西秦岭阳山金矿带安坝矿床热液蚀变作用*
2015-03-15张志超李楠戢兴忠韩忠郭耀宇李在春
张志超 李楠 戢兴忠 韩忠 郭耀宇 李在春
ZHANG ZhiChao1,LI Nan1,JI XingZhong1,HAN Zhong2,GUO YaoYu1 and LI ZaiChun1
1. 中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室,北京 100083
2. 中国人民武装警察部队黄金第三总队,成都 610000
1. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources,China University of Geosciences,Beijing 100083,China
2. No.3 Gold Geological General Party of Chinese Armed Police Force,Chengdu 610036,China
2015-02-10 收稿,2015-06-04 改回.
1 引言
在热液蚀变作用过程中,流体与围岩进行化学成分的置换导致矿物种类的变化(Putnis,2002)。其中主量元素的变化可以体现出岩石矿物组合的变化,微量元素的变化则可以反映热液交代过程中的微观作用(Whitbread and Moore,2004)。因此,蚀变岩石的元素含量异常值可用于识别肉眼通常无法观察到的矿物成分的变化,并用于进一步分析热液蚀变机制、以及厘定蚀变与矿化的关系(Christie and Brathwaite,2003;Chinnasamy and Mishra,2013)。目前,许多学者运用岩石地球化学手段厘定热液矿床蚀变过程中矿物组合特征,研究热液蚀变强度和元素迁移规律,以揭示各种蚀变过程与成矿作用的关系(Klemm and Kräutner,2000;Craw,2002;Dugdale et al.,2006;Putnis,2009;袁峰等,2012;王翠云等,2012;张炳林等,2014)。
西秦岭造山带位于扬子与华北板块之间,记录了大规模的构造-岩浆活动和成矿事件,是理解构造演化和复合造山过程中成矿作用的理想选区(邓军等,2010,2011,2013;Deng et al.,2013b,2014b,c;邱昆峰等,2014;Yang et al.,2015d,e,f)。阳山金矿带位于西秦岭造山带南缘,从西到东主要有泥山、葛条湾、安坝、高楼山、观音坝和张家山6 个金矿床,目前已发现含金矿脉100 余条,金总资源量超过300t(图1b)。金矿带内各矿床发育的蚀变类型主要有硅化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化和粘土化等。金储量最大的安坝金矿床(阎凤增等,2010),蚀变非常发育,是该金矿带内研究热液蚀变在成矿过程中作用的理想选区。李楠(2013)对阳山金矿带热液蚀变特征进行了研究,在系统地总结其野外地质特征的基础上,运用质量平衡的方法对矿区千枚岩中三种不同蚀变过程中元素迁入和迁出情况进行了分析,认为硅化与成矿的关系最为密切,碳酸盐化和粘土化与成矿关系不大。前人研究未考虑断裂带和岩浆岩对蚀变空间分带的影响,也未厘清蚀变在成矿过程中的作用。
Yang and Badal(2013)、Yang et al. (2014b,2015c,2016a)和杨立强等(2014a,2015a)通过对成矿系统的研究,强调构造-流体耦合成矿作用机制在成矿系统中的重要性,并认为多期次复合造山作用、构造体制转换与金成矿密切相关(杨立强等,2003,2010,2011a,b;邱昆峰和杨立强,2011;邓军等,2012;Wang et al.,2014;Deng et al.,2014a;Yang et al.,2016a)。流体在金成矿过程中起到非常重要的作用(邓军等,2001;Yang et al.,2008,2009),尤其在热液矿床中,流体与金的成矿和热液蚀变作用关系密切(邱昆峰等,2015;熊伊曲等,2015),然而,热液蚀变作用尚缺乏系统的研究,这在一定程度上制约了安坝金矿床的成因研究的深入和进一步找矿勘探的工作部署。本文通过野外及手标本观察,了解不同蚀变的野外特征,并结合野外断裂带及岩浆岩的出露情况,分析蚀变的空间分布规律;通过显微镜下的详细观察,理清了不同蚀变的矿物组合特征,并分析了不同蚀变矿物形成的先后顺序;通过元素地球化学的方法和质量平衡的计算,讨论元素的迁移规律,理清了蚀变与金矿化的关系。
2 地质背景
西秦岭阳山金矿带位于西秦岭勉略断裂带内的文县弧形构造带(杜子图和吴淦国,1998;阎凤增等,2010),它由一系列近东西向的逆冲断裂构造(松柏-梨坪断裂、马家磨-魏家坝断裂和白马-临江断裂)及其相关褶皱构成(图1a)。
阳山金矿带地层主要有中晚元古界碧口群、上古生界的泥盆系、石炭系、二叠系和中生界的三叠系及侏罗系,新生界主要为第四系黄土和陆相冲积物。泥盆系是安坝金矿床的主要赋矿地层,出露的岩性为钙泥质千枚岩、炭质千枚岩、灰岩和砂岩。
阳山金矿带内岩浆岩的岩性主要为斜长花岗斑岩脉,且普遍发育硅化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、硫化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化和粘土化蚀变。岩浆岩在矿区范围内走向NEE 向,分布广泛且零散,多沿区域性断裂分布,与区域构造线平行,明显受区域构造控制(Yang et al.,2015b;王宏伟,2012;华北,2013)。锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 测年结果显示阳山金矿带岩浆岩侵位于晚三叠世(215Ma)(Yang et al.,2015b)。
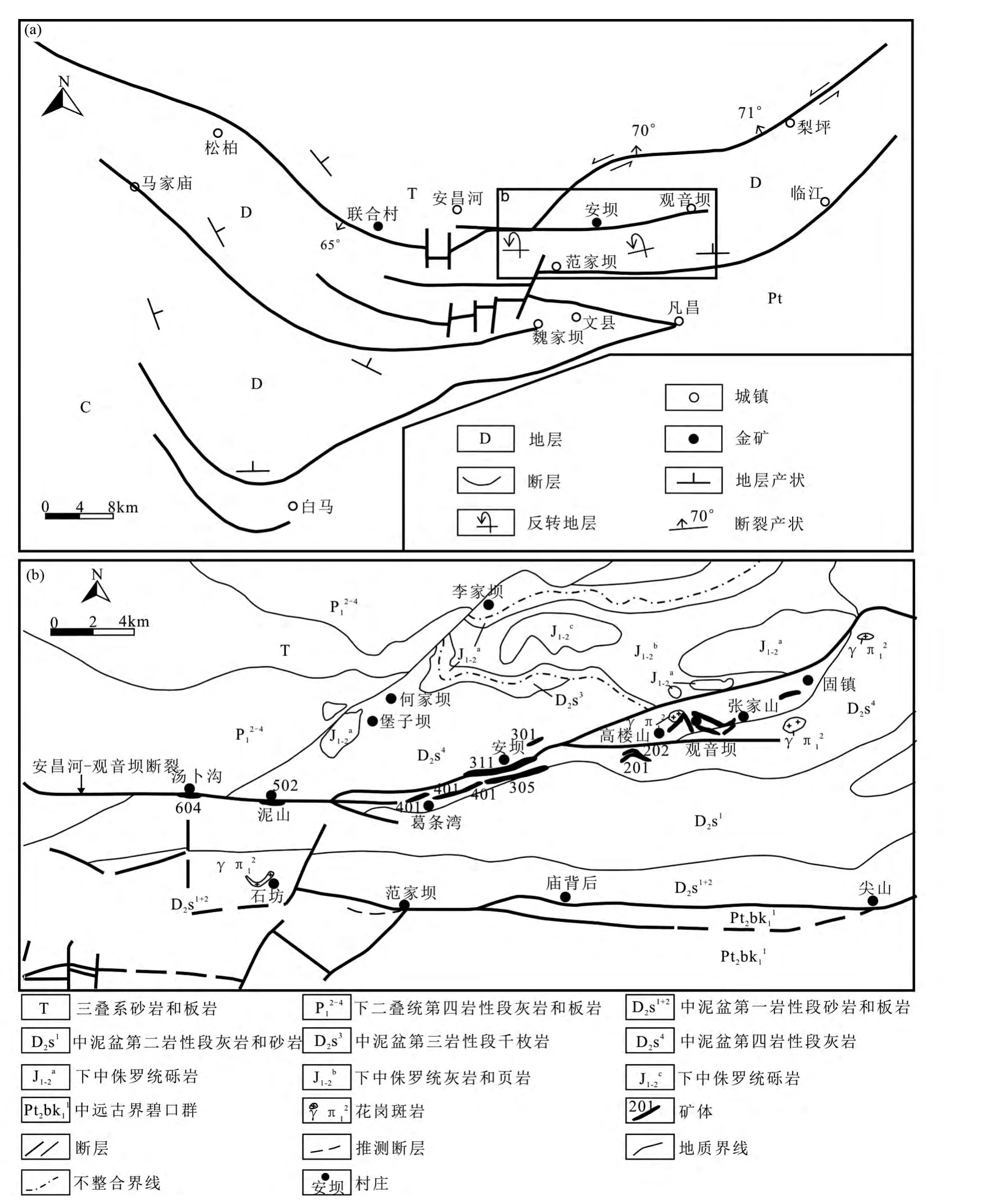
图1 文县弧形构造(a,据杜子图,1997)和阳山金矿带地质图(b,据赵成海,2009 修改)Fig.1 Geological sketch map of the Wenxian arc structure (a,after Du,1997)and the Yangshan gold belt (b,modified after Zhao,2009)
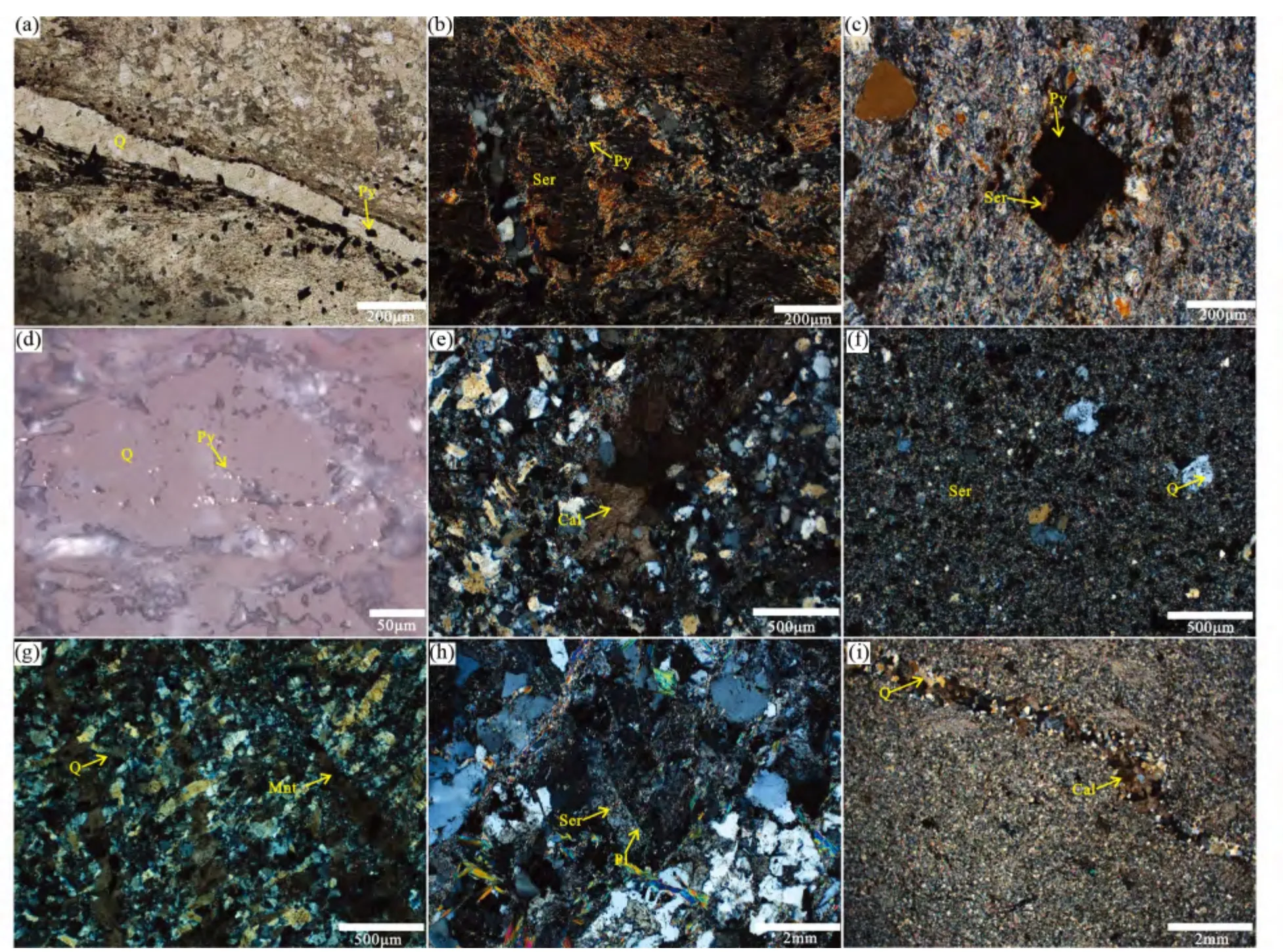
图2 安坝金矿床不同类型热液蚀变显微镜下照片(a)石英脉中有黄铁矿发育(-);(b)千枚岩发育绢云母化和黄铁矿化(+);(c)绢云母被黄铁矿包裹(+);(d)石英颗粒内发育黄铁矿颗粒;(e)方解石呈颗粒状分布于岩石中(+);(f)斜长花岗斑岩中鳞片状绢云母和粒状石英(+);(g)蒙脱石脉切穿石英颗粒(+);(h)斜长石蚀变为绢云母(+);(i)石英-方解石脉(+). Py-黄铁矿;Q-石英;Ser-绢云母;Mnt-蒙脱石;Cal-方解石;Pl-斜长石;Asp-毒砂Fig.2 Micrographs of the different altered rock samples from the Anba gold deposit(a)pyrite in the quartz vein (-);(b)sericitization and pyrite develop in the phyllite (+);(c)pyrite includes sericite (+);(d)quartz grain includes pyrite grain;(e)the calcite grains in the rock (+);(f)scaly sericite and granular quartz in the plagioclase granite porphyry (+);(g)montmorillonite vein cuts across silica grains (+);(h)plagioclase was altered to sericite (+);(i)quartz-calcite vein (+). Py-pyrite;Q-quartz;Ser-sericite;Mnt-montmorillonite;Cal-calcite;Pl-plagioclase;Asp-arsenopyrite
阳山金矿带的控矿构造为安昌河-观音坝断裂带,该断裂带是由多条次级断裂分支复合而成的。这些次级断裂发育于矿区内的葛条湾-草坪梁复背斜两翼中,矿体就产在复背斜两翼的次级层间断裂中。
安坝金矿床位于阳山金矿带中部,为矿带主要矿化集中区。矿床东至草坪梁,西至三角地,共发现31 条矿脉,矿脉长200 ~2200m,厚0.75 ~7.42m,延深>1000m,品位1.15 ~6.55g/t。矿脉由南向北分为305#、306#和311#3 个脉群。由314#、305#、360#和311#4 条主矿脉组成,呈NE-NEE 向平行展布,累计探获(332 +333 +334)资源量281454kg,占金总资源量的91.36%(阎凤增等,2010)。安坝金矿床的矿石为原生矿石,其Au 含量与原生矿石中硫化物含量有密切关系。金矿床围岩岩性有砂岩、灰岩、千枚岩和斜长花岗斑岩,矿石以蚀变千枚岩和蚀变斜长花岗斑岩矿石为主。矿石一般均较为松散破碎。矿石结构主要有自形粒状结构、他形粒状结构、环带及环边结构、放射状结构、包含结构、交代残余结构、草莓状结构、压碎结构等。矿石构造主要有稀疏浸染状,稠密浸染状,脉状和团块状构造等。
3 蚀变岩相学特征

图3 安坝金矿床4 号硐CM19 剖面不同蚀变矿物的体积百分含量变化Fig.3 Volume percentage change of different altered minerals in the CM19 profile of the 4th adit in the Anba deposit
安坝金矿床的地层和岩浆岩普遍发育多种蚀变作用(图2),各种蚀变在空间上没有明显的分带性,通过系统的观察总结后发现蚀变与断裂、岩浆岩在空间分布上具有一定关系(图3)。硅化在矿区内普遍发育,尤其在断裂附近发育程度较强;绢云母化在斜长花岗斑岩及其附近的千枚岩中发育程度较强;粘土化发育于断裂带附近;绿泥石化-绿帘石化主要发育于斜长花岗斑岩和砂岩中;碳酸盐化主要呈面状发育于斜长花岗斑岩中,或在千枚岩和斜长花岗斑岩中以脉状产出,并与石英矿物伴生。各种蚀变类型的特征如下:
硅化是发育最为广泛的蚀变,见于不同岩性的岩石中。硅化在空间上未见到明显的分带,但一般靠近断裂带的地方发育程度强,主要形成于成矿前、成矿期和成矿后。硅化表现为脉状和面状硅化。脉状硅化以石英脉的形式出现,石英脉宽几厘米到十几厘米,脉体主要为中粗粒石英,呈乳白色,有时含少量金属硫化物(图2a),主要为成矿期和成矿后的产物。面状硅化表现为斜长花岗斑岩或地层(千枚岩、灰岩)中的石英呈极细粒的他形粒状。蚀变斜长花岗斑岩中的石英通常呈他形粒状与绢云母伴生,多以基质的形式出现,反映了较为快速的结晶过程(图2f)。
绢云母化主要发育在斜长花岗斑岩及其附近的千枚岩中,主要形成于成矿前和成矿期。斜长花岗斑岩中的斜长石蚀变形成鳞片状的绢云母和细粒石英(图2f)。此外,千枚岩中的绢云母一般为鳞片状,顺千枚理定向排列,有些绢云母与黄铁矿和毒砂共生(图2b),可见其为成矿期的产物;此外,还有部分绢云母被黄铁矿包裹(图2c),该绢云母为成矿前的产物。
绿泥石-绿帘石化仅见于斜长花岗斑岩脉和部分砂岩中,且两种蚀变经常共生。常呈鳞片浸染状、粒状集合体或微细脉产出。
碳酸盐化主要为成矿晚阶段和成矿后的产物。一般有两种表现形式,一种是面状的碳酸盐化,其中方解石矿物均匀地分布在岩石中(图2e);另一种呈方解石-石英脉产出。后一种形式的碳酸盐化出现在成矿后,切穿了早期的矿化(图2i)。
粘土化主要表现为高岭土化和蒙脱石化,常见于断裂带附近,主要形成于成矿后。粘土化蚀变有两种形式,一种是粘土矿物以微细浸染状存在于矿物表面,另一种是粘土矿物呈脉状切穿石英脉(图2g)。
通过对西秦岭安坝金矿床蚀变矿物和金属矿物的观察,并结合李楠等(2012)、李楠(2013)和Li et al. (2014)对阳山金矿带的成矿期次和阶段的划分,对西秦岭安坝金矿床的蚀变矿物和金属矿物生成顺序进行了重新划分(表1)。
4 样品采集及分析方法
样品主要采自阳山金矿带安坝金矿床4 号平硐,共19件岩矿石样品(图3)。其中16 件采自平硐CM19 巷道的千枚岩,3 件采自CM19 巷道的斜长花岗斑岩。从千枚岩中选取了2 件新鲜的样品作为原岩,2 件硅化样品,以及3 件绢云母化样品。在平硐内对距离断裂带不同远近、不同岩性及不同蚀变类型的样品均进行了系统的采集。
全岩粉末样处理工作在河北廊坊市地源矿物测试分选技术服务有限公司进行。首先选取一小块岩石磨制探针片后,剩余岩石样粉碎至200 目,用于主微量元素分析测试。
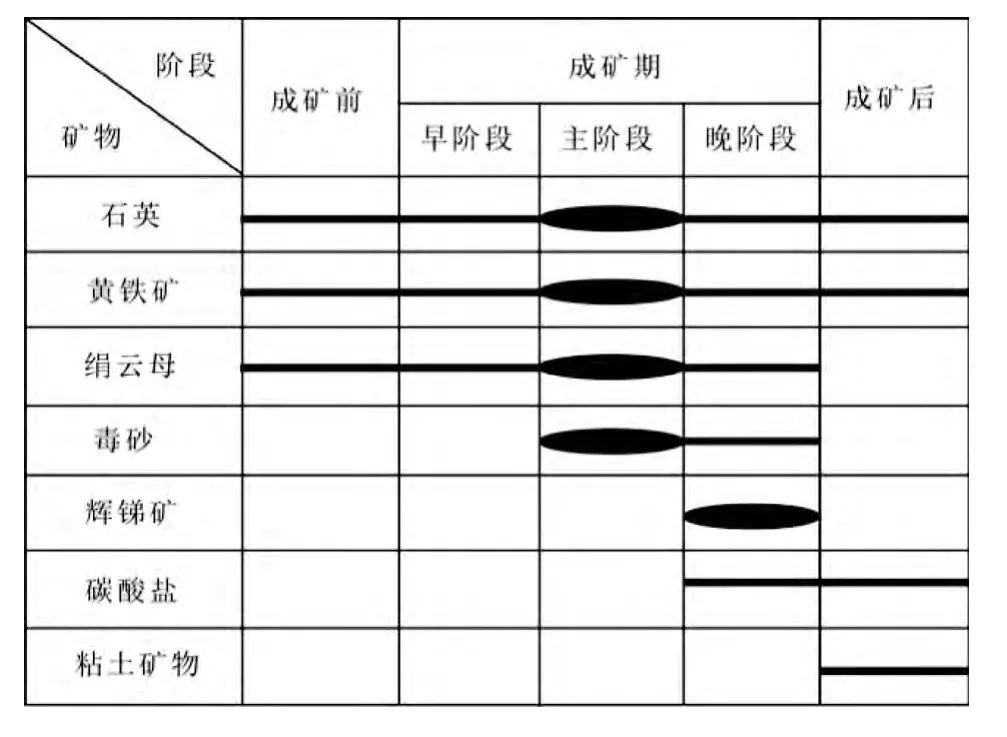
表1 安坝金矿床热液矿物成顺序与成矿期次划分Table 1 The paragenetic sequences of hydrothermal minerals in the Anba deposit
主量和微量元素分析工作在中国核工业集团核工业北京地质研究所完成。其中,主量元素采用X 射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)完成,稀土元素及微量元素采用等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测试完成。主元素的分析精度优于1%,微量元素分析精度优于5%。其主微量、稀土元素分析结果如表2。
5 元素质量迁移及活动性
质量平衡方法主要研究各种地质体系中组分迁移和质量变化,Gresens(1967)率先以实际岩石化学分析研究岩石质量平衡,并导出了著名的Gresens 方程;Grant(1986)对该方程进行了有效的简化,得到“等浓度方程”;Brimhall et al.(1988)和Brimhall and Dietrich(1987)等从简单直观的质量平衡出发,导出了以不活动元素为参考物种的质量变化和体积变化表达式。邓海琳等(1999)对前人关于质量平衡法的主要研究成果进行分析比较,指出前人研究中存在的问题和不足,并提出了相应的改进方法,推导出新的质量平衡方程。上述各种方法提出后被广泛地应用于相关的研究中,对人们深入理解各种地质作用过程中岩石体系元素活动及质量迁移起到了至关重要的作用。
在热液蚀变过程中,常量元素Al 和Ti 通常被认为是不活动的(Ague,1991;Condie and Sinha,1996;Klammer,1997),但Al 在变形变质作用过程中仍有一定的活动性(Ague,1991,1997;唐红峰等,2000),尤其是长石绢云母化过程中有部分析出(O’Hara,1988;O’Hara and Blavkburn,1989),硅化、绢云母化蚀变的发育导致Al 并不适合作为不活动组分来研究安坝金矿床热液蚀变过程元素迁移情况。Ti 在岩石中活动性最小,在流体渗滤过程中是相对稳定的,在岩石变形变质过程中的活动性相当有限,是一个理想的参照元素(Ague,1991,1997;O’Hara,1988;郭顺等,2013;刘德良等,1996;钟增球和游振东,1995;张可清和杨勇,2002)。通过以上分析,本文选定TiO2作为不活动组分。通过ΔCi=CiA/k-Cio(Cio、CiA为原岩、蚀变岩中第i 种元素的含量;k =Mo/MA=CA/Co,Co、CA为原岩和蚀变岩中不活动元素的质量;Mo、MA分别为原岩和蚀变岩的质量)计算安坝金矿床蚀变过程中主量元素和部分微量元素的得失变化(表3、图4)。由于碳酸盐化、粘土化和绿泥石-绿帘石化样品中蚀变叠加严重,没有只发育其中一种蚀变的样品,因此只对与成矿有关的硅化和绢云母蚀变进行了质量平衡计算。
从表3 和图4 中可知,在硅化蚀变过程中,明显带入的组分有SiO2、Fe2O3、FeO、MgO、CaO、C、S、Au、As、Hg、Pb、Zn;Rb 和Ba 元素被明显带出。在绢云母化蚀变过程中明显带入的组分为SiO2、Fe2O3、CaO、C、S、Au、As、Hg、Pb、Zn、Rb 和Ba;带出组分为Na2O。
6 讨论
6.1 元素迁移规律
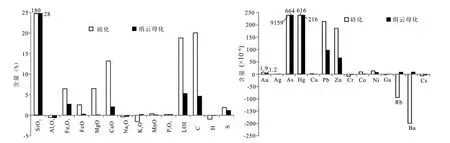
图4 安坝金矿床不同蚀变过程中的元素得失图Fig.4 Gain-loss diagram for elements in the different alteration processes in the Anba deposit

表3 安坝金矿床蚀变过程中主微量元素平均得失量Table 3 Average gain or loss contents of major and trace elements during alteration processes of the Anba gold deposit
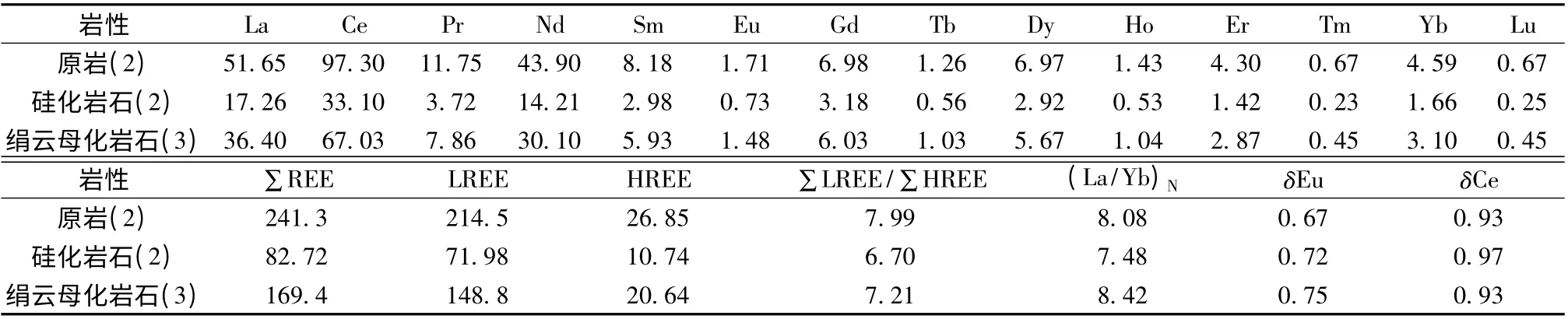
表4 安坝金矿床不同类型蚀变岩石稀土元素分析数据(×10 -6)及部分计算参数值Table 4 The date analysis (×10 -6)and related calculated parameters of rare earth elements of altered rocks in the Anba gold deposit
研究区内可见硅化石英、绢云母和黄铁矿共生,表明研究区普遍发育含硫量较高的酸性含矿流体(Parsapoor et al.,2009),此外,矿区内硅质岩发育,说明含矿流体中Si 的含量很高(戢兴忠等,2014)。这些酸性的流体淋滤原岩时产生硅化(Stoffregen,1987)。硅化蚀变与矿化关系密切,随着SiO2的带入,中低温成矿元素(Au、As、Hg、Pb 和Zn)也被带入到系统中,成矿元素组成配合物与硅元素组成的配合物具有相似的稳定性,它们在热液中一同运移、析出(孟良义,1998)。蚀变过程中有C 元素的带入,说明了含矿流体中含有CO2,该结果与李晶等(2007)通过对石英脉中流体包裹体的研究结果一致。Fe2O3、FeO 和S 的带入,与矿区内黄铁矿化有关。此外,含矿流体从围岩带走了大量的Rb、Ba 元素,这是由于Rb、Ba 的不相容性及其在含矿流体中的高迁移性所致(Helba et al.,2001)。
绢云母化蚀变过程中发生反应为:
3NaAlSi3O8(斜长石)+ 2H++ K+= KAl2[AlSi3O10](OH)2(绢云母)+6SiO2+3Na+
在该过程中,K+可能来自于外界流体,也可能来自于钾长石的蚀变所释放出的K+,反应后表现为K+的带入和Na+的带出。在斜长石蚀变为绢云母(图2h)过程中,斜长石是很重要的Eu 来源,但此时的流体环境造成了一小部分的Eu进入云母中,大部分的Eu 则被流体带走,而Eu 与Ca2+是替代关系(Budzinski and Tischendorf,1989),由此造成了CaO的带入。虽然从上述反应中可以看出有SiO2的形成,但并未被流体带走,而是与围岩反应形成含硅矿物或是以石英脉的形式产出于千枚岩中,导致SiO2的富集,在绢母化蚀变的过程中,一定会伴随着轻微硅化蚀变过程的发生。绢云母化蚀变与矿化关系密切。随着蚀变过程的进行,中低温成矿元素(Au、As、Hg、Pb 和Zn)也带入到系统中。蚀变过程中有C元素的带入,说明了含矿流体中含有CO2。Rb 主要赋存于含K 的矿物中,在千枚岩中含K 的矿物主要为绢云母,因此,在绢云母化蚀变的过程中有Rb 的明显带入(凌其聪和刘从强,2002)。此外,在绢云母化蚀变过程中有Ba 的大量带入,李裕能(1986)对阳山金矿带内的重晶石进行了研究,Ba的大量带入与本区出现的重晶石有关(凌其聪和刘从强,2002)。Fe2O3和S 的带入,与矿区内黄铁矿化和毒砂化有关(卢焕章等,2013)。
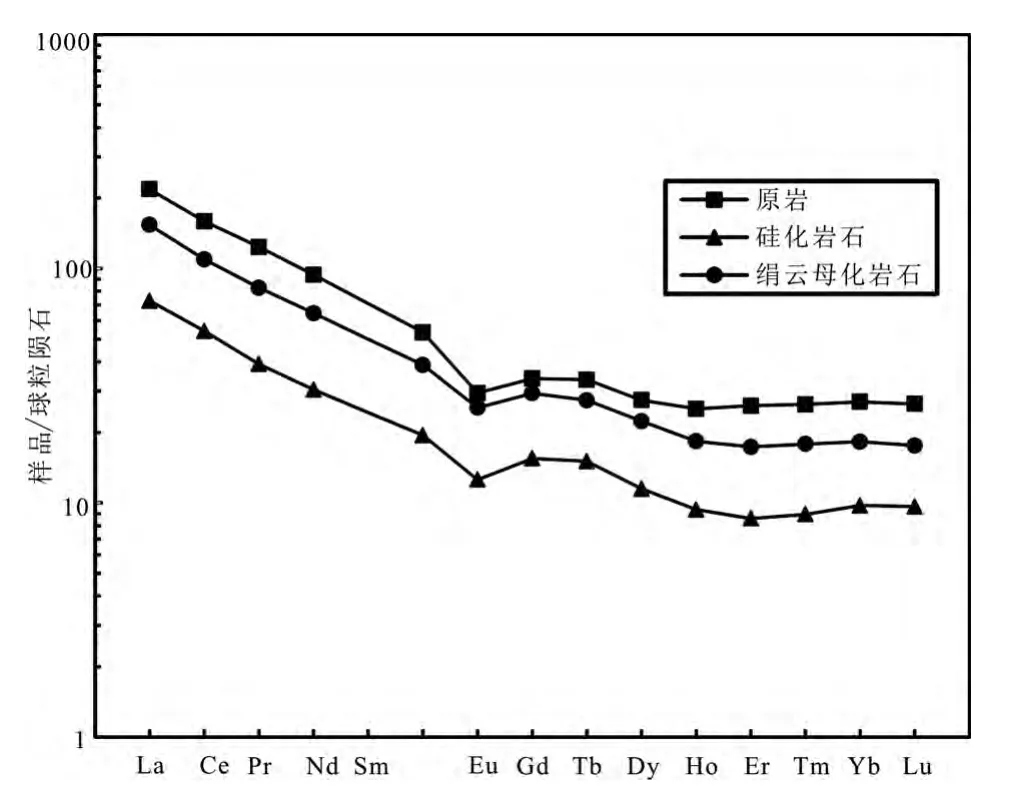
图5 蚀变围岩与原岩的稀土元素配分模式图Fig.5 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the altered rock and the original rock
对不同蚀变过程的稀土元素投蛛网图(图5),并对稀土元素的一些参数进行了计算(表4),从图表中可以看出蚀变岩与原岩的REE 球粒陨石标准化配分模式曲线变化趋势相似,曲线为右倾型,有明显的Eu 负异常,并且δEu 值介于0.70 ~0.76 之间,原岩的Eu 负异常值要比蚀变岩值低,凌其聪和刘从强(2002)认为是热液蚀变作用造成了Eu 活化迁出,从而导致了蚀变围岩的Eu 含量的降低和Eu 负异常扩大的现象。δCe 的值在1 左右,未发现Ce 异常。千枚岩原岩与蚀变千枚岩均富集轻稀土,而不富集重稀土,说明在蚀变过程中有流体REE 的加入(凌其聪和刘从强,2002)。此外,千枚岩原岩的稀土含量要比硅化和绢云母化千枚岩中的稀土含量要高,说明了在蚀变过程中伴随着稀土元素的流失。
在绢云母化蚀变过程中,可以看出LREE 的减少和K2O的增加,该现象表明了斜长石蚀变为绢云母的过程伴随着REE 加入到流体中(Genna et al.,2014)。此外,斜长石是Eu 的一个非常重要的来源(Budzinski and Tischendorf,1989),然而,斜长石蚀变为绢云母的过程中只有很少一部分Eu 能够进入到绢云母中(Alderton et al.,1980)。绢云母形成时流体的温度<250℃,此时Eu 容易被流体带走,进而造成该区域Eu 的负异常(Genna et al.,2014)。
6.2 断裂对蚀变的控制作用
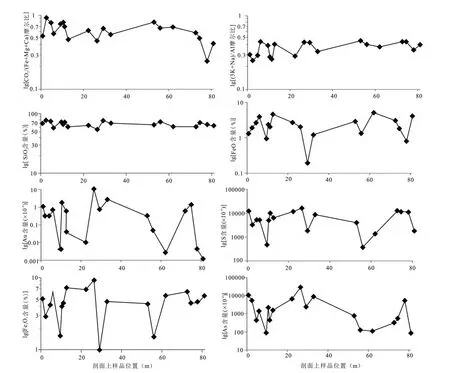
图6 安坝金矿床4 号硐CM19 剖面元素含量变化Fig.6 Elements content variation in the CM19 profile of the 4th adit in the Anba deposit
对安坝金矿床4 号硐CM19 剖面上样品的主微量数据进行了相应的投图(图6)。图中CO2/(Fe+Mg+Ca)摩尔质量比代表了碳酸盐化程度(Chinnasamy and Mishra,2013;McCuaig and Kerrich,1998),从图中可以看出,在靠近断裂带的地方碳酸盐化程度较高,说明了碳酸盐化在安坝金矿床内受断裂带控制。(3K+Na)/Al 摩尔质量比代表碱金属浓度集中程度,即代表含有碱金属的云母矿物含量(Chinnasamy and Mishra,2013;McCuaig and Kerrich,1998),在安坝金矿床主要以绢云母为主。在岩浆岩中或距离岩浆岩较近的千枚岩中往往绢云母化蚀变的程度较高,可见绢云母化蚀变的空间分布受岩浆岩的控制。在阳山金矿带内,岩浆岩的空间分布在区域上明显受断裂带的控制(王宏伟,2012;华北,2013),因此,绢云母化在空间分布上受断裂带的控制。SiO2含量在一定程度上代表硅化的程度,从图中可知,在断裂带发育的地方硅化程度强。在野外常常可见在断裂带附近往往石英脉较发育,含矿流体一般都是沿断裂带运移的,并在断裂带附近的围岩中形成石英脉;此外,围岩与含矿流体也更容易接触发生交代反应而形成含SiO2的矿物。以上两种原因致使断裂带附近的围岩硅化程度较高。粘土化发育于断裂带附近,而且越靠近断裂带的地方蚀变程度越高。
6.3 蚀变与金矿化的关系
对安坝金矿床4 号硐CM19 剖面上Au、S、FeO、As 和Fe2O3的含量进行了投图(图6)。结合图3 发现,在剖面上(3K+Na)/Al 摩尔比曲线在样品3B-6、3B-9、3B-13、3B-16、3B-17、3B-19、3B-26、3B-27 处出现峰值;金含量曲线显示在样品3B-6、3B-9、3B-11、3B-16、3B-18、3B-27 处出现峰值;而观察SiO2含量曲线可以发现在样品3B-7、3B-11、3B-15、3B-17、3B-18、3B-20、3B-27 处硅化程度较高。样品3B-6 发育绢云母化、粘土化和轻微的硅化,镜下可见该样品的硅化、粘土化蚀变与矿化没有关系,而绢云母化伴随有黄铁矿化发育(图2b),表明样品3B-6 金含量高与绢云母化蚀变有关。样品3B-9 仅发育绢云母化蚀变,并且镜下可见绢云母化伴随黄铁矿化,说明了该样品中矿化与绢云母化关系密切。样品3B-11 发育硅化,镜下见硅化伴有黄铁矿化(图2d)。样品3B-16、3B-27 发育硅化和绢云母化,样品3B-18 发育硅化、绢云母化和碳酸盐化,镜下可见硅化和绢云母化伴随黄铁矿化,这三个样品中矿化与硅化、绢云母化有关。样品3B-7、3B-15、3B-17、3B-20 镜下可见硅化,且硅化与矿化无关。样品3B-13、3B-17、3B-19、3B-26 镜下可见绢云母化,且绢云母化与矿化无关,该绢云母应该为成矿前的产物。
此外,在剖面上还发现S 百分含量呈现出6 个峰,这6个峰与Au 的含量呈现出的6 个峰位置相同,并且二者有相同的变化趋势,主要是因为在安坝金矿床内金主要赋存于金属硫化物(黄铁矿和毒砂)中。FeO 在剖面上的变化与Au 的变化趋势仅局部变化一致,这是因为Fe2+主要赋存于黄铁矿中(FeS),金不仅赋存于黄铁矿中,还有部分金赋存于毒砂中。而在毒砂中Fe 以二价和三价的形式存在,并与As 和S结合。在剖面上25m 处的Au 含量特别高,此时Fe2+、Fe3+、As、S 的含量也很高,主要是因为这四种元素形成了大量的毒砂和黄铁矿,Au 同时也发生了沉淀,并赋存于黄铁矿和毒砂中(Fleet et al.,1993;Reich et al.,2005;Deditius et al.,2008;Zhang et al.,2013)。
硅化蚀变过程,含矿流体沿断裂带向上运移,在运移时温度、压力逐渐下降,氧逸度升高。当氧逸度升高时,含矿流体呈弱酸性,而弱酸性、温度压力降低、氧逸度升高的条件促使SiO2沉淀,产生硅化(申婉妮,2010),并且硅化蚀变过程伴随着黄铁矿和毒砂的形成。安坝金矿床内Au 以配离子[AuS]-的形式存在(谢广东,1994;李楠,2013;朱光儒等,2014;Wang et al.,2015)。硅化蚀变过程中黄铁矿和毒砂的沉淀,引起含矿流体中还原硫活度降低,从而导致金沉淀(李楠,2013)。
在绢云母化蚀变过程中能够改变含矿流体的pH 值,而含矿流体的pH 值反过来影响金属矿物的溶解度(Guilbert and Park,1986)。流体与围岩反应过程中消耗H+,并使溶液pH 值增大显弱碱性(Helba et al.,2001;李晶等,2007)。含矿流体中含有丰富的Fe 和S 元素。

从上述反应可以看出,绢云母化蚀变过程中有大量硫化物的形成。此外,K+和H+的减少和CO2的增加,可以降低Au 的溶解度(Kishida and Kerrich,1987;Gao and Kwak,1997)。所以,随着Fe 含量的增加,含Au 的硫化物开始沉淀(Helba et al.,2001)。
7 结论
(1)安坝金矿床发育的蚀变有硅化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化和粘土化,其中与成矿有关系的蚀变为硅化和绢云母化。在时间上,硅化蚀变贯穿发育于成矿前、成矿期和成矿后,绢云母化蚀变为成矿前和成矿期的产物,碳酸盐化蚀变主要发育于成矿晚阶段和成矿后,而粘土化蚀变为成矿后的产物。在空间上,不同类型的蚀变均受矿区内断裂带的控制。
(2)在硅化蚀变过程中,明显带入的组分有SiO2、Fe2O3、FeO、MgO、CaO、C、S、Au、As、Hg、Pb、Zn;Rb 和Ba 元素被明显带出。在绢云母化蚀变过程中明显带入的组分为SiO2、Fe2O3、CaO、C、S、Au、As、Hg、Pb、Zn、Rb 和Ba;带出组分为Na2O。绢云母化过程中绢云母是由斜长石蚀变而形成的。
(3)在稀土元素方面,表现为明显的Eu 负异常、无Ce 异常。原岩的δEu=0.70,δCe =0.95;硅化岩石的δEu =0.72,δCe=1.00;绢云母化岩石的δEu=0.76,δCe=0.95。稀土元素的配分模式曲线变化趋势相似,为右倾型曲线,并且富集轻稀土,而不富集重稀土。稀土元素的变化揭示了蚀变过程中有流体REE 的加入和稀土元素的流失。
(4)在硅化过程中,由于含矿流体温度、压力和氧逸度的变化,并伴随着黄铁矿和毒砂的形成,引起含矿流体中还原硫活度降低而导致金沉淀。在绢云母化过程中,含矿流体的pH 增大及K+和H+的减少和CO2的增加导致了Au 溶解度的降低,最终致使黄铁矿和Au 沉淀。
致谢 野外工作得到了中国黄金集团阳山金矿有限公司工作人员、武警黄金部队十二支队官兵的帮助与支持;岩石主微量元素测试工作得到了核工业北京地质研究院地质分析测试研究中心相关人员的协助;论文成文过程中得到了中国地质大学(北京)杨立强教授的悉心指导,同时也得到了邱昆峰博士、李瑞红博士和刘向东硕士的帮助;审稿人对本文提出了宝贵修改意见;在此对他们表示最诚挚的谢意。
Ague JJ. 1991. Evidence for major mass transfer and volume strain during regional metamorphism of pelites. Geology,19(8):855 -858
Ague JJ. 1997. Compositional variations in metamorphosed sediments of the Littleton Formation,New Hamp shire. American Journal of Science,297(4):440 -449
Alderton DHM,Pearce JA and Potts PJ. 1980. Rare earth element mobility during granite alteration:Evidence from southwest England.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,49(1):149 -165
Brimhall GH and Dietrich WE. 1987. Constitutive mass balance relations between chemical composition,volume,density,porosity,and strain in metasomatic hydrochemical systems:Results on weathering and pedogenesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,51(3):567 -587 Brimhall GH,Lewis CJ,Ague JJ,Dietrich WE,Hampel J,Teague T and Rix P. 1988. Metal enrichment in bauxites by deposition of chemically mature aeolian dust. Nature,333(6176):819 -824
Budzinski H and Tischendorf G. 1989. Distribution of REE among minerals in the Hercynian postkinematic granites of Westerzgebirge-Vogtland,GDR. Zeitschrift für Geologische Wissenschaften,17(11):1019 -1031
Chinnasamy SS and Mishra B. 2013. Greenstone metamorphism,hydrothermal alteration,and gold mineralization in the genetic context of the granodiorite-hosted gold deposit at Jonnagiri,Eastern Dharwar Craton,India. Economic Geology,108(5):1015 -1038
Christie AB and Brathwaite RL. 2003. Hydrothermal alteration in metasedimentary rock-hosted orogenic gold deposits, Reefton goldfield,South Island,New Zealand. Mineralium Deposita,38(1):87 -107
Condie KC and Sinha AK. 1996. Rare earth and other trace element mobility during mylonitization:A comparison of the Brevasrd and Hope Valley shear zones in the Appalachian Mountains,USA.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,14(2):213 -226
Craw D. 2002. Geochemistry of late metamorphic hydrothermal alteration and graphitisation of host rock,Macraes gold mine,Otago Schist,New Zealand. Chemical Geology,191(4):257 -275
Deditius AP,Utsunomiya S,Renock D,Ewing RC,Ramana CV,Becker U and Kesler SE. 2008. A proposed new type of arsenian pyrite:Composition,nanostructure and geological significance. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,72(12):2919 -2933
Deng HL,Tu GZ,Li CY and Liu CQ. 1999. Mass balance of open geochemical systems:1. Theory. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,19(2):121 -131 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng J,Yang LQ,Liu W,Sun ZS,Li XJ and Wang QF. 2001. Gold origin and fluid ore-forming effect of Zhao-Ye ore deposits concentrating area in Jiaodong,Shandong,China. Chinese Journal of Geology,36(3):257 -268 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng J,Hou ZQ,Mo XX,Yang LQ,Wang QF and Wang CM. 2010.Superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis in Sanjiang Tethys.Mineral Deposit,29 (1):37 - 42 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng J,Yang LQ and Wang CM. 2011. Research advances of superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis in the Sanjiang Tethys.Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(9):2501 - 2509 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng J,Wang CM and Li GJ. 2012. Style and process of the superimposed mineralization in the Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(5):1349 -1361 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng J,Ge LS and Yang LQ. 2013. Tectonic dynamic system and compound orogeny:Additionally discussing the temporal-spatial evolution of Sanjiang orogeny,Southwest China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(4):1099 -1114 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng J,Yuan WM,Carranza EJM,Yang LQ,Wang CM,Yang LY and Hao NN. 2014a. Geochronology and Thermochrononometry of the Jiapigou Gold Belt,northeastern China:New evidence for multiple episodes of mineralization. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,89:10-27
Deng J,Wang QF,Li GJ and Santosh M. 2014b. Cenozoic tectonomagmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region,southwestern China. Earth-Science Reviews,138:268 -299
Deng J,Wang QF,Li GJ,Li CS and Wang CM. 2014c. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region,SW China. Gondwana Research,26(2):419 -437
Deng J and Wang QF. 2015. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research,doi:10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003
Du ZT. 1997. Study on tectonic systems and their controlling to the gold deposits distribution in the region of West Qinling. Ph. D.Dissertation. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Geological Science,1 -159 (in Chinese)
Du ZT and Wu GG. 1998. Study on the compound juxtaposed arcuate structure system in Wudu region and it's controlling to the gold mineralization. Geoscience,12(4):532 -536 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dugdale AL,Wilson CJL and Squire RJ. 2006. Hydrothermal alteration at the Magdala gold deposit,Stawell,western Victoria. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences,53(5):733 -757
Fleet ME,Chryssoulis SL,MacLean PJ,Davidson R and Weisener CG.1993. Arsenian pyrite from gold deposits:Au and As distribution investigated by SIMS and EMP,and color staining and surface oxidation by XPS and LIMS. Canadian Mineralogist,31(1):1 -17
Gao ZL and Kwak TAP. 1997. The geochemistry of wall rock alteration in turbidite-hosted gold vein deposits,central Victoria,Australia.Journal of Geochemical Exploration,59(3):259 -274
Genna D,Gaboury D and Roy G. 2014. Evolution of a volcanogenic hydrothermal system recorded by the behavior of LREE and Eu:Case study of the Key Tuffite at Bracemac-McLeod deposits,Matagami,Canada. Ore Geology Reviews,63:160 -177
Grant JA. 1986. The isocon diagram:A simple solution to Gresens equation for metasomatic alteration. Economic Geology,81(8):1976 -1982
Gresens RL. 1967. Composition-volume relationships of metasomatism.Chemical Geology,2:47 -65
Guilbert JM and Park CF. 1986. The Geology of Ore Deposits. New York:W. H. Freeman and Co.,1 -985
Guo S,Ye K,Chen Y,Liu JB and Zhang LM. 2013. Introduction of mass-balance calculation method for component transfer during the opening of a geological system. Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(5):1486 -1498 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Helba HA,Khalil KI and Abou NMF. 2001. Alteration patterns related to hydrothermal gold mineralizaition in meta-andesites at Dungash Area,Eastern Desert,Egypt. Resource Geology,51(1):19 -30
Hua B. 2013. Ore-controlling structural system in the Yangshan Gold Belt,Western Qinling Orogen,Central China. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,1 - 104 (in Chinese)
Ji XZ,Li N,Zhang C,Qiu KF,Hua B,Yu JY,Wu CJ and Han R.2014. Theelemental geochemistry characteristics and forming environment of cherts in the Mianlue tectonic zone. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(9):2619 -2630 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kishida A and Kerrich R. 1987. Hydrothermal alteration zoning and gold concentration at the Kerr-Addison Archean lode gold deposit,Kirkland Lake,Ontario. Economic Geology,82(3):649 -690
Klammer D. 1997. Mass change during extreme acid-sulphate hydrothermal alteration of a Tertiary latite,Styria,Austria. Chemical Geology,141(1 -2):33 -48
Klemm DD and Kräutner HG. 2000. Hydrothermal alteration and associated mineralization in the Freda-Rebecca gold deposit,Bindura District,Zimbabwe. Mineralium Deposita,35(2 -3):90 -108
Li J,Chen YJ,Li QZ,Lai Y,Yang RS and Mao SD. 2007. Fluid inclusion geochemistry and genetic type of the Yangshan gold deposit,Gansu,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,23(9):2144 -2154 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li N,Yang LQ,Zhang C,Zhang J,Lei SB,Wang HT,Wang HW and Gao X. 2012. Sulfur isotope characteristics of the Yangshan gold belt,West Qinling:Constraints on ore-forming environment and material source. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(5):1577 -1587 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li N. 2013. Geochemistry of ore-forming processes in the Yangshan gold belt,West Qinling,central China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,1 -147 (in Chinese)
Li N,Deng J,Yang LQ,Goldfarb RJ,Zhang C and Marsh EE. 2014.Paragenesis and geochemistry of ore minerals in the epizonal gold deposits of the Yangshan gold belt, West Qinling, China.Mineralium Deposita,49(4):427 -449
Li YN. 1986. Barite deposit geological characteristics and vision analysis,Gansu Province. Chemical Geology,(1):22 - 29 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ling QC and Liu CQ. 2002. Geochemical behavior of trace element during hydrothermal alteration in low-metamorphic rock:A case study for Shuangqiaoshan Group in Yinshan area,Northwest Jiangxi Province,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,18(1):100 -108 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu DL,Yang XY,Yang HT and Yu QN. 1996. The deformational condition and component migration of mylonites in Fuchashan ductile shear zones in the southern Tanchen-Lujiang fault belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica,12(4):573 - 588 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu HZ,Zhu XQ,Shan Q and Wang ZG. 2013. Hydrothermal evolution of gold-bearing pyrite and arsenopyrite from different types of gold deposits. Mineral Deposits,32(4):823 -842 (in Chinese with English abstract)
McCuaig TC and Kerrich R. 1998. P-T-t-deformation-fluid characteristics of lode gold deposits:Evidence from alteration systematics. Ore Geology Reviews,12(6):381 -453
Meng LY. 1998. The silicide and metallogenetic in the hydrothermal deposit. Chinese Science Bulletin,43(6):575 -579 (in Chinese)
O’Hara K. 1988. Fluid flow and volume loss during mylonitization:An origin for phyllonite in an overthrust setting,North Carolina,U. S.A. Tectonophysics,156(1 -2):21 -36
O’Hara K and Blavkburn WH. 1989. Volume-loss model for trace element enrichments in mylonite. Geology,17(6):524 -527
Parsapoor A,Khalili M and Mackizadeh MA. 2009. The behaviour of trace and rare earth elements (REE)during hydrothermal alteration in the Rangan area (Central Iran). Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,34(2):123 -134
Putnis A. 2002. Mineral replacement reactions:From macroscopic observations to microscopic mechanisms. Mineralogical Magazine,66(5):689 -708
Putnis A. 2009. Mineral replacement reactions. Reviews in Mineralogy &Geochemistry,70(1):87 -124
Qiu KF and Yang LQ. 2011. Genetic feature of monazite and its U-Th-Pb dating:Critical considerations on the tectonic evolution of Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(9):2721 -2732 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qiu KF,Li N,Taylor RD,Song YH,Song KR and Han WZ. 2014.Timing and duration of metallogeny of the Wenquan deposit in the West Qinling,and its constrain on a proposed classification for porphyry molybdenum deposits. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(9):2631 -2643 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qiu KF,Song KR and Song YH. 2015. Magmatic-hydrothermal fluid evolution of the Wenquan porphyry molybdenum deposit in the north margin of the western Qinling,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,31(11):3391 -3404 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Reich M,Kesler SE,Utsunomiya S,Palenik CS,Chryssoulis SL and Ewing RC. 2005. Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,69(11):2781 -2796
Shen WN. 2010. Wallrock alteration and mineralization of the Bilihe porphyry gold-deposit in Inner Mongolia China. Master Degree Thesis. Tangshan:Hebei Polytechnic University,1 - 75 (in Chinese)
Stoffregen RE. 1987. Genesis of acid-sulphate alteration and Au-Cu-Ag mineralization at Summitville,Colourado. Economic Geology,82(6):1575 -1591
Tang HF,Liu CQ and Xie GG. 2000. Mass transfer and element mobility of rocks during regional metamorphism: A case study of metamorphosed pelites from the Shuangqiaoshan Group in Lushan.Geological Review,46(3):245 - 254 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang CY,Li XF,Xiao R,Bai YP,Yang F,Mao W and Jiang SK.2012. Elements mobilization of mineralized porphyry rocks during hydrothermal alteration at Zhushahong porphyry copper deposit,Dexing district,South China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(12):3869 -3886 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang HW. 2012. Relationship between gold minerlization and acid dike of the Yangshan Gold Deposit in the Western Qinling Belt,Central China. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences,1 -117 (in Chinese)
Wang ZL,Yang LQ,Deng J,Santosh M,Zhang HF,Liu Y,Li RH,Huang T,Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2014. Gold-hosting high Ba-Sr granitoids in the Xincheng gold deposit,Jiaodong Peninsula,East China:Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,95:274 -299
Wang ZL,Yang LQ,Guo LN,Marsh E,Wang JP,Liu Y,Zhang C,Li RH,Zhang L,Zheng XL and Zhao RX. 2015. Fluid immiscibility and gold deposition in the Xincheng deposit,Jiaodong Peninsula,China:A fluid inclusion study. Ore Geology Reviews,65:701-717
Whitbread MA and Moore CL. 2004. Two lithogeochemical approachest to the identification of alteration patterns at the Elura Zn-Pb-Ag deposit,Cobar,New South Wales,Australia:Use of Pearce Element Ratio analysis. Geochemistry:Exploration,Environment,Analysis,4(2):129 -141
Xie GD. 1994. Research progresses on the transport forms and depositional mechanisms of gold. Geoscience,8(3):357 -363 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiong YQ,Yang LQ,Shao YJ,Zhao K,Li P,Lu YG and Du DY.2015. Metallogenic process in Jinchang gold-nickel deposit,Mojiang County,SW Yunnan,China:Constraints from occurrence of gold and nickel. Acta Petrologica Sinica,31(11):3309 - 3330 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yan FZ,Qi JZ and Guo JH. 2010. The Geology and Exploration in Yangshan Gold Deposit, Gansu Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House,1 -232 (in Chinese)
Yang LQ,Xiong ZQ,Deng J,Zhang ZJ,Wang JP and Li XJ. 2003.Transition of tectonic stress fields and its effects of metallogenic geochemistry on multi-scales. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,27(3):243 -249 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang LQ,Deng J,Zhang J,Guo CY,Gao BF,Gong QJ,Wang QF,Jiang SQ and Yu HJ. 2008. Decrepitation thermometry and compositions of fluid inclusions of the Damoqujia gold deposit,Jiaodong Gold Province,China:Implications for metallogeny and exploration. Journal of China University of Geosciences,19(4):378 -390
Yang LQ,Deng J,Guo CY,Zhang J,Jiang SQ,Gao BF,Gong QJ and Wang QF. 2009. Ore-forming fluid characteristics of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China.Resource Geology,59(2):182 -195
Yang LQ,Liu JT,Zhang C,Wang QF,Ge LS,Wang ZL,Zhang J and Gong QJ. 2010. Superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis:An example from the orogenic gold deposits in Ailaoshan gold belt,Southwest China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,26(6):1723 -1739 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang LQ,Deng J,Zhao K and Liu JT. 2011a. Tectono-thermochronology and gold mineralization events of orogenic gold deposits in Ailaoshan orogenic belt,Southwest China:Geochronological constraints. Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(9):2519 -2532 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang LQ,Deng J,Zhao K,Liu JT,Ge LS,Zhou DQ,Li SH and Cao BB. 2011b. Geological characteristics and genetic type of Daping gold deposit in the Ailaoshan orogenic belt,SW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(12):3800 -3810 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang LQ and Badal J. 2013. Mirror symmetry of the crust in the oil/gas region of Shengli,China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,78:327-344
Yang LQ,Deng J,Goldfarb RJ,Zhang J,Gao BF and Wang ZL. 2014.40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit:New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold province,China. Gondwana Research,25(4):1469 -1483
Yang LQ,Deng J,Wang ZL,Zhang L,Guo LN,Song MC and Zheng XL. 2014. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province,eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(9):2447 -2467 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang LQ,Deng J,Dilek Y,Qiu KF,Ji XZ,Li N,Taylor RD and Yu JY. 2015a. Structure,geochronology,and petrogenesis of the Late Triassic Puziba granitoid dikes in the Mianlue suture zone,Qinling orogen,China. Geological Society of America Bulletin,127(11 -12):1831 -1854
Yang LQ,Deng J,Guo RP,Guo LN,Wang ZL,Chen BH and Wang XD. 2015b. World-class Xincheng gold deposit:An example from the giant Jiaodong gold province. Geoscience Frontiers,doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2015.08.006
Yang LQ,Deng J,Gao X and He WY. 2015c. Late Cretaceous porphyry metallogenic system of the Yidun arc,SW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,31(11):3155 -3170 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang LQ,Ji XZ,Santosh M,Li N,Zhang ZC and Yu JY. 2015d.Detrital zircon U-Pb ages,Hf isotope,and geochemistry of Devonian chert from the Mianlue suture:Implications for tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,doi. org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.04.013
Yang LQ,Deng J,Dilek Y,Meng JY,Gao X,Santosh M,Wang D and Yan H. 2015e. Melt source and evolution of I-type granitoids in the SE Tibatan Plateau:Late Cretaceous magmatism and mineralization driven by collision-induce transtensional tectonics. Lithos,doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.10.005
Yang LQ,Deng J,Qiu KF,Ji XZ,Santosh M,Song KR,Song YH,Geng JZ,Zhang C and Hua B. 2015f. Magma mixing and crustmantle interaction in the Triassic monzogranites of Bikou Terrane,central China:Constraints from petrology,geochemistry,and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic systematic. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,98:320 -341
Yang LQ,Deng J,Guo LN,Wang ZL,Li XZ and Li JL. 2016a. Origin and evolution of ore fluid,and gold deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit,Jiaodong Peninsula,eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews,72:585 -602
Yang LQ,Deng J,Wang ZL,Zhang L,Goldfarb RJ,Yuan WM,Weinberg RF and Zhang RZ. 2016b. Thermochronologic constraints on evolution of the Linglong Metamorphic Core Complex and implications for gold mineralization:A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit,Jiaodong Peninsula,eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews,72:165 -178
Yuan F,Zhou TF,Wang SW,Fan Y,Tang C,Zhang QM,Yu CH and Shi C. 2012. Characteristic of alteration and mineralization of the Shaxi porphyry copper deposits,Luzong area,Anhui Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(10):3099 -3112 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang BL,Yang LQ,Huang SY,Huang SY,Liu Y,Liu WL,Zhao RX,Xu YB and Liu SG. 2014. Hydrothermal alteration in the Jiaojia gold deposit,Jiaodong,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(9):2533 -2545 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang J,Deng J,Chen HY,Yang LQ,Cookeb D,Danyushevsky L and Gong QJ. 2013. LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of pyrite from the Chang’an gold deposit,Sanjiang region,China:Implication for oreforming process. Gondwana Research,26(2):557 -575
Zhang KQ and Yang Y. 2014. Introduction of the method for mass balance calculation in altered rocks. Geological Science and Technology Information,21 (3):104 - 107 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao CH. 2009. Discussion of the genesis of super-large gold deposit in Yangshan, Gansu. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry,28 (3):286 - 293 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhong ZQ and You ZD. 1995. The composition variation and the loss of volume in the shear zone-take the shear zone in Hetai as an example.Chinese Science Bulletin,40(10):913 -916 (in Chinese)
Zhu GR,Wang ZH,Zhi SY and Meng FM. 2014. Migration forms and deposition mechanisms of gold in Dashui gold deposit. Gansu Geology,23(2):41 -45 (in Chinese with English abstract)
附中文参考文献
邓海琳,涂光炽,李朝阳,刘丛强. 1999. 地球化学开放系统的质量平衡:1. 理论. 矿物学报,19(2):121 -131
邓军,杨立强,刘伟,孙忠实,李新俊,王庆飞. 2001. 胶东招掖矿集区巨量金质来源和流体成矿效应. 地质科学,36(3):257-268
邓军,侯增谦,莫宣学,杨立强,王庆飞,王长明. 2010. 三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用. 矿床地质,29(1):37 -42
邓军,杨立强,王长明. 2011. 三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用研究进展. 岩石学报,27(9):2501 -2509
邓军,王长明,李龚建. 2012. 三江特提斯叠加成矿作用样式及过程. 岩石学报,28(5):1349 -1361
邓军,葛良胜,杨立强. 2013. 构造动力体制与复合造山作用:兼论三江复合造山带时空演化. 岩石学报,29(4):1099 -1114
杜子图. 1997. 西秦岭地区构造体系对金矿分布规律的控制作用.博士学位论文. 北京:中国地质科学院,1 -159
杜子图,吴淦国. 1998. 论武都复合型斜叠弧形构造及其控矿作用.现代地质,12(4):532 -536
郭顺,叶凯,陈意,刘景波,张灵敏. 2013. 开放地质体系中物质迁移质量平衡计算方法介绍. 岩石学报,29(5):1486 -1498
华北. 2013. 阳山金矿带控矿构造系统. 硕士学位论文. 北京:中国地质大学,1 -104
戢兴忠,李楠,张闯,邱昆峰,华北,于金元,吴春俊,韩日. 2014.勉略构造带硅质岩元素地球化学特征及其形成环境. 岩石学报,30(9):2619 -2630
李晶,陈衍景,李强之,赖勇,杨荣生,毛世东. 2007. 甘肃阳山金矿流体包裹体地球化学和矿床成因类型. 岩石学报,23(9):2144 -2154
李楠,杨立强,张闯,张静,雷时斌,王恒涛,王宏伟,高雪. 2012.西秦岭阳山金矿带硫同位素特征:成矿环境与物质来源约束.岩石学报,28(5):1577 -1587
李楠. 2013. 阳山金矿带成矿作用地球化学. 博士学位论文. 北京:中国地质大学,1 -147
李裕能. 1986. 甘肃重晶石矿床地质特征及远景分析. 化工地质,(1):22 -29
凌其聪,刘丛强. 2002. 低级变质岩在热液蚀变过程中的微量元素地球化学行为——以赣东北银山地区双桥山群为例. 岩石学报,18(1):100 -108
刘德良,杨晓勇,杨海涛,余青霓. 1996. 郯庐断裂带南段桴槎山韧性剪切带糜棱岩的变形条件和组分迁移系. 岩石学报,12(4):573 -588
卢焕章,朱笑青,单强,王中刚. 2013. 金矿床中金与黄铁矿和毒砂的关系. 矿床地质,32(4):823 -842
孟良义. 1998. 热液矿床中的硅化与成矿. 科学通报,43(6):575 -579
邱昆峰,杨立强. 2011. 独居石成因特征与U-Th-Pb 定年及三江特提斯构造演化研究例析. 岩石学报,27(9):2721 -2732
邱昆峰,李楠,Ryan DT,宋耀辉,宋开瑞,韩旺珍,张东旭. 2014. 西秦岭温泉钼矿床成矿作用时限及其对斑岩型钼矿床系统分类制约. 岩石学报,30(9):2631 -2643
邱昆峰,宋开瑞,宋耀辉. 2015. 西秦岭温泉斑岩钼矿床岩浆-热夜演化. 岩石学报,31(11):3391 -3404
申婉妮. 2010. 内蒙古毕力赫斑岩型金矿床围岩蚀变特征与成矿.硕士学位论文. 唐山:河北理工大学,1 -75
唐红峰,刘丛强,谢国刚. 2000. 区域变质作用中岩石的质量迁移和元素活动——以庐山双桥山群变泥质岩系为例. 地质论评,46(3):245 -254
王翠云,李晓峰,肖荣,白艳萍,杨锋,毛伟,蒋松坤. 2012. 德兴朱砂红斑岩铜矿热液蚀变作用及元素地球化学迁移规律. 岩石学报,28(12):3869 -3886
王宏伟. 2012. 西秦岭阳山金矿带酸性脉岩与金成矿关系. 硕士学位论文. 北京:中国地质大学,1 -117
谢广东. 1994. Au 的迁移形式及沉淀机制研究的某些进展. 现代地质,8(3):357 -363
熊伊曲,杨立强,邵拥军,赵凯,李坡,卢宜冠,杜达洋. 2015. 滇西南墨江金厂金镍矿床金、镍赋存状态及成矿过程探讨. 岩石学报,31(11):3309 -3330
阎凤增,齐金忠,郭俊华. 2010. 甘肃省阳山金矿地质与勘查. 北京:地质出版社,1 -232
杨立强,熊章强,邓军,张中杰,王建平,李新俊. 2003. 构造应力场转换的成矿地球化学响应. 大地构造与成矿学,27(3):243-249
杨立强,刘江涛,张闯,王庆飞,葛良胜,王中亮,张静,龚庆杰.2010. 哀牢山造山型金成矿系统:符合造山构造演化与成矿作用初探. 岩石学报,26(6):1723 -1739
杨立强,邓军,赵凯,刘江涛. 2011a. 哀牢山造山带金矿成矿时序及其动力学背景探讨. 岩石学报,27(9):2519 -2532
杨立强,邓军,赵凯,刘江涛,葛良胜,周道卿,李士辉,曹宝宝.2011b. 滇西大坪金矿床地质特征及成因初探. 岩石学报,27(12):3800 -3810
杨立强,邓军,王中亮,张良,郭林楠,宋明春,郑小礼. 2014. 胶东中生代金成矿系统. 岩石学报,30(9):2447 -2467
杨立强,邓军,高雪,和文言. 2015. 义敦岛弧晚白垩世斑岩成矿系统. 岩石学报,31(11):3155 -3170
袁峰,周涛发,王世伟,范裕,汤诚,张千明,俞沧海,石诚. 2012.安徽庐枞沙溪斑岩铜矿蚀变及矿化特征研究. 岩石学报,28(10):3099 -3112
张炳林,杨立强,黄锁英,刘跃,刘文龙,赵荣新,徐咏彬,刘胜光.2014. 胶东焦家金矿床热液蚀变作用. 岩石学报,30(9):2533-2545
张可清,杨勇. 2002. 蚀变岩质量平衡计算方法介绍. 地质科技情报,21(3):104 -107
赵成海. 2009. 甘肃阳山超大型金矿成因研究评述. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,28(3):286 -293
钟增球,游振东. 1995. 剪切带的成分变异及体积亏损——以河台剪切带为例. 科学通报,40(10):913 -916
朱光儒,王志虎,芝世玉,孟凡敏. 2014. 大水金矿床金的迁移形式和沉淀机制探讨. 甘肃地质,23(2):41 -45
