远震P波接收函数揭示的张家口(怀来)
—中蒙边境(巴音温多尔)剖面地壳厚度与泊松比
2016-07-29龚辰李秋生叶卓张洪双李文辉贺传松李英康
龚辰,李秋生*,叶卓,张洪双,李文辉,贺传松,李英康
1 中国地质科学院地质研究所,国土资源部“深部探测与地球动力学”重点实验室,北京 100037 2 中国地震局地球物理研究所,北京 100081 3 国土资源实物地质资料中心,河北燕郊 065201
远震P波接收函数揭示的张家口(怀来)
—中蒙边境(巴音温多尔)剖面地壳厚度与泊松比
龚辰1,李秋生1*,叶卓1,张洪双1,李文辉1,贺传松2,李英康3
1 中国地质科学院地质研究所,国土资源部“深部探测与地球动力学”重点实验室,北京1000372中国地震局地球物理研究所,北京1000813 国土资源实物地质资料中心,河北燕郊065201
摘要本文使用时间域迭代反褶积算法,从张家口(怀来)—巴音温多尔一线布设的41个宽频地震台站、1年期间记录的连续三分量数据中提取到高质量的P波接收函数1844个.用H-κ扫描方法获得了测线下方Moho深度与波速比值(VP/VS)进而计算出泊松比,用共转换点(CCP)叠加方法获得了沿测线Moho面起伏图像.
结果显示:(1)测线下方Moho深度平均40 km,仅各块体边界处出现Moho深度小尺度急剧变化.整体上,Moho面产状相对于索伦缝合带大致对称,在缝合带南侧的温都尔庙带和白乃庙带下方呈南倾趋势,在缝合带北侧的宝力道带、贺根山杂岩带下方呈北倾趋势.(2)华北克拉通北缘泊松比总体较高,兴蒙造山带整体较低;各次级块体内部泊松比分布相对稳定,块体分界带附近往往存在泊松比值的升降扰动.(3)整条测线地壳厚度和泊松比之间存在弱的负相关关系,表明存在构造作用的影响.(4)整条测线泊松比呈现以索伦缝合带南缘为对称轴的非线性分布.
本文所获得的地壳上地幔结构以及泊松比分布特征,支持古亚洲(索伦)洋(南北)双向俯冲,最终沿林西断裂闭合的动力学模式.
关键词兴蒙造山带; 古亚洲洋; 接收函数; 地壳上地幔结构; 泊松比
Structures and some major discontinuities beneath stations can be imaged by the receiver function method.In recent years,this method has become a mature and effective tool for studying the velocity structure of the crust and upper mantle.By the H-κ stacking method,the P-to-S converted waves at the Moho discontinuity and their multiple reflections are used to calculate crust thickness and VP/VSratio,which provide a way to study the rock composition of the crust and stress condition under stations.
Funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China,Institute of Geology,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences deployed 41 portable broadband seismic stations from Huailai county in northern North China to Bayinondor town near the China-Mongolia border.The profile extends along the reflection and refraction profile funded by Sinoprobe project,crossing the Yinshan-Yanshan orogenic belt,the Inner Mongolia paleo-uplift,the Bainaimiao arc,the Ondor sum subduction accretion complex,the Solonker suture zone (the Solonder suture zone,located between the North China plate and Siberia plate,representing the closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean),the Baolidao arc accretion complex,the Hegenshan ophiolite arc accretion complex and the Uliastai active continental margin from south to north.Recorders were set to the continuous recording mode and the sampling frequency was set to 50 Hz.The average distance between two neighbouring stations is 15 km and the length of the profile is about 650 km.Up to December 2014,we got 421 GB raw data in total.
First,we select 746 teleseismic events of mb>5 from 30 to 95 degrees and obtain their P waveforms from -20 s to 100 s with respect to the first P arrival time.Then,3-component waveform data with high signal-noise ratio are pre-processed (including mean removal and linear removal) and pre-filtering at 0.02~2 Hz and then rotated Z-N-E to the Z-R-T coordinate system.Finally we obtain 1844 P-wave receiver functions by the time domain iterative deconvolution method.After that we obtain the crustal thicknesses,VP/VSratios and Poisson ratios beneath the profile by the H-κ stacking method and image extension of the Moho interface by the Common Coversion Point (CCP) stacking method.The results are as follows:
(1) The Moho depth on average is 40 km along the profile.The crust thickness changes little across different tectonic blocks but shows evident variation at the boundaries between the blocks.The Moho dips southward beneath the Ondor sum belt and the Bainaimiao belt,while dips northward beneath the Baolidao belt and the Hegenshan belt.The Linxi fault seems to be as the boundary dividing the northern margin of North China Craton (NCC) and the southern CAOB.(2) The Poisson ratio shows a correlation with the tectonic unit along the profile.The averaged Poisson ratio in the northern margin of NCC is larger than the southern part of CAOB.The Poisson ratio changes little within the blocks except nearby the boundaries of different blocks.(3) There is a negative correlation between the crust thickness and the Poisson ratio that indicates the lateral heterogeneities of the crust structure resulted from the tectonic deformation.(4) Poisson ratio of the crust along the profile presents an approximately nonlinear symmetric shape relating to the south margin of Solonker suture zone.The characteristics of the crust and mantle structure and distribution of Poisson ratio along the profile support the geodynamic model that the Paleo-Asian Ocean subducted and closed at the southern margin of the Solon suture zone (along the Linxi fault).
1引言
中亚造山带(CAOB)是西伯利亚古陆与塔里木—中朝板块之间的古亚洲洋消减而形成的规模宏大的造山带.该区域中-新生代处于亚欧大陆的核心地域,系统保存了亚欧大陆形成和演化的完整信息.复杂的地壳变形、强烈的壳幔相互作用和全球最典型的陆内盆山体系,引起全球地质学界的普遍关注(engör et al.,1993;engör and Natal′in,1996;Gao et al.,1994,1997,2004; Jahn et al.,2004;Zorin et al.,1989,2002,2003;Xiao et al.,2003,2004,2008,2009;Zhao et al.,2006;Kröner et al.2007;Mordvinova et al.,2007;Windley et al.,2007;Jian et al.,2008;Nielsen and Thybo,2009;Fullea et al.,2012;Li et al.,2013;Zhang et al.,2014;任纪舜等,1997;翟明国,2008;张风雪等,2014;何静等,2014),一直是地球科学研究的前沿热点之一.
兴蒙造山带是中亚造山带的东段,包括加里东和海西等不同时期形成的造山带.兴蒙造山带与华北克拉通北缘以白云鄂博—化德—赤峰断裂为界.
围绕兴蒙造山带的形成演化前人开展了大量的地质调查和研究工作(Hsu et al.,1991; Xiao et al.,2003,2009;Jahn et al.,2004;Jong et al.,2006; Jian et al.,2008;李锦轶等,2009;徐备等,2014)并取得了重要进展.索伦山蛇绿岩带被认为是古亚洲洋最终闭合的位置.然而,由于露头稀少,地质过程复杂,索伦山以东蛇绿岩呈多个条带分布,导致对古亚洲洋最终闭合时间、古亚洲洋板片俯冲方向、主缝合带确切位置以及碰撞后演化过程等问题尚存较大争议.虽然地质学家们依据所掌握资料的分析结果各自建立了构造演化模式,但是这些模式并不兼容,造成这种状况的重要原因之一是缺乏与地质调查比例尺相当的深部地球物理资料的约束,最基本的造山带地壳结构的几何样式尚未建立,从而制约着对该区构造演化、地球动力学和资源环境问题的深入探讨.
多年来,我国对华北克拉通及北部邻区进行了大量探测研究(Li et al.,2006;Zheng et al.,2006,2007; Zhao et al.,2008; Chen et al.,2008; Chen,2010;Tian et al.,2011; 王峻等,2009;王未来等,2009; 陈凌等,2010a,2010b; 危自根等,2011; 葛粲等,2011;Lei,2012; Li et al.,2013; Zhang et al.,2014),这些工作包括人工源地震探测和天然源地震观测.
宽频带地震流动观测剖面接收函数揭示燕山带下方具有尖锐的莫霍面,地壳内部结构复杂,明显区别于华北克拉通内部和太行山(Zheng et al.,2007).人工地震宽角反射与折射地震剖面揭示燕山造山带下方对应3~5 km的莫霍面下凹(深度最大处达38 km)和相对薄的下地壳,暗示燕山带仍保存着中生代区域收缩变形形成的地壳基本结构,但已明显受到区域伸展作用的影响(李秋生等,2008).几条横过燕山造山带的宽角反射与折射地震剖面(孙武城等,1992;张先康等,1998)都表明其下地壳速度值(6.5 km·s-1)比正常大陆下地壳速度值(6.5~6.8 km·s-1)(邱瑞照等,2004;Wedepohl,1995)偏低,且存在自西向东地壳变薄的趋势.
大致与本文测线重合的Sinoprobe深反射地震剖面和宽角反射与折射剖面揭示了测线下方地壳的几何学样式和速度分布特征:突出的特征是Moho面在整条测线下方平缓延展,地壳厚度~40 km,仅阴山—燕山带下方Moho面局部加深到46 km,在白乃庙带下方可见Moho面微隆(39.5 km);在整条测线下方,下地壳速度值偏低,速度分布变化剧烈;西拉木伦断裂等断裂带下方存在莫霍面深度或结构特征突变(Li et al.,2013;李文辉等,2014;李英康等,2014).在深反射地震剖面上可见下地壳存在一系列北倾的反射,在空间上其发育不受华北克拉通北缘断裂(赤峰断裂)的限制,一直延续到索伦缝合带(张广成等,2013).
但是上述观测多数集中在华北克拉通主体范围内,仅有少数人工源地震剖面(如柏各庄—正蓝旗剖面,昌黎—承德—达来诺尔剖面和辽宁东沟—内蒙古乌珠沁旗剖面)和天然源地震剖面(如NCISP Ⅲ,Ⅵ剖面)延伸到华北克拉通北缘并进入兴蒙造山带.华北克拉通北缘以北,即中亚造山带南部的地壳结构及其变化缺乏控制;Sinoprobe人工源深反射地震剖面和宽角反射与折射地震剖面揭示了测线下方地壳的变形样式和速度分布特征,但仍缺乏地壳物质组成和岩石圈结构方面的信息,制约着华北克拉通北缘与中亚造山带南部地壳演化、壳幔相互作用等地球动力学问题的研究.
地壳厚度和泊松比是地壳结构和属性的重要参数,地壳厚度与泊松比的关系,对地质构造演化过程重建有较强的约束作用(李永华等,2006;嵇少丞等,2009;Tian and Zhang,2013).接收函数H-κ方法利用径向接收函数的Ps、PpPs和PpSs/PsPs震相与直达P波的到时关系,共同约束Moho面深度与地壳平均速度比(VP/VS),被认为是求取地壳厚度与泊松比的最有效途径之一(Zhu and Kanamori,2000;Tian and Zhang,2013;高延光和李永华,2014).近年来,众多学者利用中国地震台网(固定台)和流动观测资料,采用接收函数方法获得了大量的地壳厚度与泊松比数据(王峻等,2009;张洪双等,2009;李传金等,2010;葛粲等,2011;武岩等,2011;危自根等,2011; 危自根和陈凌,2012;张广成等,2013;吴庆举和曾融生,1998;Pan and Niu,2011;许卫卫和郑天愉,2005;刘琼林等,2011),这些地壳结构和属性参数(如地壳厚度、波速、泊松比分布等)为地震波场模拟和提高地震层析成像的横向分辨力提供了重要基础资料和约束.
张家口(怀来)—巴音温多尔剖面近南北向大交角穿越华北克拉通北缘和兴蒙造山带的各个构造带(块体),测线两侧的蛇绿岩露头和岩石地球化学和构造研究程度较高,被认为是研究古亚洲洋最终关闭的理想地区之一.宽频带地震观测剖面大致重合人工源深反射地震和宽角反射与折射地震剖面布设,基于三种地震学方法的各自优势,有助于对测线下方地壳上地幔速度结构的多侧面成像和相互约束.
本文通过远震P波接收函数H-κ扫描和共转换点(CCP)叠加获得速度比(VP/VS)信息和Moho速度间断面的产状和起伏特征,结合前人的人工源地震剖面结果,讨论华北克拉通北缘和兴蒙造山带地壳厚度和泊松比之间关系,及其隐含的大陆地壳形成和区域构造演化过程的意义.
最新报道2011—2013年中国地震局地球物理研究所与蒙古科学院天文与地球物理研究中心合作在蒙古中南部(本研究区北段二连浩特西北)布设了69个台站的阵列观测(张风雪等,2014;何静等,2014),上述工作为本研究提供了基础和壳幔结构的重要参考信息.
2数据与方法
2.1数据采集及预处理
由国家自然科学基金资助,中国地质科学院地质研究所分别于2012年10月—2014年12月在华北北部怀来—张家口—苏尼特右旗—二连浩特—中蒙边境(巴音温多尔)一线布设了41个宽频地震流动观测台(Reftek-130数字采集器配置Guralp CMG-3T(25台)或CMG-3ESP(16台)地震计).测线基本重合Sinoprobe反射/折射地震测线(Li et al.,2013;Zhang et al.,2014)(图1),采用连续记录方式,采样频率50 Hz.自南向北横跨阴山—燕山造山带、内蒙古地轴、白乃庙岛弧、温都尔庙增生杂岩带、索伦缝合带(被认为是标志古亚洲洋消亡,华北克拉通与蒙古微板块(属西伯利亚板块)汇聚的板块缝合带)、贺根山杂岩带,乌里雅斯太主动大陆边缘直至中蒙边界,测线走向为NW—SE向,台站间距平均15 km,测线总长约为650 km.至2014年12月底,采集到原始连续记录数据421 GB.
研究选用来自USGS(美国地质调查局)地震目录的震中距在30°~95°,震级大于5级的地震事件746个(地震分布如图2示),从原始数据中截取P 波到时前20 s 至后100 s 数据,用以计算接收函数.首先对截取的波形数据进行挑选,选择P波初至比较明显的波形数据,然后对ZNE(垂直、南北、东西)三分量原始波形数据经过去均值、去线性,预滤波采用0.02~2 Hz拐角频率范围的二级Butterworth带通滤波,然后旋转到ZRT(垂向、径向和切向)坐标系.
2.2P波接收函数分析
远震P波传播到接收台站下方时可认为是近似垂直入射的,远震P波波形数据携带震源、传播路径以及接收区下方结构等信息.Langston(1979)在Phinney(1964)的基础上提出用等效震源的方法可以消除震源及传播路径等对波形的影响.本文利用时间域迭代反褶积算法实现接收函数的计算(Ligorría and Ammon,1999).在计算过程中,高斯系数α取2.5.
由近地表松散沉积地段台站记录计算出来的接收函数,其波形不同程度遭到畸变,导致H-κ方法 失效或结果的不确定.固定台站观测可通过另外选址或井下观测从工程上较好地解决这个问题,流动台站观测受投入成本的限制,目前可采取的措施只保留那些Ps和PpPs震相清晰且一致性较好的接收函数参与下一步分析计算,最终有1844个接收函数(如图3)被用于求取地壳厚度和波速比.其中JIQN(7#)、BAYR(41#)台站的接收函数如图4所示.
2.3接收函数H-κ叠加扫描

图1 华北北部宽频地震流动观测台站分布示意图(构造线据Xiao et al.,2003)蓝色三角示意宽频带流动台站位置.阴影区示意索伦缝合带;角图示意研究区位置.F1:尚义—赤城—古北口—平泉断裂;F2:赤峰—白云鄂博断裂; F3:西拉木伦断裂; F4:林西断裂; F5:锡林浩特断裂; F6:二连浩特断裂; F7:查干敖包断裂.

图2 远震事件分布图(MS>5,震中距 30°~95°)矩形框为研究区.
远震P波穿过Moho面时一部分转换为S波,还有一部分P波和发生转换的S波会经过地表及Moho的反射形成多次波,其中Pms、PpPms、PsPms、PpSms震相在接收函数中能量最强.Zhu和Kanamori(2000)提出利用给定的平均P波速度以及多次波与直达P波的时间差可以求出地壳厚度(即H)与纵波横波波速比(VP/VS,即κ).在一定范围内对H及κ进行扫描,用扫描到的H、κ值求出Pms、PpPms、PsPms、PpSms震相与直达P波的到时差,继而构造目标函数:
S(H,κ)=ω1r(TPms)+ω2r(TPpPms)
-ω3r(TPsPms+TPpSms),
(1)
ωi为各震相的权重系数,且ω1+ω2+ω3=1,由于Ps震相能量较强,选取ω1>ω2+ω3;TPs、TPpPs、TPsPs、TPpSs为各个震相相对于直达P波的到时差.当三个震相交叉得到真实H、κ值时S(H,κ)最大.
H-κ扫描中,参考研究区人工源宽角反射地震 剖面探测结果(Li et al.,2013;李英康等,2014),将研究区地壳平均P波速度取为6.3 km·s-1,地壳厚度变化的范围取为10~70 km,P、S波波速比VP/VS搜索范围定为1.5~2.0,另外,根据所得接收函数的特征(图3),经多次测试,最终将Moho面的转换波Pms震相和它的两个多次波震相PpPms,PpSms+PsPms的叠加权系数分别定为0.6,0.3和0.1,实际上不同加权值组合对结果影响非常小(危自根和陈凌,2012).泊松比σ则由关系式:σ =0.5×[1-1/(κ2-1)]计算得到,其中JIQN、CHGD、SARL、BAYR四个台站的接收函数H-κ扫描结果如图5所示.

图3 华北北部怀来—巴音温多尔剖面接收函数图上边框字符为台站代码(参见表1),纵轴为相对直达P波的到时,图中为按每个台站10个接收函数抽取的共计410个接收函数.

图4 JIQN(7#)、BAYR(41#)台站的接收函数排列接收函数按反方位角(右侧图中红色矩形表示)排列.黑色三角表示地震震中距分布.左图左侧数字为接收函数序号,横轴为相对于直达P波的延迟时间.Moho转换波Pms震相和它的两个多次波震相(PpPms,PsPms+PpSms)用红色虚线标出.
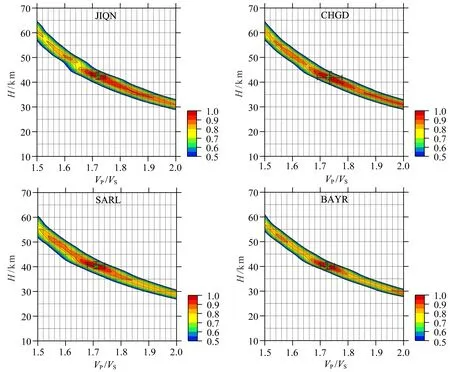
图5 H-κ方法获得的地壳厚度和VP/VS波速比估计
对41个台站接收函数进行了H-κ扫描计算,结果如表1所示.
不同震相的有效识别对H-κ叠加结果的可靠性至关重要.由于测线跨度650 km,台站场地条件、深部结构沿测线变化较大,各台站接收函数的数据质量存在一定差别.Moho面转换波Pms和多次反射波的波形特征和可识别程度,是台站接收函数质量评价的主要依据.41个台站中Pms和PpPms震相清晰且一致性较好的台站有36个,用H-κ叠加方法获得了可靠的地壳厚度和波速比,有5个台站(表1中粗体所示)的远震接收函数波形受浅层多次波干扰严重,计算出来的H,κ值可信度较低,这些台站主要集中在二连盆地(占4个)和怀来盆地.
沿线地壳厚度值分布于37~43 km之间,整条测线地壳厚度平均40.3 km,接近全球陆壳平均厚度(39.2 km)(Christensen and Mooney,1995).所经各构造带地壳厚度差异不大,起伏幅度±3 km,未见明显山根.怀来盆地Moho深度37~39 km.华北克拉通北缘(阴山—燕山带+内蒙古地轴)Moho深度为37~43 km.索伦缝合带Moho深度为 ~40 km.贺根山杂岩带向北至中蒙边境(乌里雅斯太)Moho深度为38~41 km.
沿线地壳波速比VP/VS分布在1.66~1.86之间,平均泊松比分布在0.215~0.297之间.
对各构造带内的泊松比值做简单平均,不难发现,位于华北克拉通北缘的各构造带的泊松比普遍大于华北克拉通东部的泊松比平均值0.26 (王峻等,2009),其中怀来盆地、阴山—燕山带泊松比0.270,内蒙古地轴平均0.281.而西拉木伦断裂以北的各构造带普遍小于0.26,其中白乃庙带平均0.252;温都尔庙带平均0.233;索伦缝合带平均0.244;宝力道带平均0.237;贺根山杂岩带平均 0.261;乌里雅斯太带平均0.259.
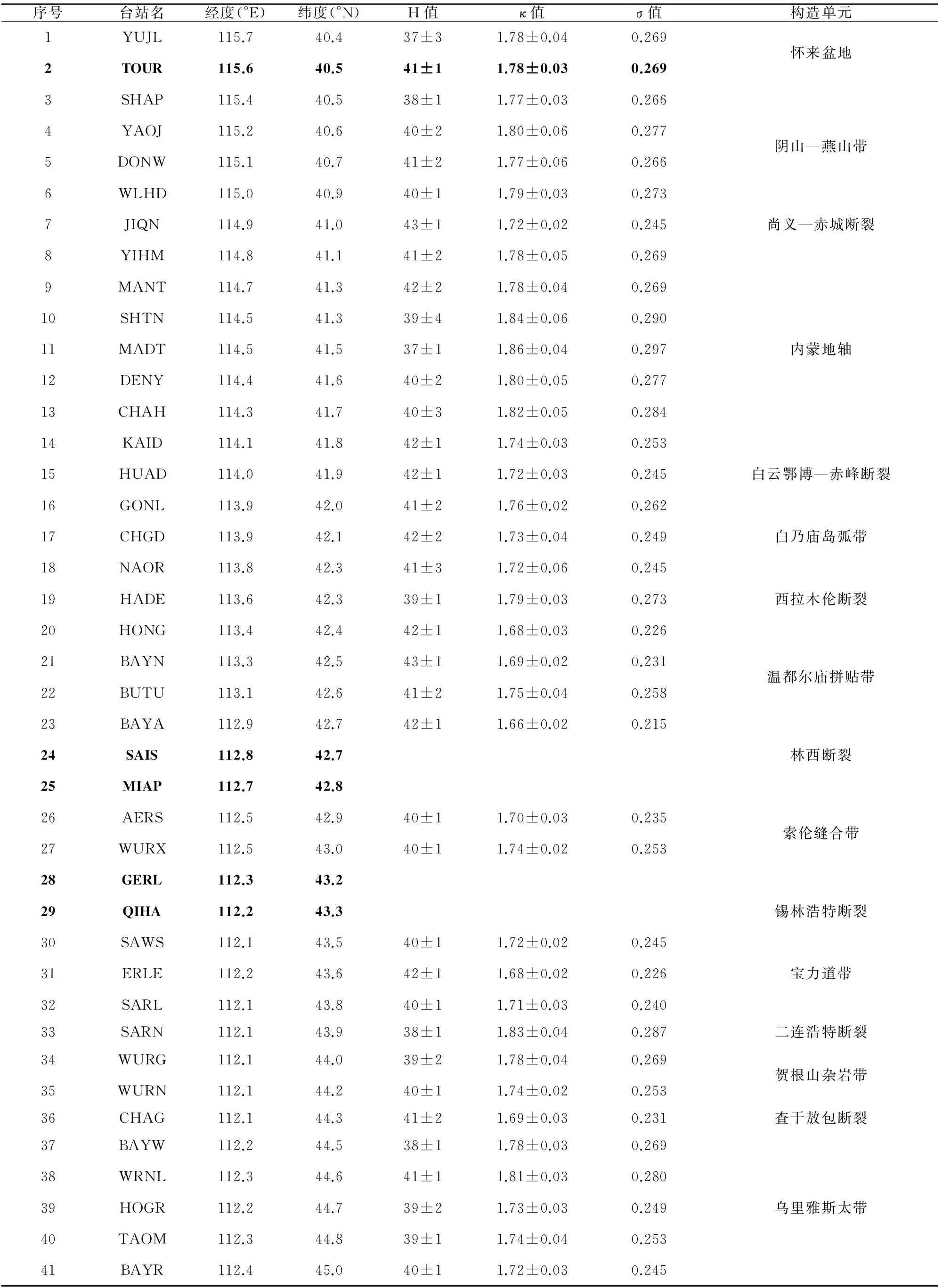
表1 沿线台站下方地壳厚度(H)与泊松比(σ)及其与沿线构造带的对应关系
在空间上,沿测线泊松比分布表现出与构造单元的相关性:各构造带内部泊松比(σ)分布相对稳定,每一处σ值的突升或骤降,基本都能找到对应的构造边界断裂带.
2.4共转换点叠加
共转换点(CCP)叠加技术被广泛用于对较密集台站下方速度界面的接收函数成像(Zhu and Kanamori,2000; Zhu,2000,2002; Zhu et al.,2006; Yuan et al.,1997,2002).
参考同测线人工地震宽角反射与折射剖面得到的速度模型(Li et al.,2013;李文辉等2014;李英康等,2014),对IASP91全球速度模型的地壳部分进行修正作为共转换点叠加的背景速度模型.将地下空间划分成沿测线方向1 km,深度1 km,宽度150 km(垂直于测线方向)的叠加单元,将台站的每个接收函数按方位角及射线路径排列并投影到深度域上,再对同一叠加单元的振幅进行叠加,每一振幅都代表地下速度的变化情况.0~200 km深度范围的CCP叠加结果如图6所示.

图6 台站测线下方0~200 km CCP叠加剖面图(成像位置如图1中AA′、A′A′′所示)红色代表P波从界面速度高一侧向速度低一侧的转换;图6a中小黑点代表H-κ叠加结果所得地壳厚度减去高程所得地壳埋深,小竖线代表误差.F1:尚义—赤城—古北口—平泉断裂; F2:赤峰—白云鄂博断裂; F3:西拉木伦断裂; F4:林西断裂; F5:锡林浩特断裂; F6:二连浩特断裂; F7:查干敖包断裂.
3讨论与结论
3.1地壳厚度
整条测线地壳厚度平均40.3 km,接近全球陆壳平均厚度(39.2 km),所经各构造带地壳厚度差异不大,起伏幅度±3 km,仅不同构造带边界保留了Moho深度的小尺度急剧变化.
最大的地壳厚度仅43 km,测线上有两处连续3个台站以上出现地壳厚度40~43 km,它们分别位于阴山—燕山造山带由东西走向转为北东走向的转折部位和温都尔庙拼贴带的中部.
“燕山运动”期间,华北克拉通北缘经历了强烈的构造变形,阴山—燕山造山带广泛发育指向华北克拉通内部的逆冲断层(赵越,1990;Meng,2003;郑亚东等,2000),地质学家通过还原深源捕掳体和埃达克岩源区的温度、压力条件估算,阴山—燕山造山带地壳厚度曾达到或超过50 km,现今的厚度可能是经历了新生代区域伸展后的残余,区域伸展从东向西逐步减弱(李文辉等,2014).
温都尔庙拼贴带南部,靠近西拉木伦断裂,可能存在P波速度局部高(李英康等,2014)、泊松比大的镁铁质岩块,北部Moho面有局部下凹,暗示地壳整体经历过强烈的挤压缩短.
测线上小于地壳厚度平均值连续超过3个台站间距的地段仅出现于怀来盆地,构造上位于汾渭地堑—山西地堑与银川—河套地堑的交叠部位,可能与鄂尔多斯周缘的新生代陆内裂谷作用有关.
3.2Moho形态与产状
西拉木伦断裂带(图6b,F3)以南,华北克拉通北缘,包括白乃庙弧、温都尔庙杂岩带的Moho面对应的Pms震相明显,深度一致性较好.在构造带内部地壳厚度一致,较少小尺度起伏,更接近一级速度间断面的尖锐和相对刚性的物理特征,与白乃庙弧、温都尔庙杂岩带较早拼贴到华北克拉通北缘,地壳经历了克拉通化有关.
锡林浩特断裂(图6b,F5)以北,宝力道带、贺根山杂岩带和乌里雅斯太构造带的Moho界面宽缓,但界面产状稳定.
索伦带(图6b,F4、F5之间)Moho面横向急剧变化,与两侧各构造带的Moho界面特征形成鲜明对比.分辨率更高的深地震反射剖面显示,带内Moho反射只能分段追踪,其上覆地壳既有南倾也有北倾的反射和透明反射区,被认为是镁铁质下地壳残块、大陆边缘沉积(增生楔)与后期伸展侵入的花岗岩混杂堆积(Zhang et al.,2014).
整体上,Moho面产状相对于索伦缝合带对称,南侧的温都尔庙带和白乃庙带向南倾,北侧的宝力道带、贺根山杂岩带向北倾.
Moho深度整体与地表高程呈镜像对称关系(图7).

图7 测线地壳厚度与地表高程示意图F1:尚义—赤城—古北口—平泉断裂; F2:赤峰—白云鄂博断裂; F3:西拉木伦断裂; F4:林西断裂; F5:锡林浩特断裂; F6:二连浩特断裂;F7:查干敖包断裂.
3.3泊松比
泊松比已成为人类了解地球内部物质成分、构造和物理状态重要途径之一(Holbrook et al.,1988;Ji and Salisbury,1993; Ji et al.,2002;Zandt and Ammon,1995;Christensen,1996).
泊松比的大小取决于岩石中P 波和S波速度的比值(VP/VS),反映在挤压与剪切条件下造岩矿物晶格原子间的性质以及岩石内部显微构造特征.例如,微裂隙的几何形状与空间分布、孔隙度以及各矿物相在三维空间中的连接性和连续性等(嵇少丞等,2009).泊松比的变化范围介于-1~0.5之间,但对绝大多数岩石来说,泊松比介于0~0.5之间.
对造岩矿物的实验室测定的定性结论是泊松比主要与岩石的物质组成相关,受温度和压力的影响较小(Christensen,1996).长英质岩中,岩石的泊松比随石英含量的增加而减小,随长石含量的增加而增加;基性岩如辉长岩、辉绿岩以及基性片麻岩不含石英,基性斜长石所占比例较高,具有较大的泊松比(嵇少丞等,2009).新鲜的橄榄岩较基性岩具有较小的泊松比.蛇纹石的泊松比特别高,故橄榄岩的泊松比随其蛇纹石化程度的增加而增大.榴辉岩的泊松比主要受其主要造岩矿物石榴子石和绿辉石的制约,所含石榴子石化学成分(Wang and Ji,1999)以及退变质程度起决定性的作用(Ji et al.,2003).
从地震波接收函数分析得到的波速比(VP/VS)只是该台站下面整个地壳的平均值.沿测线获得的波速比(VP/VS)与地壳厚度呈负相关关系,如图8所示.由关系式:σ =0.5×[1-1/(κ2-1)]可知,泊松比与地壳厚度也呈负相关关系.

图8 测线地壳厚度与泊松比关系
泊松比与地壳厚度呈负相关关系反映构造变形作用对地壳泊松比的影响.地壳由厚度不一、横向起伏的不同岩性层叠合而成.在构造挤压缩短(增厚)或拉张伸展(减薄)过程中,应变总是优先集中于弱岩层面.相同温度、压力条件下,受到构造挤压的长英质岩石比起基性岩石更容易形成褶皱和推覆构造,使长英质岩石在整个地壳柱体内的所占比例增大,其结果导致地壳泊松比随地壳厚度增加而减少.
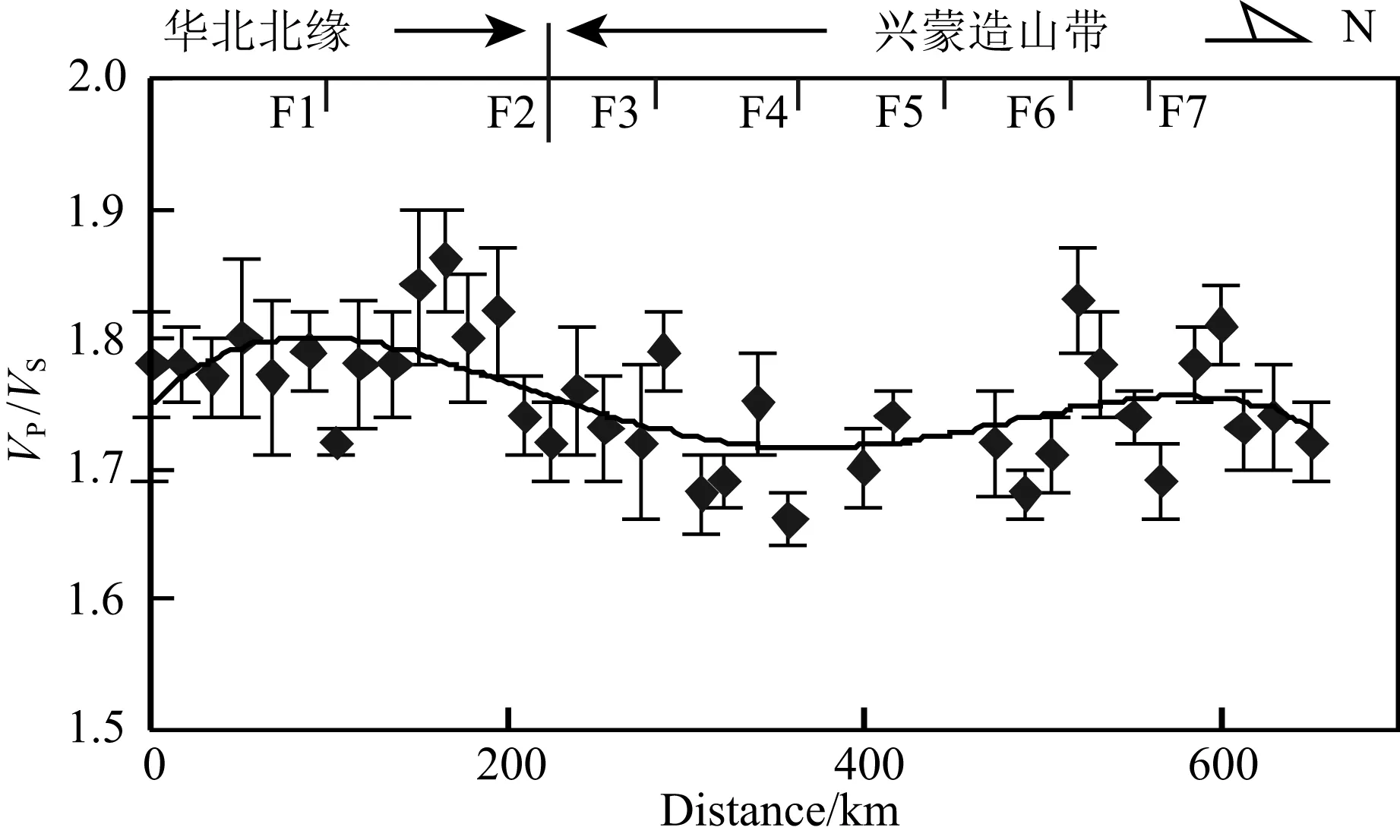
图9 波速比沿测线变化示意图F1:尚义—赤城—古北口—平泉断裂; F2:赤峰—白云鄂博断裂; F3:西拉木伦断裂; F4:林西断裂; F5:锡林浩特断裂; F6:二连浩特断裂; F7:查干敖包断裂.
流体或熔体能有效地影响岩石的泊松比.地下存在流体时,S波衰减很快,导致波速比高于周围地区(Christensen and Fountain,1975),二连浩特断裂(0.287)下方可能是断裂带破碎或裂隙流体的作用.
整条测线波速比(VP/VS)和泊松比呈现以索伦缝合带南缘为对称轴的非线性分布(图9):怀来盆地、阴山—燕山带泊松比0.270,内蒙古地轴平均0.281.而西拉木伦断裂以北的各构造带普遍小于0.26,其中白乃庙带平均0.252;温都尔庙带平均0.233;索伦缝合带平均0.244;宝力道带平均0.237;贺根山杂岩带平均0.261;乌里雅斯太带平均0.259.
这种分布,支持古亚洲(索伦)洋,分别向南、北双向俯冲,最终沿林西断裂闭合的动力学模式.张北台站附近泊松比奇高,与新生代汉诺坝裂隙溢流玄武岩对地壳的添加有关.
综合张家口(怀来)—中蒙边境(巴音温多尔)宽频地震数据的远震P波接收函数结果和前人成果,可得以下结论:
(1) 测线下方Moho深度平均40 km,所经各构造带地壳厚度差异不大,但各块体边界处存在Moho深度小尺度急剧变化.整体上,Moho面产状相对于索伦缝合带对称,南侧的温都尔庙带和白乃庙带下方向南倾,北侧的宝力道带、贺根山杂岩带下方向北倾.
(2) 沿测线泊松比分布表现出与断层分割的构造带较好的相关性:华北克拉通北缘总体较高,兴蒙造山带整体较低;各构造带内部泊松比分布相对稳定,泊松比值的局部扰动往往出现在各块体边界附近.
(3) 整条测线地壳厚度和泊松比之间存在弱的负相关关系.反映地壳结构的横向不均匀性很大部分是构造变形的结果.
(4) 整条测线泊松比分布和地壳上地幔结构特征支持古亚洲(索伦)洋,最终沿林西断裂闭合的动力学模式.
本文结果存在的不足之处是:以二连盆地为主的厚沉积层覆盖区的部分台站,接收函数的波形畸变,个别甚至无法获得稳定的H-κ结果.我们正在探索利用主动源地震浅层层析成像的结果,改善较厚沉积层台站的接收函数波形,以期获得更加可靠的地壳厚度和泊松比图像.
致谢感谢河北省张家口市国土资源局、内蒙古自治区锡林郭勒盟国土资源局、乌兰察布市国土资源局对野外工作的支持,感谢方霖、周大为、钮增欣等野外台站布设人员的辛勤劳动,感谢刘启民博士、郑丹硕士在数据处理过程中给予的帮助,感谢审稿专家提出的建设性修改意见.
References
Chen L,Wang T,Zhao L,et al.2008.Distinct lateral variation of lithospheric thickness in the northeastern North China Craton.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,267(1-2): 56-68.
Chen L.2010.Concordant structural variations from the surface to the base of the upper mantle in the North China Craton and its tectonic implications.Lithos,120(1-2): 96-115.
Chen L,Wei Z G,Cheng C.2010a.Significant structural variations in the Central and Western North China craton and its implications for the craton destruction.Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese),17(1): 212-228.
Chen L,Cheng C,Wei Z G.2010b.Contrasting structural features at different boundary areas of the North China Craton and its tectonic implications.Advances in Earth Science (in Chinese),25(6): 571-581.
Christensen N I,Fountain D M.1975.Constitution of the lower continental crust based on experimental studies of seismic velocities in granulite.Bulletin of the Geological Society of America,86(2): 227-236.
Christensen N I,Mooney W D.1995.Seismic velocity structure and composition of the continental crust: a global view.J.Geophys.Res.,100(B6): 9761-9788.
Christensen N I.1996.Poisson′s ratio and crustal seismology.J.Geophys.Res.,101(B2): 3139-3156.
Fullea J,Lebedev S,Agius M R,et al.2012.Lithospheric structure in the Baikal-central Mongolia region from integrated geophysical-petrological inversion of surface-wave data and topographic elevation.Geochem.Geophys.Gepsyst.,13(8): Q0AK09.
Gao S,Davis P M,Liu H,et al.1994.Seismic anisotropy and mantle flow beneath the Baikal rift zone.Nature,371(6493): 149-151.
Gao S,Davis P M,Liu H,et al.1997.SKS splitting beneath continental rift zones.J.Geophys.Res.,102(B10): 22781-22797.
Gao S S,Liu K H,Chen C Z.2004.Significant crustal thinning beneath the Baikal rift zone: New constraints from receiver function analysis.Geophys.Res.Lett.,31(20): L20610.
Gao Y G,Li Y H.2014.Crustal thickness and VP/VSin the Northeast China-North China region and its geological implication.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),57(3): 847-857,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140314.
Ge C,Zheng Y,Xiong X.2011.Study of crustal thickness and Poisson ratio of the North China Craton.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),54(10): 2538-2548,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.10.011.
He J,Wu Q J,Gao M T,et al.2014.Crustal structure and Poisson ratio beneath the central and southern Mongolia derived from receiver functions.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),57(7): 2386-2394,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140732.
Holbrook W S,Gajewski D,Krammer A,et al.1988.An interpretation of wide-angle compressional and shear wave data in southwest Germany: Poisson′s ratio and petrological implications.J.Geophys.Res.,93(B10): 12081-12106.
Hsu K J,Wang Q C,Li J,et al.1991.Geologic evolution of the Neimonides: a working hypothesis.Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae,84(1): 1-31.
Jahn B M,Windley B,Natal′in B,et al.2004.Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asia.J.Asian Earth Sci.,23(5): 599-603.
Ji S C,Salisbury M H.1993.Shear-wave velocities,anisotropy and splitting in high-grade mylonites.Tectonophysics,221(3-4): 453-473.
Ji S C,Wang Q,Xia B.2002.Handbook of Seismic Properties of Minerals,Rocks and Ores.Montreal: Polytechnic International Press,630.Ji S C,Saruwatari K,Mainprice D,et al.2003.Microstructures,petrofabrics and seismic properties of ultra high-pressure eclogites from Sulu region,China: implications for rheology of subducted continental crust and origin of mantle reflections.Tectonophysics,370(1-4): 49-76.
Ji S C,Wang Q,Yang W C.2009.Correlation between crustal thickness and Poisson′s ratio in the North China Craton and its implication for lithospheric thinning.Acta Geologica Sinica (in Chinese),83(3): 324-330.
Jian P,Liu D Y,Kröner A,et al.2008.Time scale of an early to mid-Paleozoic orogenic cycle of the long-lived Central Asian Orogenic Belt,Inner Mongolia of China: implications for continental growth.Lithos,101(3-4): 233-259.
Jong K D,Xiao W J,Windley B F,et al.2006.Ordovician40Ar/39Ar phengite ages from the blueschist-facies Ondor Sum subduction-accretion complex (Inner Mongolia) and implications for the early Paleozoic history of continental blocks in China and adjacent areas.American Journal of Science,306(10): 799-845.
Kröner A,Windley B F,Badarch G,et al.2007.Accretionary growth and crust formation in the central Asian Orogenic Belt and comparison with the Arabian-Nubian shield.Geological Society of America Memoir,200: 181-209.
Langston C A.1979.Structure under Mount Rainier,Washington,inferred from teleseismic body waves.J.Geophys.Res.: Solid Earth,84(B9): 4749-4762.
Lei J S.2012.Upper-mantle tomography and dynamics beneath the North China Craton.J.Geophys.Res.: Solid Earth,117(B6): B06313.
Li C J,Xu P F,Sun Y J,et al.2010.The Jinzhong transition belt and its geological significance by receiver function in Shanxi region.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),53(5): 1143-1148,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.05.015.
Li J Y,Zhang J,Yang T N,et al.2009.Crustal tectonic division and evolution of the southern part of the north Asian orogenic region and its adjacent areas.Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition) (in Chinese),39(4): 584-605.
Li Q S,Gao R,Zhang C K,et al.2008.Remainder crustal root and decoupling-main characteristics of crust structure beneath the Yanshan intracontinent orogen.Acta Geoscientica Sinica (in Chinese),29(2): 129-136.
Li S L,Mooney W D,Fan J C.2006.Crustal structure of mainland China from deep seismic sounding data.Tectonophysics,420(1-2): 239-252.
Li W H,Keller G R,Gao R,et al.2013.Crustal structure of the northern margin of the North China Craton and adjacent region from SinoProbe02 North China seismic WAR/R experiment.Tectonophysics,606: 116-126.
Li W H,Gao R,Randy K,et al.2014.Crustal structure of the northern margin of north China craton from Huailai to Sonid Youqi profile.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),57(2): 472-483,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140213.
Li Y H,Tian X B,Wu Q J,et al.2006.The Poisson ratio and crustal structure of the central Qinghai-Xizang inferred from INDEPTH-Ⅲ teleseismic waveforms: Geological and geophysical implications.Chinses J.Geophys.(in Chinese),49(4): 1037-1044.
Li Y K,Gao R,Yao Y T,et al.2014.Crustal velocity structure from the northern margin of the North China Craton to the southern margin of the Siberian plate.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),57(2): 484-497.
Liu Q L,Wang C Y,Yao Z X,et al.2011.Study on crustal thickness and velocity ratio in mid-western North China Craton.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),54(9): 2213-2224,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.09.003.
Ligorría J P,Ammon C J.1999.Iterative deconvolution and receiver-function estimation.Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,89(5): 1395-1400.
Meng Q R.2003.What drove late Mesozoic extension of the northern China-Mongolia tract? Tectonophysics,369(3-4): 155-174.
Mordvinova V V,Deschamps A,Dugarmaa T,et al.2007.Velocity structure of the lithosphere on the 2003 Mongolian-Baikal transect from SV waves Izvestiya.Physics of the Solid Earth,43(2): 119-129.
Nielsen C,Thybo H.2009.No Moho uplift below the Baikal rift zone: Evidence from a seismic refraction profile across southern Lake Baikal.J.Geophys.Res.,114(B8): B08306.
Pan S Z,Niu F L.2011.Large contrasts in crustal structure and composition between the Ordos plateau and the NE Tibetan plateau from receiver function analysis.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,303(3-4): 291-298.
Phinney R A.1964.Structure of the Earth′s crust from spectral behavior of long-period body waves.J.Geophys.Res.,69(14): 2997-3017.
Qiu R Z,Deng J F,Zhou S,et al.2005.Lithosphere types in North China: evidence from geology and geophysics.Science China Earth Sciences,48(11): 1809-1827.
Sun W C,Ma B L,Song S Y,et al.1992.Explanation of Geotransect from Suizhou,Hubei Province to Kalaqin Qi,Inner Mongolia (in Chinese).Beijing: Seismological Press.
Tian X B,Zhang Z J.2013.Bulk crustal properties in NE Tibet and their implications for deformation model.Gondwana Research,24(2): 548-559.
Tian X B,Teng J W,Zhang H S,et al.2011.Structure of crust and upper mantle beneath the Ordos Block and the Yinshan Mountains revealed by receiver function analysis.Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,184(3-4): 186-193.
Wang J,Liu Q Y,Chen J H,et al.2009.The crustal thickness and Poisson′s ratio beneath the Capital Circle Region.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),52(1): 57-66.
Wang W L,Wu J P,Fang L H.2009.Crust and upper mantle S-wave velocity structure beneath Tanghai-Shangdu seismic array profile.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),52(1): 81-89.
Wang Z C,Ji S C.1999.Deformation of silicate garnets: brittle-ductile transition and its geological implications.The Canadian Mineralogist,37(2): 525-541.
Wedepohl K H.1995.The composition of the continental crust.Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,59(7): 1217-1232.
Wei Z G,Chen L,Yang X L.2011.Transverse variations of crustal thickness and VP/VSratio under the stations in the Liaodong anteclise-Yanshan belt-Xingmeng orogenic belt and their tectonic implications.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),54(11): 2799-2808,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.11.010.
Wei Z G,Chen L.2012.Regional differences in crustal structure beneath northeastern China and northern North China Craton: constraints from crustal thickness and VP/VSratio.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),55(11): 3601-3614,doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.009.
Windley B F,Alexeiev D,Xiao W J,et al.2007.Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic belt.Journal of the Geological Society,164(1): 31-47.
Wu Q J,Zeng R S.1998.The crustal structure of Qinghai-Xizang plateau inferred from broadband teleseismic waveform.Chinese J.Geophys.(Acta Geophysica Sinica) (in Chinese),41(5): 669-679.
Wu Y,Ding Z F,Zhu L P.2011.Mapping the upper mantle discontinuities beneath North China Craton from common conversion points method with teleseismic receiver functions.CT Theory and Applications (in Chinese),20(4): 485-494.
Xiao W J,Windley B F,Hao J,et al.2003.Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture,Inner Mongolia,China: termination of the Central Asian orogenic belt.Tectonics,22(6): 1069.
Xiao W J,Windley B F,Badarch G,et al.2004.Palaeozoic accretionary and convergent tectonics of the southern Altaids: implications for the growth of Central Asia.Journal of the Geological Society,161(3): 339-342.
Xiao W J,Han C M,Yuan C,et al.2008.Middle Cambrian to Permian subduction-related accretionary orogenesis of Northern Xinjiang,NW China: implications for the tectonic evolution of Central Asia.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,32(2-4): 102-117.
Xiao W J,Windley B F,Huang B C,et al.2009.End-Permian to mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids: implications for the geodynamic evolution,Phanerozoic continental growth,and metallogeny of Central Asia.International Journal of Earth Sciences,98(6): 1189-1217.
Xu B,Zhao P,Bao Q Z,et al.2014.Preliminary study on the pre-Mesozoic tectonic unit division of the Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt (XMOB).Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese),30(7): 1841-1857.
Xu W W,Zheng T Y.2005.Distribution of Poisson′s ratios in the northwestern basin-mountain boundary of the Bohai Bay Basin.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),48(5): 1077-1084.
Yuan X H,Ni J,Kind R,et al.1997.Lithospheric and upper mantle structure of southern Tibet from a seismological passive source experiment.J.Geophys.Res.,102(B12): 27491-27500.
Yuan X,Sobolev S V,Kind R.2002.Moho topography in the central Andes and its geodynamic implications.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,199(3-4): 389-402.
Zandt G,Ammon C J.1995.Continental crust composition constrained by measurements of crustal Poisson′s ratio.Nature,374(6518): 152-154.
Zhai M G.2008.Lower crust and lithospheric mantle beneath the North China Craton before the Mesozoic lithospheric disruption.Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese),24(10): 2185-2204.
Zhang F X,Wu Q J,Li Y H,et al.2014.The P wave velocity structure of the upper mantle beneath the Central and Southern Mongolia area.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),57(9): 2790-2801,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140906.
Zhang G C,Wu Q J,Pan J T,et al.2013.Study of crustal structure and Poisson ratio of NE China by H-K stack and CCP stack methods.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),56(12): 4084-4094,doi: 10.6038/cjg20131213.
Zhang H S,Tian X B,Teng J W.2009.Estimation of crustal VP/VSwith dipping Moho from receiver functions.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),52(5): 1243-1252,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.05.013.
Zhang S H,Gao R,Li H Y,et al.2014.Crustal structures revealed from a deep seismic reflection profile across the Solonker suture zone of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt,northern China: An integrated interpretation.Tectonophysics,612-613: 26-39.
Zhang X K,Zhu Z P,Zhang C K.1998.Crustal and upper mantle structure of the Zhangjiakou-Bohai seismic zone.∥ Institute of geology of Chinese Seismic Bureau Eds.research on Active Fault (6) (in Chinese).Beijing: Seismological Press,1-16.
Zhao D P,Lei J S,Inoue T,et al.2006.Deep structure and origin of the Baikal rift zone.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,243(3-4): 681-691.
Zhao L,Zheng T Y,Lü G.2008.Insight into craton evolution: Constraints from shear wave splitting in the North China Craton.Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,168(3-4): 153-162.
Zhao Y.1990.The Mesozoic orogenies and tectonic evolution of the Yanshan area.Geological Review (in Chinese),36(1): 1-13.
Zheng T Y,Chen L,Zhao L,et al.2006.Crust-mantle structure difference across the gravity gradient zone in North China Craton: Seismic image of the thinned continental crust.Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,159(1-2): 43-58.
Zheng T Y,Chen L,Zhao L,et al.2007.Crustal structure across the Yanshan belt at the northern margin of the North China Craton.Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,161(1-2): 36-49.
Zheng Y D,Davis G A,Wang C,et al.2000.Major Mesozoic tectonic events in the Yanshan belt and the plate tectonic setting.Acta Geologica Sinica (in Chinese),74(4): 289-302.
Zhu L P.2000.Crustal structure across the San Andreas Fault,southern California from teleseismic converted waves.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,179(1): 183-190.
Zhu L P,Kanamori H.2000.Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions.J.Geophys.Res.,105(B2): 2969-2980.
Zhu L P.2002.Deformation in the lower crust and downward extent of the San Andreas Fault as revealed by teleseismic waveforms.Earth Planets Space,54(11): 1005-1010.
Zhu L P,Mitchell B J,Akyol N,et al.2006.Crustal thickness variations in the Aegean region and implications for the extension of continental crust.J.Geophys.Res.: Solid Earth,111(B1): B01301.Zorin Y A,Kozhevnikov V M,Novoselova M R,et al.1989.Thickness of the lithosphere beneath the Baikal rift zone and adjacent regions.Tectonophysics,168(4): 327-337.
Zorin Y A,Mordvinova V V,Turutanov E K,et al.2002.Low seismic velocity layers in the Earth′s crust beneath eastern Siberia (Russia) and central Mongolia: Receiver function data and their possible geological implication.Tectonophysics,359(3-4): 307-327.
Zorin Y A,Turutanov E K,Mordvinova V V,et al.2003.The Baikal rift zone: The effect of mantle plumes on older structure.Tectonophysics,371(1-4): 153-173.
附中文参考文献
陈凌,危自根,程骋.2010a.从华北克拉通中、西部结构的区域差异性探讨克拉通破坏.地学前缘,17(1): 212-228.
陈凌,程骋,危自根.2010b.华北克拉通边界带区域深部结构的特征差异性及其构造意义.地球科学进展,25(6): 571-581.
高延光,李永华.2014.中国东北—华北地区地壳厚度与泊松比及其地质意义.地球物理学报,57(3): 847-857,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140314.
葛粲,郑勇,熊熊.2011.华北地区地壳厚度与泊松比研究.地球物理学报,54(10): 2538-2548,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.10.011.
何静,吴庆举,高孟潭等.2014.利用接收函数方法研究蒙古中南部地区地壳结构.地球物理学报,57(7): 2386-2394,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140732.
嵇少丞,王茜,杨文采.2009.华北克拉通泊松比与地壳厚度的关系及其大地构造意义.地质学报,83(3): 324-330.
李传金,徐佩芬,孙勇军等.2010.用远震接收函数研究山西地区地壳厚度变化: “晋中坡折带”及其地质意义探讨.地球物理学报,53(5): 1143-1148,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.05.015.
李锦轶,张进,杨天南等.2009.北亚造山区南部及其毗邻地区地壳构造分区与构造演化.吉林大学学报(地球科学版),39(4): 584-605.
李秋生,高锐,张成科等.2008.残余壳根与“三明治”结构——燕山造山带中段地壳结构的主要特征.地球学报,29(2): 129-136.
李文辉,高锐,Randy K等.2014.华北克拉通北缘(怀来—苏尼特右旗)地壳结构.地球物理学报,57(2): 472-483,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140213.
李永华,田小波,吴庆举等.2006.青藏高原INDEPTH-Ⅲ剖面地壳厚度与泊松比: 地质与地球物理含义.地球物理学报,49(4): 1037-1044.
李英康,高锐,姚聿涛等.2014.华北克拉通北缘—西伯利亚板块南缘的地壳速度结构特征.地球物理学报,57(2): 484-497.
刘琼林,王椿镛,姚志祥等.2011.华北克拉通中西部地区地壳厚度与波速比研究.地球物理学报,54(9): 2213-2224,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.09.003.
邱瑞照,邓晋福,周肃等.2004.华北地区岩石圈类型: 地质与地球物理证据.中国科学,34(8): 698-711.
任纪舜,王作勋,陈炳蔚等.1997.中国及邻区大地构造图简要说明.北京: 地质出版社.
孙武城,马宝林,宋松岩等.1992.湖北随州至内蒙古喀喇沁旗地学断面说明书.北京: 地震出版社.
王峻,刘启元,陈九辉等.2009.首都圈地区的地壳厚度及泊松比.地球物理学报,52(1): 57-66.
王未来,吴建平,房立华.2009.唐海—商都地震台阵剖面下方的 地壳上地幔S波速度结构研究.地球物理学报,52(1): 81-89.
危自根,陈凌,杨小林.2011.辽东台隆、燕山带和兴蒙造山带台站下方地壳厚度和平均波速比(VP/VS)的横向变化及其构造意义.地球物理学报,54(11): 2799-2808,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.11.010.
危自根,陈凌.2012.东北地区至华北北缘地壳结构的区域差异: 地壳厚度与波速比的联合约束.地球物理学报,55(11): 3601-3614,doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.009.
吴庆举,曾融生.1998.用宽频带远震接收函数研究青藏高原的地壳结构.地球物理学报,41(5): 669-679.
武岩,丁志峰,朱露培.2011.利用远震接收函数的共转换点叠加方法研究华北克拉通上地幔过渡带结构.CT理论与应用研究,20(4): 485-494.
徐备,赵盼,鲍庆中等.2014.兴蒙造山带前中生代构造单元划分初探.岩石学报,30(7): 1841-1857.
许卫卫,郑天愉.2005.渤海湾盆地北西盆山边界地区泊松比分布.地球物理学报,48(5): 1077-1084.
翟明国.2008.华北克拉通中生代破坏前的岩石圈地幔与下地壳.岩石学报,24(10): 2185-2204.
张风雪,吴庆举,李永华等.2014.蒙古中南部地区的上地幔P波速度结构.地球物理学报,57(9): 2790-2801,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140906.
张广成,吴庆举,潘佳铁等.2013.利用H-K叠加方法和CCP叠加方法研究中国东北地区地壳结构与泊松比.地球物理学报,56(12): 4084-4094,doi: 10.6038/cjg20131213.
张洪双,田小波,滕吉文.2009.接收函数方法估计Moho倾斜地区的地壳速度比.地球物理学报,52(5): 1243-1252,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.05.013.
张先康,祝治平,张成科.1998.张家口—渤海地震带及其两侧地壳上地幔构造与速度结构研究.∥ 国家地震局地质研究所编.活动断裂研究(6).北京: 地震出版社,1-16.
赵越.1990.燕山地区中生代造山运动及构造演化.地质论评,36(1): 1-13.
郑亚东,Davis G A,王琮等.2000.燕山带中生代主要构造事件与板块构造背景问题.地质学报,74(4): 289-302.
(本文编辑何燕)
基金项目国家自然科学基金(41174081)和“深部探测技术与实验研究”专项(Sinoprobe-02-03,公益科研专项项目编号201311156)联合资助.
作者简介龚辰,1989年生,中国地质科学院与中国地质大学(北京)联合培养硕士研究生在读,主要从事地壳上地幔结构的宽频带地震探测研究.E-mail:gc_gongchen@163.com *通讯作者李秋生,1958年生,研究员,主要从事大陆深部结构地震学探测与地球动力学研究.E-mail:liqiusheng@cags.ac.cn
doi:10.6038/cjg20160312 中图分类号P315
收稿日期2015-02-05,2015-10-28收修定稿
Crustal thickness and Poisson ratio beneath the Huailai-Bayinonder profile derived from teleseismic receiver functions
GONG Chen1,LI Qiu-Sheng1*,YE Zhuo1,ZHANG Hong-Shuang1,LI Wen-Hui1,HE Chuan-Song2,LI Ying-Kang3
1InstituteofGeology,ChineseAcademyofGeologicalSciences,KeyLaboratoryofEarthprobeandGeodynamics,MinistryofLandandResource,Beijing100037,China2InstituteofGeophysics,ChinaEarthquakeAdministration,Beijing100081,China3CoreandSamplesCenterofLandandResources,HebeiYanjiao065201,China
AbstractThe Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB) between the Siberia paleo-continent and the North China paleo-continent has a close relationship with the evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean.The Xing′an-Mongolia Orogenic Belt (XMOB) as eastern part of the CAOB is located in North China.It is generally considered that the closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean resulted in the formation of the XMOB,but there remain some disputes about the tectonic attribute of the northern margin of the North China Craton and where the Paleo-Asian Ocean finally closed and how it behaves due to complex evolution process,extensive coverage of Cenozoic sediments and the lack of high resolution deep exploration data.
KeywordsXing′an Mongolia Orogenic Belt; Paleo-Asian Ocean; Receiver function; Crust and upper mantle structure; Poisson ratio
龚辰,李秋生,叶卓等.2016.远震P波接收函数揭示的张家口(怀来)—中蒙边境(巴音温多尔)剖面地壳厚度与泊松比.地球物理学报,59(3):897-911,doi:10.6038/cjg20160312.
Gong C,Li Q S,Ye Z,et al.2016.Crustal thickness and Poisson ratio beneath the Huailai-Bayinonder profile derived from teleseismic receiver functions.Chinese J.Geophys.(in Chinese),59(3):897-911,doi:10.6038/cjg20160312.
