甘草提取物对2,3,7,8-四氯二苯并-p-二英致建鲤肝损伤的影响
2015-07-05杜金梁曹丽萍贾睿刘英娟申玉金殷国俊
杜金梁, 曹丽萍, 贾睿, 刘英娟, 申玉金, 殷国俊,*
(1.中国水产科学研究院淡水渔业研究中心,农业部淡水渔业和种质资源利用重点实验室,江苏 无锡214081;2.中国水产科学研究院淡水渔业研究中心,农业部鱼类免疫药理学国际联合实验室,江苏 无锡214081;3.南京农业大学无锡渔业学院,江苏 无锡214081)
甘草提取物对2,3,7,8-四氯二苯并-p-二英致建鲤肝损伤的影响
杜金梁1,2, 曹丽萍1,2, 贾睿3, 刘英娟3, 申玉金3, 殷国俊1,2,3*
(1.中国水产科学研究院淡水渔业研究中心,农业部淡水渔业和种质资源利用重点实验室,江苏 无锡214081;2.中国水产科学研究院淡水渔业研究中心,农业部鱼类免疫药理学国际联合实验室,江苏 无锡214081;3.南京农业大学无锡渔业学院,江苏 无锡214081)
为了评价甘草提取物是否对2,3,7,8-四氯二苯并-p-二英(2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin,TCDD)引起建鲤肝组织损伤具有保护作用,本实验用含甘草提取物的饲料(0.1、0.5和1.0 g/kg)饲喂建鲤60 d,再腹腔注射0.6 μg/kg TCDD,72 h后收集血液和肝组织,检测血清和肝组织匀浆中谷丙转氨酶(alanine transaminase,ALT)、谷草转氨酶(aspartate transaminase,AST)、乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase,LDH)、超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,AKP)、总蛋白(total protein,TP)、白蛋白(albumin,Alb)、过氧化氢酶(hydrogen peroxidase,CAT)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GPx)、总抗氧化能力(total antioxidant capacity, T-AOC)、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)等生化指标,同时制备肝组织病理切片,观察甘草提取物对TCDD诱导建鲤肝组织损伤的影响。结果表明:1.0 g/kg甘草提取物显著降低血清中ALT、AST、LDH和AKP活性,显著提高总蛋白(TP)、白蛋白(Alb)质量浓度、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GPx)、总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,降低丙二醛(MDA)质量摩尔浓度(P<0.05或P<0.01)。病理组织切片观察结果显示,甘草提取物处理组可以明显减轻TCDD引起肝组织损伤。提示,甘草提取物对TCDD引起的建鲤肝组织损伤具有较好的保护作用,而且甘草提取物的保护作用可能与其抗氧化性能有关。
甘草提取物; 2,3,7,8-四氯二苯并-p-二英; 肝损伤; 建鲤
中药的应用在我国有着悠久的历史,随着人类对中药研究的不断深入,中草药被广泛应用于一些疾病的治疗。甘草,又名乌拉尔甘草,是一种多年生草本植物,属豆科。现已证明甘草的功能有很多,如甘草具有抗感染、增强机体免疫功能、防治病毒性肝炎、抗氧化、清除多种自由基等作用[15]。关于其在肝损伤治疗方面应用研究,曹丽萍等[16]在甘草提取物对叔丁基氢过氧化物诱导的建鲤原代培养肝细胞损伤的研究中发现,甘草提取物对叔丁基过氧化氢(tert-butyl hydroperoxide,t-BHP)造成的鱼类肝细胞损伤具有一定的保护作用;高雪岩等[17]通过研究甘草中总皂苷对四氯化碳所造成的小鼠急性肝损伤影响发现,甘草总皂苷可以明显降低四氯化碳造成的肝损伤,且效果显著。而关于甘草提取物是否也可以抑制TCDD造成的鱼类肝组织损伤,还未见相关报道。
本研究以TCDD 诱导鲤肝组织的急性损伤模型为基础,通过测定肝功能生化指标和肝组织病理切片的变化来探索甘草提取物是否对TCDD引起的建鲤急性肝组织损伤具有保护作用,以期为防治TCDD引起的肝组织损伤提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验用鱼
试验用建鲤取自中国水产科学研究院淡水渔业研究中心渔场,体质健康、无伤,体质量为(30.0±1.0) g左右,取回后将建鲤饲养于循环水系统中暂养1周。
1.2 试剂和仪器
甘草提取物(Glycyrrhizaglabraextracts,GGE)购自西安应化生物技术有限公司;二甲基亚砜 (dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO)购自美国Sigma公司;2, 3, 7, 8-四氯二苯并-p-二英购自厦门慧嘉生物科技有限公司;谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶等测定试剂盒购自南京建成生物工程研究所;723分光光度计购自上海欣茂仪器有限公司;酶标仪MK3购自美国Thermo公司。
1.3 TCDD诱导建鲤肝损伤模型建立
将大小规格基本一致的建鲤180条随机分为6个处理组,即1个对照组和5个处理组(TCDD质量比为0.1、0.3、 0.6、 1.2和2.4 μg/kg)。5个处理组按建鲤体质量来进行腹腔注射染毒,注射剂量为每10 g体质量0.05 mL,对照组仅注射同体积DMSO(0.1%的DMSO,注射剂量为0.05 mL/10 g体质量)。
1.4 试验组划分及处理
选取健康、无伤,体质量为(30.0±1.0) g左右的建鲤120尾,随机将建鲤设5个处理组和1个对照组,每组20尾鱼,即正常对照组和TCDD对照组(仅饲喂基础饲料);药物(GGE)对照组基础饲料中添加1.0 g/kg甘草提取物;3个试验组:基础饲料中分别添加质量比为0.1、0.5和1.0 g/kg甘草提取物。连续饲喂60 d,正常对照组和GGE对照组按体质量注射同体积DMSO(0.1%的DMSO,注射剂量0.05 mL/10 g体质量)。TCDD组和3个试验组一次性腹腔注射0.6 μg/kg TCDD(用最终不超过体积分数0.1%的DMSO将TCDD助溶),注射量:按照建鲤体质量来进行注射(0.05 mL/10 g体质量)。72 h后采集血液和肝组织。
1.5 血清及肝组织匀浆制备
于建鲤尾静脉处进行采血,用4 ℃低温离心机,3 500 r/min离心10 min,分离上层血清,将分离好血清置于-20 ℃保存待用。
用0.9%氯化钠溶液将建鲤肝组织中残存血液清洗干净后,用干净滤纸吸干其表面水分,称取肝组织0.1 g,然后加入9倍体积的0.9%氯化钠溶液,用玻璃匀浆器在冰浴上制备10%的肝组织匀浆液。用4 ℃低温离心机,3 000 r/min离心10 min,收集肝组织匀浆上清液,于-20 ℃保存备用。
1.6 生化指标测定
参照南京建成生物工程研究所试剂盒说明书测定谷丙转氨酶(alanine transaminase,ALT)、谷草转氨酶(aspartate transaminase,AST)、乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase,LDH)、白蛋白(albumin,Alb)、总蛋白(total protein,TP)、 超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,AKP)、过氧化氢酶(hydrogen peroxidase,CAT)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GPx)、总抗氧化能力(total antioxidant capacity,T-AOC)和丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)等各项生化指标。
1.7 肝组织切片制备与观察
将采集好的肝组织放入波恩氏固定液中固定48 h后,制备石蜡组织切片,通过苏木精-伊红(hatmatoxylin-eosin,HE) 染色来观察TCDD对建鲤肝组织的影响。
1.8 数据分析

2 结果与分析
2.1 不同质量比的TCDD对建鲤血清和肝组织中生化指标的影响
由图1可以看出,腹腔注射TCDD质量比≥0.3 μg/kg后,建鲤血清中ALT、AST和LDH的活性在注射72~96 h出现显著升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。
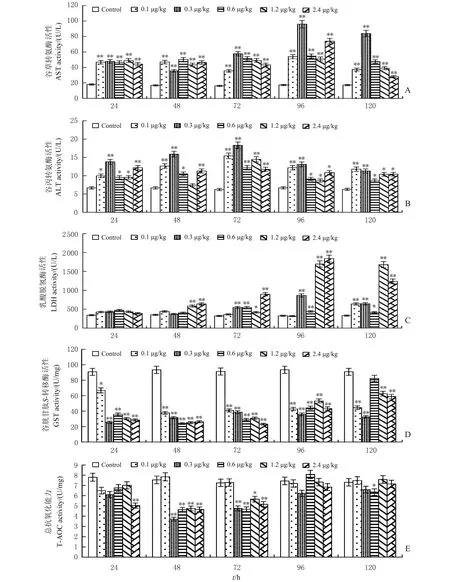
n=5; *,**分别表示与对照组相比在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异有统计学意义。n=5; *,** indicate statistically significant difference from control group at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability levels, respectively.图1 TCDD致建鲤肝损伤血清和对肝组织中AST(A)、ALT(B)、LDH(C)、GST(D)和T-AOC(E)活性的影响Fig.1 Effects of TCDD on AST (A), ALT (B), LDH (C), GST (D) and T-AOC (E) activities in serum and liver tissue of Jian carp
建鲤肝组织中谷胱甘肽S-转移酶(glutathioneS-transferase,GST)和T-AOC活性在腹腔注射TCDD质量比≥0.3 μg/kg后,48 h和72 h出现显著降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),综合结果,以72 h损伤较为严重。
2.2 甘草提取物对建鲤血清中ALT、AST、LDH、AKP活性的影响
图2显示,建鲤肝组织受到损伤后,血清中ALT、AST、LDH、AKP活性显著升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。饲料中添加3种不同质量比的甘草提取物饲喂建鲤后,血清中ALT、AST、LDH、AKP活性出现不同程度降低。
2.3 甘草提取物对建鲤血清中TP和Alb质量浓度的影响
由图3显示,建鲤肝组织的损伤引起了血清中TP和Alb质量浓度显著降低(P<0.01)。这种降低趋势在加入甘草提取物后被抑制,以1.0 g/kg甘草提取物效果最好。

n=10; *,**分别表示与TCDD组相比在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异有统计学意义。n=10; *,** indicate statistically significant difference from TCDD group-treated at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability levels, respectively.图2 甘草提取物对TCDD致建鲤肝损伤血清中ALT(A)、AST(B)、LDH(C) 和AKP(D)活性的影响Fig.2 Effects of GGE on the serum ALT (A), AST (B), LDH (C) and AKP (D) in TCDD-treated Jian carp

n=10; *,**分别表示与TCDD组相比在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异有统计学意义。n=10; *,** indicate statistically significant difference from TCDD group-treated at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability levels, respectively.图3 甘草提取物对TCDD致建鲤肝损伤血清中TP和Alb质量浓度的影响Fig.3 Effects of GGE on the serum TP (A) and Alb (B) in TCDD-treated Jian carp
2.4 甘草提取物对建鲤肝组织中抗氧化指标的影响
由图4显示,经过TCDD处理后的建鲤肝组织中抗氧化指标(SOD、GPx、CAT和T-AOC)出现显著的降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。饲料中添加甘草提取物后发现,0.5 g/kg和1.0 g/kg甘草提取物处理组效果最好,可以显著增加肝组织中SOD、CAT和T-AOC活性,GPx在1.0 g/kg甘草提取物处理组也显著升高,而0.1 g/kg甘草提取物处理组仅显著增加了SOD活性值。

n=10; *,**分别表示与TCDD组相比在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异有统计学意义。n=10; *,** indicate statistically significant difference from TCDD group-treated at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability levels, respectively.图4 甘草提取物对TCDD致建鲤肝损伤组织中SOD(A)、GPx(B)、CAT(C)和T-AOC(D)的影响Fig.4 Effects of GGE on liver SOD (A), GPx (B), CAT (C) and T-AOC (D) in TCDD-treated Jian carp
2.5 甘草提取物对建鲤肝组织中MDA质量摩尔浓度的影响
肝组织的损伤引起MDA的大量生成(P<0.01)(图5),与TCDD 组相比,0.5和1.0 g/kg甘草提取物有效地抑制了MDA的生成(P<0.01),对肝组织起到有效的保护作用。
2.6 病理组织学观察
在光学显微镜下观察发现,正常对照组肝细胞核和细胞质未见有异常变化(图6A,B),细胞质均匀、细胞界线清晰、细胞核清晰可见;TCDD 对照组肝组织结构明显遭到破坏,肝细胞体积明显增大,细胞界限变得不清楚,肝细胞核仁大部分消失,细胞呈蜂窝状,出现大小不等的空泡化(图6C);加入3种不同质量比的甘草提取物后,肝组织结构发生了不同变化,加入0.1 g/kg甘草提取物后,肝细胞病变未出现明显改变(图6D);0.5 g/kg的甘草提取物组

n=10;**表示与TCDD组相比在P<0.01水平差异有高度统计学意义。 n=10; ** indicate highly statistically significant difference from TCDD group-treated at the 0.01 probability level.图5 甘草提取物对TCDD 致建鲤肝组织中MDA质量摩尔浓度的影响Fig.5 Effects of GGE on liver MDA contents in TCDD-treated Jian carp

HE染色. A:正常组;B:药物对照组;C:TCDD对照组;D:0.1 g/kg甘草提取物处理组;E: 0.5 g/kg甘草提取物处理组;F:1.0 g/kg甘草提取物处理组. HE stain. A: Control group; B: GGE control group; C: TCDD control group; D: 0.1 g/kg GGE treatment group; E: 0.5 g/kg GGE treatment group; F: 1.0 g/kg GGE treatment group.图6 甘草提取物对建鲤肝组织损伤的影响Fig.6 Effects of GGE on liver injury induced by TCDD in Jian carp
肝细胞损伤程度变小,细胞数量增多,细胞空泡化减少,细胞轮廓逐渐清晰(图6E);质量比为1.0 g/kg的甘草提取物效果最好,损伤程度明显降低,细胞核位于细胞中心清晰可见 (图6F)。
3 讨论
当前研究表明,TCDD可以对肝组织产生损害作用,可以导致鱼类肝肿大且表面结节、脂肪肝、肝萎缩等[18]。关于TCDD的毒性机制研究,目前认为TCDD发挥毒性作用主要通过2种途径,一种是芳香烃受体/芳香烃受体核转运蛋白质途径,另一种是芳香烃受体/蛋白质磷酸化信号转导途径。当前研究热点主要集中在第一种途径,主要引起机体一系列氧化应激反应,从而改变酶的活性。能否成功制备TCDD诱导的肝损伤模型是本实验成功开展的关键所在。本研究根据前期造模实验结果确定以0.6 μg/kg的TCDD腹腔注射来制备肝损伤模型,实验结果显示0.6 μg/kg的TCDD可以造成ALT、AST等肝指标的变化,这说明造模实验是成功的,可以进行后续实验研究。
肝组织受损伤后,肝细胞内的ALT、AST、AKP、LDH溢出量显著增高,这4个指标是反映肝细胞受损的敏感指标[19]。在本实验中,TCDD引起建鲤肝组织损伤,导致4种酶活性显著升高,饲料中添加不同质量比的甘草提取物后发现,ALT、AST、AKP和LDH 4种酶的升高趋势被抑制,出现显著性降低。推测其具体保护作用可能与甘草提取物中甘草酸成分有关,能够保护正常肝细胞免受TCDD损害,对肝细胞有修复作用[20]。类似结果在小鼠和鱼上也有相关报道,如陈红艳等[21]研究发现甘草提取物对于四氯化碳诱导急性化学性肝损伤具有较好的保护作用。曹丽萍等[16]报道甘草提取物对t-BHP引起建鲤原代肝细胞损伤具有良好保护作用。
肝在蛋白质代谢过程中起着重要作用,血浆内主要的蛋白质几乎全部由肝制造,肝合成的蛋白质主要为白蛋白(Alb)。血清中总蛋白(TP)和白蛋白(Alb)是反映肝中蛋白质丢失情况的重要指标,当肝受到外界物质损害时,就会造成肝合成蛋白质出现紊乱,使得白蛋白合成变少[22-23]。在本实验中,TCDD 诱导肝组织损伤后,导致了血清中TP和Alb质量浓度的降低,但饲料中加入甘草提取物可以明显升高其质量浓度,说明甘草提取物可以降低TCDD对肝造成的损害,促进肝恢复合成蛋白质功能。
SOD、GPx、CAT和T-AOC是机体内重要的抗氧化酶指标[24],SOD的主要功能是对抗氧自由基,将氧自由基歧化,防止催化产生的H2O2与O2-结合形成危害更大的羟基自由基。过氧化氢酶(CAT)是生物体内的一种末端氧化酶,主要功能是催化H2O2,防止其含量过高,对机体造成损伤[25]。谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GPx)的功能较多,不仅可以清除过氧化氢还可以清除脂质过氧化物产物。总抗氧化能力T-AOC的测定很重要,它可直接反映体内抗氧化酶的活力高低,其强弱与生物体健康程度存在密切关系。在本实验中,图4数据显示,TCDD使建鲤肝组织显著的损伤,引起SOD、GPx、CAT和T-AOC活性的降低,而用甘草提取物饲喂后的建鲤4种酶指标被有效地提高,表明甘草提取物能增强建鲤抗氧化能力,抵抗TCDD造成的肝组织损伤。已有研究报道甘草提取物中总多酚与黄酮类含量与机体抗氧化能力密切相关[26],因此可以推断甘草中多酚和黄酮类物质可能是抵抗肝组织氧化损伤的主要因素。
当机体受到自由基攻击后就会出现脂质过氧化反应,MDA就是其中一个判定指标,其质量摩尔浓度高低反映了机体受损伤程度[27]。TCDD作为一种肝毒物可以引起脂质过氧化,使得MDA质量摩尔浓度升高,边芳等[28]研究结果显示,甘草提取物可以显著降低MDA质量摩尔浓度,通过抑制自由基和脂质过氧化物的产生。在本实验中,MDA在质量比为0.5和1.0 g/kg甘草提取物中被显著地抑制。这种抑制作用可能和甘草提取物增强自由基清除能力有关[29]。
4 结论
综合以上结果发现,甘草提取物对于建鲤肝组织的保护呈剂量效应关系,以质量比为1.0 g/kg甘草提取物保肝效果最好,可以很好地清除氧自由基、羟自由基,具有良好的抗氧化能力,可以明显抵抗TCDD造成的肝组织损伤。本实验的顺利开展为以后防治TCDD诱导的肝组织损伤奠定了基础。
[1] 刘燕群,周宜开,吕斌,等.二英的毒性与生物学检测研究进展.环境与职业医学,2004,21(5):417-421. Liu Y Q, Zhou Y K, Lü B,etal. Toxicity and bioassay of dioxins in environment.JournalofEnvironment&OccupationalMedicine, 2004,21(5):417-421.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] Fletcher C L, Mckay W A. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDD) and dibenzofurans (PCDF) in the aquatic environment: A literature review.Chemosphere,1993,26(6):1041-1069.
[3] 黄汝广,李莎,李毓阳,等.二英污染及其防控措施的研究进展.安徽农业科学,2007,35(30):9670-9671,9698. Huang G R, Li S, Li S Y,etal. Research advances in the dioxin pollution and its control measure.JournalofAnhuiAgriculturalSciences, 2007,35(30):9670-9671,9698. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 丁园,史蓉蓉,刘燕红,等.城市垃圾焚烧过程中二英的产生与防治.江西化工,2008(1):66-70. Ding Y, Shi R R, Liu Y H,etal. The production of dioxins in incineration of municipal refuses and their control.JiangxiChemicalIndustry, 2008(1):66-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Wu Y D, Jiang L, Zhou Z,etal. CYP1A/regucalcin gene expression and edema formation in zebrafish embryos exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.BulletinofEnvironmentalContaminationandToxicology,2008,80(6):482-486.
[7] King Heiden T C, Spitsbergen J, Heideman W,etal. Persistent adverse effects on health and reproduction caused by exposure of zebrafish to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin during early development and gonad differentiation.ToxicologicalSciences, 2009,109(1):75-87.
[8] 宋士波,惠阳,徐旭东,等.14C标记1,2,7,8-TCDD在鲤体内分布及代谢的初步研究.水生生物学报,2005,29(4):439-443. Song S B, Hui Y, Xu X D,etal。Preliminary studies on metabolism and distribution of14C labeled 1,2,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in common carp.ActaHydrobiologicaSinica, 2005,29(4):439-443. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] Arnold H, Pluta H J, Braunbeck T. Sublethal effects of prolonged exposure to disulfoton in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchusmykiss): Cytological alterations in the liver by a potent acetylcholine esterase inhibitor.EcotoxicologyandEnvironmentalSafety, 1996,34(1):43-55.
[10] Turkez H, Geyikoglu F, Yousef M I. Beneficial effect of astaxanthin on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced liver injury in rats.ToxicologyandIndustrialHealth, 2013,29(7):591-599.
[11] Turkez H, Geyikoglu F, Yousef M I. Modulatory effect ofL-glutamine on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin -induced liver injury in rats.ToxicologyandIndustrialHealth,2012,28(7):663-672.
[12] Turkez H, Geyikoglu F. The effect of laurel leaf extract against toxicity induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in cultured rat hepatocytes.ArchivesofIndustrialHygieneandToxicology, 2011,62(4):309-315.
[13] Turkez H, Geyikoglu F, Mokhtar Y I,etal. Eicosapentaenoic acid protects against 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced hepatic toxicity in cultured rat hepatocytes.Cytotechnology, 2012,64(1):15-25.
[14] 刘燕群,谭佑铭,沈红兵,等.茶多酚对二英所致肝损的作用及机理研究.现代预防医学,2008,35(7):1232-1233. Liu Y Q, Tan Y M, Shen H B,etal. Effects of tea polyphenols on liver damage caused by TCDD and its possible mechanism.ModernPreventiveMedicine, 2008,35(7):1232-1233. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 郭雷,李慧,王振华,等.甘草提取物、石见穿提取物、紫参汤对四氯化碳致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用的比较.石河子大学学报:自然科学版,2010,28(6):727-730. Guo L, Li H, Wang Z H,etal. Comparison of hepatoprotective effect ofGlycyrrhiza,SalviachinensisBenth, Zishentang on acute hepatic injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice.JournalofShiheziUniversity:NaturalScience, 2010,28(6):727-730. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 曹丽萍,贾睿,杜金梁,等.甘草提取物对叔丁基氢过氧化物(t-BHP)诱导的建鲤原代培养肝细胞损伤的保护作用.农业生物技术学报,2012,20(10):1192-1200. Cao L P, Jia R, Du J L,etal. Protective effect ofGlycyrrhizaglabraextract againsttert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced hepatotoxicity in primary cultured hepatocytes of Jian carp (Cyprinuscarpiovar. Jian).JournalofAgriculturalBiotechnology, 2012,20(10):1192-1200. (in English with Chinese abstract)
[17] 高雪岩,郑巧云,孙建宁,等.甘草总皂苷的制备及其保肝作用的研究.中药药理与临床,2011,27(2):78-81. Gao X Y, Zheng Q Y, Sun J N,etal. Preparation of total licorice saponin and research on its hepatoprotective effect.PharmacologyandClinicsofChineseMateriaMedica, 2011,27(2):78-81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 董丽,汤乃军.四氯并二英的肝脏毒性.中华劳动卫生职业病杂志,2005,23(1):60-62. Dong L, Tang N J. Liver toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.ChineseJournalofIndustrialHygieneandOccupationalDiseases, 2005,23(1):60-62. (in Chinese)
[19] Visen P K S, Saraswat, B, Dhawan, B N. Curative effect of picroliv on primary cultured rat hepatocytes against different hepatotoxins: Aninvitrostudy.JournalofPharmacologicalandToxicologicalMethods, 1998,40:173-179.
[20] van Rossum T G J, Vulto A G, de Man R A,etal. Glycyrrhizin as a potential treatment for chronic hepatitis C.AlimentaryPharmacologyandTherapeutics,1998,12(3):199-205.
[21] 陈红艳,严莉,王建华,等.甘草提取物对小鼠四氯化碳急性肝损伤的影响.中国中医药信息杂志,2009,16(7):24-25. Chen H Y, Yan L, Wang J H,etal. Protective effect of extraction ofGlycyrrhizauralensisFisch. on CCl4induced acute hepatic injury in mice.ChineseJournalofInformationonTraditionalChineseMedicine, 2009,16(7):24-25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] Kim S H, Cheon H J, Yun N,etal. Protective effect of a mixture ofAloeveraandSilybummarianumagainst carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatotoxicity and liver fibrosis.JournalofPharmacologicalSciences, 2009,109(1):119-127.
[23] 张淑艳,熊惠顺.肝病患者血清前白蛋白和白蛋白的检测及临床意义.临床军医杂志,2010,38(2):279-280. Zhang S Y, Xiong H S. Serum prealbumin and album in tests in patients with liver diseases and their clinical significance.ClinicalJournalofMedicalOfficers, 2010,38(2): 279-280. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] Moron M S, Depierre J W, Mannervik B. Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathioneS-transferase activities in rat lung and liver.BiochimicaetBiophysicaActa-GeneralSubjects, 1979,582:67-78.
[25] Ozden S, Catalgol B, Gezginci-Oktayoglu S,etal. Methiocarb-induced oxidative damage following subacute exposure and the protective effects of vitamin E and taurine in rats.FoodandChemicalToxicology, 2009,47(7):1676-1684.
[26] 张改平,朱华泽,杨建雄.甘草提取物的体外抗氧化活性.生物加工过程,2010,8(3):53-57. Zhang G P, Zhu H Z, Yang J X. Antioxidant activity of licorice extractsinvitro.ChineseJournalofBioprocessEngineering, 2010,8(3):53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] Hu Y Y, Liu C H, Wang R P,etal. Protective actions of salvianolic acid A on hepatocyte injured by peroxidationinvitro.WorldJournalGastroenterology, 2000,6:402-404.
[28] 边芳,杨桂兰,杜华,等.传统中药提取物对小鼠光老化皮肤中SOD活力与MDA含量的影响.西北国防医学杂志,2011,32(5):324-326. Bian F, Yang G L, Du H,etal. Effect of extracts from four Chinese traditional medicines on SOD and MDA in photoaging BALB/c mice skin.MedicalJournalofNationalDefendingForcesinNorthwestChina, 2011,32(5):324-326. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 吴碧华,龙存国,王晓明,等.甘草总黄酮清除羟自由基作用的体外实验探讨.川北医学院学报,2001,16(1):3-5. Wu B H, Long C G, Wang X M,etal. The scavenging effect of flavoniods of glycyrrhiza on hydroxyl radical studiedinvitro.JournalofNorthSichuanMedicalCollege, 2001,16(1):3-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects ofGlycyrrhizaglabraextracts against TCDD-induced hepatocyte damage in Jian carp (Cyprinuscarpiovar. Jian).
Du Jinliang1,2, Cao Liping1,2, Jia Rui3, Liu Yingjuan3, Shen Yujin3, Yin Guojun1,2,3*
(1.KeyLaboratoryofFreshwaterFisheriesandGermplasmResourcesUtilization,MinistryofAgriculture,FreshwaterFisheriesResearchCenter,ChineseAcademyofFisherySciences,Wuxi214081,Jiangsu,China; 2.InternationalJointResearchLaboratoryforFishImmunopharmacology,FreshwaterFisheriesResearchCenter,ChineseAcademyofFisherySciences,Wuxi214081,Jiangsu,China; 3.WuxiFisheriesCollege,NanjingAgriculturalUniversity,Wuxi214081,Jiangsu,China)
In recent years, the mechanism of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) toxicity has been a focal point in research. Generally it enriched in adipose tissue, and gradually amplified through food chains. It is seriously interfered with the normal function of the endocrine system of the organism, and displayed a wide spectrum of toxic effects, including dermal toxicity, reproductive toxicity, immunotoxicity and hepatotoxicity. The current research about the toxic mechanism of TCDD was mainly focused on the oxidative stress reaction, which was considered to be playing an important role in TCDD toxic research. Normally, the production and elimination of activated oxygen through the antioxidant system was in a balanceable and dynamic state. The antioxidant system could prevent excessive reactive oxygen species causing oxidative stress, keep the body balance, maintain the normal structure and function of cells. TCDD combined with aromatic hydrocarbon receptor and entered the nucleus, which changed the mRNA transcription of target gene, caused adverse change in the activity of enzymes and proteins, produced a series of oxidative stress reaction. Chinese medicinal herbs had been widely used in animal disease prevention due to their characteristics of rich bioactive components, free pollution, low side effects and immune enhancement. Many studies had reported that natural antioxidants were efficacious in preventing oxidative stress-related liver pathologies due to particular interactions and synergisms.Glycyrrhizaglabraextracts (GGE) was one of the common traditional Chinese herbal medicine, it could adjust the immunity, and had anti-tumor, anti-virus, antioxidant effects and so on. Although numerous studies had reported its beneficial effects on mammals, there was a lack of reports on its function in aquatic animals.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of GGE on the TCDD-induced liver injury in Jian carp (Cyprinuscarpiovar. Jian).
Jian carp were fed with diet containing 3 doses of GGE (0.1, 0.5 and 1.0 g/kg diet) for 60 days before a single intraperitoneal injection of TCDD (0.6 μg/kg), 72 h after TCDD injection, blood and liver samples were taken for biochemical analysis.
The results showed that GGE at 1.0 g/kg diet for 60 days prior to TCDD intoxication significantly reduced the elevated activities of ALT, AST, LDH, AKP and increased the reduced levels of total protein (TP), albumin (Alb) in the serum, markedly inhibited the reduction of the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase (CAT), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and reduced the malondialdehyde (MDA) formation in liver tissue. Meanwhile, histopathological observation also showed that GGE can significantly relieve TCDD induced liver injury.
It is concluded that GGE exhibited protective effect against TCDD-induced hepatotoxicity in fish, which is likely related to its antioxidant activity, and it is suggested that GGE may potentially be used as a hepatoprotective agent for fish liver injury.
Glycyrrhizaglabraextracts; 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; liver injury;Cyprinuscarpiovar. Jian
Journal of Zhejiang University (Agric. & Life Sci.), 2015,41(5):593-601
国家自然基金青年科学基金(31202002;31200918);中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费专项资金 (2013JBFM12);中国水产科学研究中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费专项资金项目(2014A08YQ01)。
联系方式:杜金梁(http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4924-3527),E-mail:dujl@ffrc.cn
2015-03-06;接受日期(Accepted):2015-06-24;网络出版日期(Published online):2015-09-18
X 503.225
A
*通信作者(Corresponding author):殷国俊(http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6261-7506),Tel:+86-510-85558876;E-mail:yingj@ffrc.cn
URL:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1247.s.20150918.1804.020.html
