例进行说明。研究选取初期、正常、急剧磨损状态下各60组样本,每个样本取8 192个采样点。图2为YT15硬质合金刀具与T10组合切削在不同磨损阶段10 000个采样点的AE信号时域波形。由图2可见,不同磨损阶段的AE信号在时域结构上波动复杂且具有较明显的差异,磨损状态信号隐藏于背景噪声中,如果直接采用此信号来分析,则难以提取正确的磨损阶段特征。将采集的AE信号先用小波包分析进行去噪处理,基于最小Shannon准则来确定小波包分解最佳树并重构[28-30],来达到信号初步去噪的目的。
3.2 磨损AE信号的长程相关性和分形特性
利用MF-DFA方法分析刀具磨损AE信号的多重分形特性,要求波动函数F()与子序列长度有良好的对数线性关系[31-32]。当取40,多项式拟合阶数取1~6,=[-10,-9, …, 9, 10]时,讨论=2时,y()中与的关系。采用最小二乘法线性拟合Hurst指数,采用式(15)计算拟合决定系数2,2的数值都大于0.9,表明拟合直线满足统计检验。

式中为序列的均值;为q阶拟合值;为拟合序列的均值,N为序列长度。
图3给出了YT15硬质合金刀具与T10组合切削在正常磨损阶段值变化下Hurst曲线拟合结果。图3a为磨损AE信号均方误差函数F()与尺度随阶数的变化的双对数关系。每条均方误差函数F()与尺度的双对数曲线线性拟合的直线斜率就是Hurst指数,结合表2中的数值分析:Hurst指数为根据实际的logF()与log值用最小二乘线性拟合方法拟合的曲线斜率,决定系数2表示Hurst指数拟合值与实际点的决定系数,计算方法如式(15);当取不同值时,logF()与log都具有较良好的线性关系;随的增大呈现波动性,但都大于0.5小于1(0.5<<1),说明刀具磨损时间序列的是具有长程相关性的有序过程,内部波动不随机,具有维持趋势发展的能力。

图3 拟合阶数k值变化下Hurst指数拟合结果
当取不同值时,磨损AE信号的广义Hurst指数()与波动阶数关系曲线变化如图3b所示。()随的增大而减小,呈非线性递减关系,表明磨损AE信号存在不规则多重分形特征,具有不同的内在动力学特性。当=2时,()等于经典Hurst指数[33-34],对于任意,的值均大于0.5,说明磨损AE信号具有长程相关特性。
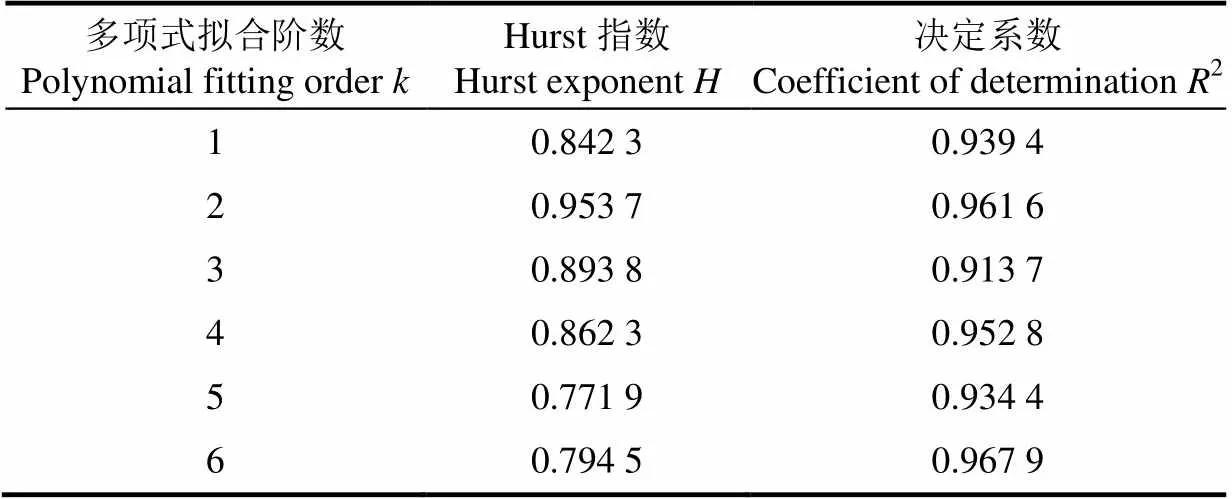
表2 Hurst指数的拟合结果
为描述刀具不同磨损阶段AE信号不同层次的波动,讨论=1时F()与的幂律关系曲线如图4所示,可以看出logF()与log呈良好的线性关系,即F()与存在幂律关系,即不同磨损阶段下的AE信号在一定尺度上存在标度不变性,具有多重分形特征。

图4 不同磨损阶段下均方误差函数Fq(s)与尺度s的幂律关系
3.3 多重分形谱特征参数


表3 不同磨损阶段的多重分形谱参数平均值
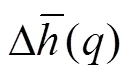
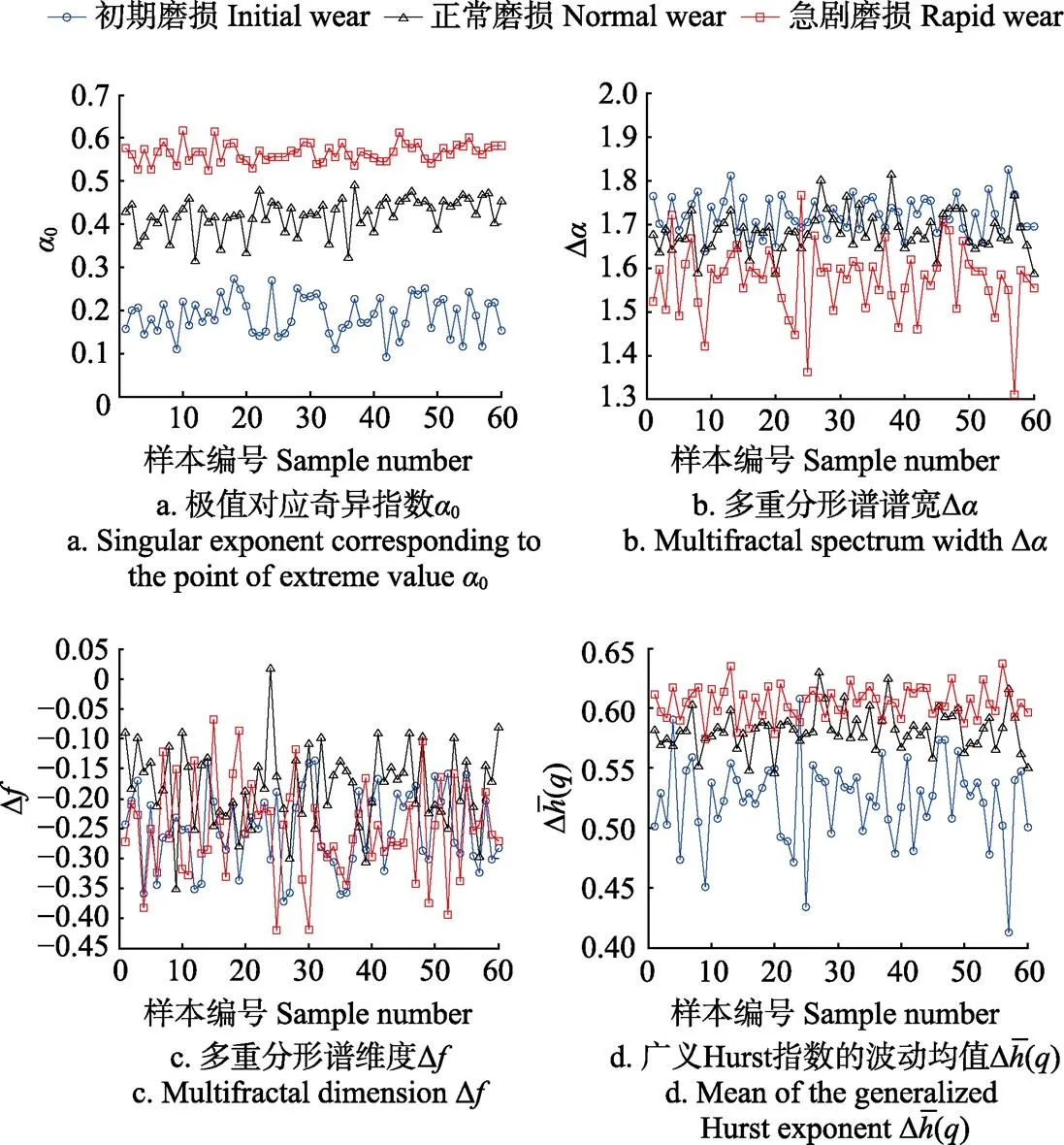
图5 不同磨损阶段AE信号特征分布
综上分析,利用MF-DFA方法计算刀具磨损AE信号的多重分形谱参数,构造表征刀具磨损阶段的三维特征向量。

计算不同磨损阶段的特征向量,绘制三维分布散度图如图6所示,可以看出:采用文中提出的方法提取的刀具磨损状态特征能很好地表征刀具的磨损状态。
注:v表示切削速度,表示进给量,a表示切削深度。
Note:vrepresents cutting speed,represents feeding rate, andarepresents cutting depth.
图6 不同刀具与切削材料组合下不同磨损阶段特征参数的三维散度图
Fig.6 Three dimensional divergence diagram of characteristic parameters in different wear stages under different cutting tools and cutting materials
3.4 刀具磨损状态识别
将YT15硬质合金刀具与T10组合下信号提取的不同磨损阶段去噪后信号的多重分形特征参数作为输入,其中90组训练样本,90组识别样本,每种磨损阶段均各30组。采用SVM和LS-SVM进行分类,核函数类型均为RBF。运用交叉验证方法[35]优化SVM分类器参数结果正则化参数2为4.128 7,核函数参数为12.351 5,优化LS-SVM得到的2为0.194 1,为3.712 3。
为验证基于LS-SVM方法识别分类器的有效性,另外采用相同的训练样本及测试样本特征量输入L-M(Levenberg-Marquardt)优化算法BP[36-37]神经网络中进行识别比较。神经网络中隐层节点数的选择至关重要[38],本文根据隐层节点数选取规则计算不同节点数下BP识别结果如表4所示,综合表中收敛次数、训练时间和识别率选择3-6-3 BP神经网络进行识别。
分别计算测试样本中成功识别的样本占总测试样本的百分比为识别准确率,表5为3种分类器的识别率比较,可以看出,采用LS-SVM方法的识别率高于传统SVM的识别率并明显高于BP神经网络的识别率。

表4 不同隐层节点数的BP模型对磨损状态识别结果

表5 三种分类器识别率对比
4 结 论

2)通过刀具磨损实测AE信号的研究,结果表明基于MF-DFA(multifractal detrended fluctuations analysis)和LS-SVM(least square support vector machine)的方法提取的多重分形谱特征能够很好地识别出刀具不同磨损阶段,验证了该识别方法的有效性,对比支持向量机和神经网络识别结果,LS-SVM算法识别率最高,平均准确率可达97.78%,为实现磨损量预测打下基础。
[1] Yu J. Machine tool condition monitoring based on an adaptive gaussian mixture model[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Science & Engineering, 2012, 134(3): 1013-1020.
[2] Xiao M H, He N, Li L. Studies on tool wear monitoring based on cutting force[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2011(697/698): 268-272.
[3] Rmili W, Ouahabi A, Serra R, et al. An automatic system based on vibratory analysis for cutting tool wear monitoring[J]. Measurement, 2016(77): 117-123.
[4] Li X. A brief review: Acoustic emission method for tool wear monitoring during turning[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2002, 42(2): 157-165.
[5] 彭昶. 基于混沌理论的刀具磨损识别研究[D]. 吉林:东北电力大学,2016. Peng Chang. Research on Tool Wear Condition Recognition Based on Chaos Theory[D]. Jilin: Northeast Electric Power University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 关山,彭昶. 金属切削过程刀具磨损信号的混沌特征[J]. 振动与冲击,2015, 34(10):28-33.
Guan Shan, Peng Chang. Chaotic characteristics of tool wear signal during metal cutting process[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(10):28-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 关山,康振兴,彭昶. 基于云理论与LS-SVM的刀具磨损识别方法[J]. 振动∙测试与诊断,2017,37(5):996-1003.
Guan Shan, Kang Zhenxing, Peng Chang. Method of tool wear based on cloud theory and LS-SVM[J]. Journal of vibration and shock, 2017, 37(5):996-1003. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] Bolgorian M, Raei R. A multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of trading behavior of individual and institutional traders in Tehran stock market[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2011, 390(21/22): 3815-3825.
[9] 张亢,程军圣,杨宇. 基于局部均值分解与形态学分形维数的滚动轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 振动与冲击,2013,32(9):90-94. Zhang Kang, Cheng Junsheng, Yang Yu. Roller bearing fault diagnosis based on local mean decomposition and morphological fractal dimension[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(9): 90-94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] Lim J H, Khang E J, Lee T H, et al. Detrended fluctuation analysis and Kolmogorov–Sinai entropy of electroencephalogram signals[J]. Physics Letters A, 2013, 377(38): 2542-2545.
[11] 刘国华,黄平捷,龚翔,等. 基于分形维和独立分量分析的声发射特征提取[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2008,36(1):76-80. Liu Guohua, Huang Pingjie, Gong Xiang, et al. Feature extraction of acoustic emission signals based on fractal dimension and independent component analysis[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(1): 76-80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张锴锋,袁惠群,聂鹏. 基于广义分形维数的刀具磨损状态监测[J]. 振动与冲击,2014,33(1):162-164. Zhang Kaifeng, Yuan Huiqun, Nie Peng. Tool wear condition mornitoring based on generalized fractal dimensions[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(1): 162-164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 郑光明,赵军,徐汝锋,等. 陶瓷刀具材料断口形貌及 裂纹扩展的分形特征[J]. 功能材料,2015,46(21): 21133-21136. Zheng Guangming, Zhao Jun, Xu Rufeng, et al. Fractal characteristic of the frature morphology and crack propagation of aceramic tool material[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2015, 46(21): 21133-21136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] Kantelhardt J W, Stephan A Zschiegner, Eva Koscielny- Bunde, et al. Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of nonstationary time series[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2002, 316(1): 87-114.
[15] 田再克,李洪儒,孙健,等. 基于改进MF-DFA和SSM- FCM的液压泵退化状态识别方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2016,37(8):1851-1860. Tian Zaike, Li Hongru, Sun Jian, et al. Degradation state identification method of hydraulic pump based on improved MF-DFA and SSM-FCM[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(8): 1851-1860. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 林近山,陈前. 基于多重分形去趋势波动分析的齿轮箱故障特征提取方法[J]. 振动与冲击,2013,32(2):97-101. Lin Jinshan, Chen Qian. Fault feature extraction of gearboxes based on multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(2): 97-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 孙斌,姚海涛. 风电场风速时间序列的多重分形去趋势波动分析[J]. 电工技术学报,2014,29(6):204-210. Sun Bin, Yao Haitao. Multi-fractal detrended fluctuation analysis of wind speed time series in wind farm[J]. Transactions of China Eletctrotechinical Society, 2014, 29(6): 204-210. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 田再克,李洪儒,孙健,等. 基于改进MF-DFA的液压泵退化特征提取方法[J]. 振动∙测试与诊断,2017,37(1): 140-146. Tian Kezai, Li Hongru, Sun Jian, et al. Degration feature extraction of hydraulic pump based on improved MF-DFA[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2017, 37(1): 140-146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] Siqueira G M, Ênio F.F. Silva, Vidal-Vázquez E, et al. Multifractal and joint multifractal analysis of general soil properties and altitude along a transect[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2018(168): 105-120.
[20] Lim J H, Khang E J, Lee T H, et al. Detrended fluctuation analysis and Kolmogorov–Sinai entropy of electroencephalogram signals[J]. Physics Letters A, 2013, 377(38): 2542-2545.
[21] 杨德友,蔡国伟. 基于因散经验模式分解与最小二乘支持向量机的风电场短期风速预测[J]. 东北电力大学学报,2015(3):44-49. Yang Deyou, Cai Guowei. Short-term wind speed prediction of wind farms based on discrete empirical mode decomposition and least squares support vector machines[J]. Journal of Northeast Dianli University, 2015(3): 44-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] Suykens J A K, Vandewalle J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 1999, 9(3): 293-300.
[23] 周绍磊,廖剑,史贤俊. 基于Fisher准则和最大熵原理的SVM核参数选择方法[J]. 控制与决策,2014,29(11): 1991-1996. Zhou Shaolei, Liao Jian, Shi Xianjun. SVM parameters selection method based on Fisher criterion and maximum entropy principle[J]. Control and Decision, 2014, 29(11): 1991-1996. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 董彩云,张超勇,孟磊磊,等. 基于谐波小波包和BSA优化LS-SVM的铣刀磨损状态识别研究[J]. 中国机械工程,2017,28(17):2080-2089. Dong Caiyun, Zhang Chaoyong, Meng Leilei, et al. State recognition of milling tool wears based on harmonic wavelet packet and BSA optimization LS-SVM[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 28(17): 2080-2089. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] Cerdà V, Cerdà J L, Idris A M. Optimization using the gradient and simplex methods[J]. Talanta, 2016, 148: 641-648.
[26] Raska P, Ulrych Z. Comparison of modified downhill simplex and differential evolution with other selected optimization methods used for discrete event simulation models[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 100: 807-815.
[27] 李锋,汤宝平,章国稳. 基于舍一交叉验证优化最小二乘支持向量机的故障诊断模型[J]. 振动与冲击,2010,29(9):170-174. Li Feng, Tang Baoping, Zhang Guowen. Fault diagnosis model based on least square support vector machine optimized by leave-one-out cross-validation[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shork, 2010, 29(9): 170-174. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] Jing Y, Fei H, Zhang K. Temperature compensation of maglev train gap sensor based on RBF neural network and LS-SVM combined model[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(15): 73-80.
[29] 关山,康振兴,彭昶. 车削刀具磨损声发射信号的云特征分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(20):63-69. Guan Shan, Kang Zhenxing, Peng Chang. Analysis on cloud characteristics of wear acoustic emission signal for vehicle cutting tool[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(20): 63-69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 闫晓玲,董世运,徐滨士. 基于最优小波包Shannon熵的再制造电机转子缺陷诊断技术[J]. 机械工程学报,2016,52(4):7-12. Yan Xiaoling, Dong Shiyun, Xu Binshi. Flaw diagnosis technology for remanufactured motor rotor based on optimal wavelet packet shannon entropy[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(4): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] Dewandaru G, Masih R, Bacha O I, et al. Developing trading strategies based on fractal finance: An application of MF- DFA in the context of Islamic equities[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2015, 438: 223-235.
[32] Gulich D, Zunino L. A criterion for the determination of optimal scaling ranges in DFA and MF-DFA[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2014, 397(397): 17-30.
[33] 闵祥宇,李新举,李奇超. 机械压实对复垦土壤粒径分布多重分形特征的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(20):274-283. Min Xiangyu, Li Xinju, Li Qichao. Influence of mechanical compaction on reclaimed soil particle size distribution multifractal characteristics[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(20): 274-283. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] Xiong Q, Zhang W H. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method using MF-DFA and LSSVM based on PSO[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shork, 2015, 34(11): 188-193.
[35] 李可,赵德安. HEV电池SOC预测的留一交叉验证优化LS-SVM方法[J]. 电源技术,2014,38(11):2059-2062.
[36] Zhao X, Ba Q, Zhou L, et al. BP neural network recognition algorithm for scour monitoring of subsea pipelines based on active thermometry[J]. Optik - International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2014, 125(18): 5426-5431.
[37] 张兵,袁寿其,成立,等. 基于L-M优化算法的BP神经网络的作物需水量预测模型[J]. 农业工程学报,2004,20(6):73-76. Zhang Bing, Yuan Shouqi, Cheng Li, et al. Model for predicting crop water requirements by using L-M optimization algorithm BP neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2004, 20(6):73-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 王姣,祁美玲. RBF云神经网络在数控机床刀具磨损状态识别中的应用[J]. 机床与液压,2011,39(15):146-149. Wang Jiao, Qi Meiling. Application of RBF cloud-neural network in identification of CNC machine tool wear[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics , 2011, 39(15): 146-149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cutting tool wear recognition based on MF-DFA feature and LS-SVM algorithm
Guan Shan, Pang Hongyang, Song Weijie, Kang Zhenxing
(132012,)
Cutting is an important process in machining. In order to improve the automatic and intelligent level of machining and improve the production efficiency and quality, it is urgent to monitor the tool wear state. The feature extraction of wear state is the key to the tool wear monitoring. In view of the unique advantages of multifractal theory in accurately depicting the nonlinear phenomena and processes of the system, a tool wear state recognition method based on multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis (MF-DFA) and least squares support vector machine (LS-SVM) is proposed. The acoustic emission (AE) signal is denoised with wavelet packet analysis, and the best tree of wavelet packet decomposition is determined and reconstruction is performed based on the minimum Shannon criterion so as to achieve the purpose of signal initial denoising. Firstly, the MF-DFA method is used to deal with the noise emission signals of the tool wear after denoising, and the long range correlation and fractal characteristics are discussed. It shows that the tool wear time sequence is an orderly process with long range correlation, and the internal fluctuation is not random, and it has the ability to maintain the trend. Then, the multifractal spectrum parameters of different wear stages were analyzed and compared. The parameters of singular exponent corresponding to the point of extreme value and multifractal spectrum widthare increasing with the progression of the wear stage, which indicates that the greater the wear amount, the greater the fluctuation of the AE signal, the more uneven the probability measurement of the whole fractal structure, the more random the fluctuation. The values of the AE signal multifractal dimensionunder different wear states are less than zero, and the multifractal spectrum is left hook like, indicating the number of the maximum subset in the probability measure is relatively large. The absolute value of the normal wear stage is the smallest, which indicates that the volatility is the smallest in this stage; the value of the parameter increases with the increase of the wear amount, indicating that the greater the fluctuation degree of generalized Hurst exponent, the stronger the multifractal characteristics. The singular exponent corresponding to the point of extreme value, the multifractal spectrum widthand the mean of the generalized Hurst exponent, which can sensitively characterize the tool wear state, were selected as the characteristic quantities, and the three-dimensional feature vectors were constructed to characterize the tool wear stage. The clustering effect of the extracted tool wear state characteristics was obvious. The LS-SVM algorithm, SVM algorithm and BP (back propagation) neural network are applied to recognize the tool wear state. Simplex iterative algorithm is used to optimize the parameters, the optimal model is constructed to determine the performance of each group of parameters, and the parameters of regularization and kernel function are determined. The average recognition accuracy is 97.78%. The results show that the tool wear AE signal has long range correlation and obvious multifractal characteristics, the multifractal parameters, i.e. singular exponent corresponding to the point of extreme value,multifractal spectrum widthand mean of the generalized Hurst exponent can be used as sensitive characterization for the feature of tool wear stage, and the tool wear stages can be clearly distinguished. The multifractal spectrum features extracted with the method based on MF-DFA and LS-SVM can identify the different wear stages of the tool well, verify the effectiveness of the recognition method, improve the accuracy of recognition, and lay a foundation for the realization of the wear prediction.
cutting tools; wear of cutting tools; acoustic emission; state recognition; multifractal; detrending wave method; support vector machine
2018-02-01
2018-05-16
吉林省科技厅科技公关计划(20170520099JH);吉林省省教育厅“十二五”科学技术研究项目(20150249)
关 山,男,吉林省吉林市人,博士,教授,主要从事机械设备故障诊断研究。Email:guanshan1970@163.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.14.008
TH165+.3;TP206
A
1002-6819(2018)-14-0061-08
关 山,庞弘阳,宋伟杰,康振兴. 基于MF-DFA特征和LS-SVM算法的刀具磨损状态识别[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(14):61-68. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.14.008 http://www.tcsae.org
Guan Shan, Pang Hongyang, Song Weijie, Kang Zhenxing. Cutting tool wear recognition based on MF-DFA feature and LS-SVM algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(14): 61-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.14.008 http://www.tcsae.org
