水中基质对硫酸自由基降解新兴污染物的影响
2017-03-15刘丹丹周雪飞
刘丹丹,周雪飞
(同济大学 长江水环境教育部重点实验室,上海 200092)
1 引言
2 硫酸自由基的产生机理
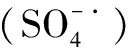
2.1 能量活化
能量活化主要通过外界提供足够的能量促使过硫酸盐中的化学键发生断裂,从而形成硫酸自由基,其反应过程可用式(1)和式(2)表示:
(1)
(2)
目前使用最多的是高温和紫外照射两种方法。
2.2 过渡金属离子活化
相对于使用高温或UV 活化过硫酸盐,使用过渡金属活化具有高效、低成本的优点,越来越多的应用于实践中。在不同价态的过渡金属离子的催化下,PMS和PS通过下列方程式生成硫酸自由基和其他的一些物质:
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
金属离子与氧化剂的反应原理上主要是金属离子与氧化剂之间的电子转移过程。Anipsitakis等研究发现,Co(Ⅱ)和Ru(Ⅲ)活化KHSO5效果最好,Ag(Ⅰ)活化K2S2O8效果最好,而Fe(Ⅱ)、Fe(Ⅲ)活化H2O2效果最好[2]。
3 硫酸自由基对污染物的去除研究
4 水中离子对硫酸自由基的影响

4.1 氯离子对硫酸自由基的影响
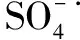
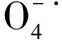
(9)
(10)

(11)

(12)

(13)
(14)

(15)

(16)
(17)
(18)
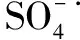
(19)

(20)
4.2 溴离子对硫酸自由基的影响
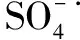
(21)

(22)
4.3 水中碳酸盐对硫酸自由基的影响
(23)
(24)
同样的,人们发现在基于硫酸自由基的高级氧化体系中,通常会发生式(25)、(26)、(27)、(28)和(29)的反应过程。
(25)
(26)
(28)
(29)
5 水中有机质对硫酸自由基的影响
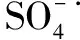
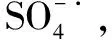

(28)
(29)
(30)
6 总结与展望
基于过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术在环境领域取到了快速的发展,人们越来越关注其在实际应用中环境基质的影响,相信随着研究的不断深入,更准确、更全面的过硫酸盐降解机理将会得到有效的解读。与其他高级氧化体系相比,基于过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术在实际应用中还存在着效率不高、使用范围有限等问题,如何根据硫酸自由基的特异性和其与环境基质物质的反应机理来提高过硫酸盐的去除有机物的效率是今后研究的一个重要方向。
[1]Neta P., Huie R.E., Ross A. B. Rate contants for reaction of inorganic radicals in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Referrence Data, 1988, 17(3):1027~1284.
[2]Anipsitakisan G., Dionysiosd D. Radical Generation by the Interaction of Transition Metals with Common Oxidants [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2004, 38(13):3705~3712.
[3]Nfodzo P., Choi H. Sulfate radicals destroy pharmaceuticals and personal care products[J]. Environmental Engineering Science, 2011, 28(8): 605~609.
[4]Liang, C., Z.-S. Wang, and N. Mohanty. Influences of carbonate and chloride ions on persulfate oxidation of trichloroethylene at 20 °C[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2006, 370(2-3): 271~277.
[5]Rickman K.A., Stephen P. M. Kinetics and mechanisms of sulfate radical oxidation of β-lactam antibiotics in water [J]. Chemosphere, 2010 (81): 359~365.
[6]Fang, G.D., et al. Transformation of polychlorinated biphenyls by persulfate at ambient temperature[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 90(5): 1573~1580.
[7]Lutze H. V., Kerlin N., Schmidt T.C. Sulfate radical-based water treatment in presence of chloride: Formation of chlorate, inter-conversion of sulfate radicals into hydroxyl radicals and in?uence of bicarbonate[J]. Water Research, 2015, 72: 349~360.
[8]Fang, G.D., et al. Sulfate radical-based degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls: Effects of chloride ion and reaction kinetics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2012. 227-228(0): 394~401.
[9]Rao Y.F., Qu L., Yang H. S., et al. Degradation of carbamazepine by Fe(II)-activated persulfate process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Material, 2014, 268(6):23~32.
[10]Bennedsen, L.R., J. Muff, and E.G. S?gaard. Influence of chloride and carbonates on the reactivity of activated persulfate[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 86(11): 1092~1097.
[11]Yang, Y., et al. Comparison of Halide Impacts on the Efficiency of Contaminant Degradation by Sulfate and Hydroxyl Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs)[J]. Environmental science and technology, 2014, 48(4): 2344~2351.
[12]Luca A.D., He X.X., Dionysios D. D. Effects of bromide on the degradation of organic contaminants with UV and Fe2+activated persulfate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016.
[13]Fang J. Y., and Shang C. Bromate Formation from Bromide Oxidation by the UV/Persulfate Process[J]. Environmental science and technology, 2012, 46(16): 8976~8983.
[14]J. Lu, J. Wu, Y. Ji, D. Kong. Transformation of bromide in thermo activated persulfate oxidation processes[J]. Water Research, 2015(78):1~8.
[15]Cavalcante, R.P., Dantas, R.F., Wender, H. Photocatalytic treatment of metoprolol with B-doped TiO2: effect of water matrix, toxicological evaluation and identification of intermediates[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015,176, 173-182.
[16]Choi, J., Lee, H., Choi, Y., Kim, et al. 2014. Heterogeneous photocatalytic treatment of pharmaceutical micropollutants: effects of waste-water ef?uent matrix and catalyst modifications[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 147(8): 8-16.
[17]Wang, X.H., Lin, A.Y.C. Is the phototransformation of pharmaceuticals a natural puri?cation process that decreases ecological and human health risks[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 186: 203-215.
[18]Brezonik, P.L., Fulkerson-Brekken, Nitrate-induced photolysis in natural waters: controls on concentrations of hydroxyl radical photo-intermediates by natural scavenging agents[J]. Environmental Science and Technology. 1998, 32 (19):3004~3010.
[19]Wang, X.H., Lin, A.Y.C. Phototransformation of cephalosporin antibiotics in an aqueous environment results in higher toxicity[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2012, 46 (22), 2417~2426.
[20]R. Zhang, P. Sun, T.H. Boyer, L. Zhao, C.-H. Huang, Degradation of pharmaceuticals and metabolite in synthetic human urine by UV, UV/H2O2, and UV/PDS[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2015, 49(5): 3056~3066.
[21]R.A. Larson, R.G. Zepp, Reactivity of the carbonate radical with aniline derivatives[J]. Environmental toxicology and chemistry, 1988, 7(4): 265~274.
[22]Qian Y J, Xin G, Zhang Y L, et al. Per?uorooctanoic Acid Degradation Using UV?Persulfate Process: Modeling of the Degradation and Chlorate Formation[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 50(2): 772~781.
[23]Y. Liu, X. He, X. Duan, Y. Fu, D. Fatta-Kassinos, D.D. Dionysiou. Significant role of UV and carbonate radical on the degradation of oxytetracycline in UV-AOPs: Kinetics and mechanism[J]. Water Research, 2016, 95: 195~204.
[24]Y. Liu, X. He, X. Duan, Y. Fu, D.D. Dionysiou. Photochemical degradation of oxytetracycline: Influence of pH and role of carbonate radical[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal , 2015,276:113~121.
[25]J. Huang, S.A. Mabury. A new method for measuring carbonate radical reactivity toward pesticides[J]. Environmental toxicology and chemistry, 2000,9(19): 1501~1507.
[26]S.-n. Chen, M.Z. Hoffman, Rate constants for the reaction of the carbonate radical with compounds of biochemical interest in neutral aqueous solution[J]. Radiation research, 1973, 56(1): 40~47.
[27]R. Zhang, P. Sun, T.H. Boyer, L. Zhao, C.-H. Huang. Degradation of pharmaceuticals and metabolite in synthetic human urine by UV, UV/H2O2, and UV/PDS[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2015, 49(5) 3056~3066.
[28]Webber W. L., Ming-Hao Hsu, Angela Yu-Chen Lin. The role of bicarbonate anions in methotrexate degradation via UV/TiO2: Mechanisms, reactivity and increased toxicity[J]. Water Research, 2017,112:157~166.
[29]Luo C.W., Jiang J., Ma J., et al. Oxidation of the odorous compound 2,4,6-trichloroanisole by UV activated persulfate: Kinetics, products, and pathways [J]. Water Research, 2016, 96: 12~21.
[30]Paul Westerhoff, Stephen P. Mezyk, William J. Cooper, et al. Electron Pulse Radiolysis Determination of Hydroxyl Radical Rate Constants with Suwannee River Fulvic Acid and Othe Dissolved Organic Matter Isolates[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2007, 41(13): 4640~4646.
[31]Fang, G.D.,Gao J., Dionysios D. D., et al. Activation of Persulfate by Quinones: Free Radical Reactions and Implication for the Degradation of PCBs[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2013, 47(9), 4605~4611.
[32]Mushtaque A, Amy L T, Richard J W. Mechanism of Persulfate Activation by Phenols[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2013, 47(11), 5864~5871.
