成人哮喘患者血清25(OH)D3水平与哮喘控制程度的关系
2014-07-18任芳萍刘玲莉杨娟利吴昌归
任芳萍,刘玲莉,杨娟利,吴昌归
成人哮喘患者血清25(OH)D3水平与哮喘控制程度的关系
任芳萍,刘玲莉,杨娟利,吴昌归
目的 了解成人哮喘患者血清25-羟维生素D3[25(OH)D3]水平与治疗前后肺功能改善程度的相关性,为哮喘控制提供新思路。方法 收集门诊确诊中度哮喘患者95例,入组后测定血清25(OH)D3浓度,给予沙美特罗替卡松(50 μg/250 μg),1吸/次,1次/12 h,规范治疗3个月。测定治疗前后患者基础肺功能,如第1秒用力呼气容积占预计值百分比(FEV1% pred)和呼气中段流速(FEF25%~75%),并记录治疗前后哮喘控制测试(ACT)评分。对25(OH)D3浓度与治疗前后FEV1% pred、FEF25%~75%以及ACT评分的改善情况进行相关性分析。结果 入组患者95例,未按规定时间随访32例,未按医嘱规范治疗23例,有效随访患者40例。患者血清25(OH)D3浓度与治疗后FEV1% pred、FEF25%~75%和ACT评分的增加值均呈正相关(P<0.01)。结论 成人哮喘患者血清25(OH)D3浓度与哮喘治疗反应呈正相关。
哮喘;25-羟维生素D3;肺功能;ACT评分;相关性
支气管哮喘(以下简称“哮喘”)是我国乃至全世界范围内最普遍的疾病之一,是特殊变应原引发的以气道炎症、气道高反应(AHR)和气道可逆性阻塞为特征的慢性疾病。虽然哮喘发病机制还不十分清楚,但既往的研究显示其与免疫功能紊乱有关[1],特别是Th1/Th2细胞平衡失调理论得到了广泛认可[2]。哮喘作为一种危害较大的气道可逆性疾病,目前还无根治性办法,其治疗重点在于达到并维持临床控制。临床中我们发现,分级相同的哮喘患者对药物的治疗反应也存在明显差异,这种差异尚未得到合理解释。
维生素D3是一类脂溶性类固醇化合物,主要参与钙、磷吸收的调节。最近发现维生素D3也可对免疫细胞发挥调节作用,进而影响哮喘发病过程[3-4],初步的临床研究发现其与哮喘的呼吸道症状相关[5-7]。然而,目前的研究主要集中于儿童人群,且主要关注维生素D3与哮喘发病的相关性,对于哮喘控制程度是否与维生素D3相关,尚未见相关报道。因此,本研究观察了成人哮喘患者血清维生素D水平与治疗前后哮喘控制程度之间的相关性。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象 选择2012年1月~2012年6月我科初诊的慢性中度持续性哮喘患者95例。病例入选标准:年龄18~80岁;入选前4 w内无使用全身糖皮质激素;试验前1 w内未口服或吸入长效β2受体激动剂,未应用白三烯受体拮抗剂;能够正确掌握药物吸入方法;诊断符合中华医学会呼吸病学分会哮喘学组2008年支气管哮喘防治指南中哮喘中度持续的诊断标准[8]。排除标准:用药依从性不佳者;未按规定时间随访;合并慢性疾病或严重的心、肝、肾疾病及其他脏器功能衰竭;有心理疾病或社会心理问题,包括使用镇静剂。
1.2 治疗方案 所有患者均给予吸入沙美特罗替卡松(50 μg/250 μg),1吸/次,1次/12 h;并按需吸入短效β2-受体激动剂沙丁胺醇气雾剂。连续治疗3个月。
1.3 观察指标
1.3.1 血清25-羟维生素D3[25(OH)D3]水平的测定 所有受试者入组后即取晨起空腹静脉血5 ml,以3000 r/min离心10 min,用电化学发光法(Cobas E411分析仪,罗氏)测定血清25(OH)D3浓度[25(OH)D3检测试剂盒,罗氏]。与我院正常值标准(>30 ng/ml)进行比对,分为不足(20~30 ng/ml)和缺乏(<20 ng/ml)。
1.3.2 肺功能测定 分别于患者治疗前和治疗后3个月测定肺功能。采用德国JAEGER MasterScreen肺功能仪测定:用力肺活量(FVC)、第1秒用力呼气容积占预计值百分比(FEV1% pred)、呼气中段流速(FEF25%~75%)等指标。
1.3.3 哮喘控制测试评分(ACT) 分别于患者治疗前和治疗后3个月进行ACT评分(表1),通过回忆过去4 w内有关自身哮喘病症的相关情况,回答5个问题,选择每个问题的得分,将分数相加,计算出哮喘控制测试的总得分,并与说明对照,就可获得哮喘控制情况的评估结果。
1.4 随访 对所有患者进行电话随访,1次/2 w,随访内容为用药依从性及饮食有无添加维生素D;治疗满3个月时门诊随访,进行肺功能检测及ACT评分。
1.5 统计学方法 数据用SPSS 13.0统计软件进行统计处理,计量资料以均数±标准差表示,两样本均数比较采用t检验;相关性检验采用双变量相关分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 一般情况 入组患者95例,试验期间,未按规定时间随访32例,未按医嘱规范治疗23例,有效随访患者40例。治疗后FEV1% pred、FEF25%~75%、ACT分别增加(20.92±8.92)%、(0.64±0.60)L/s和11.20±3.16,与治疗前相比均具有明显差异(P<0.05)。
2.2 血清25(OH)D3水平与治疗后FEV1% pred等指标增加值的相关性分析 血清25(OH)D3与治疗后FEV1% pred和FEF25%~75%增加值及ACT变化值呈正相关(r=0.445,r=0.477,r=0.557,P<0.01)。
3 讨论
细胞学研究提示,维生素D3可调节免疫细胞、气道上皮和平滑肌细胞的功能。在佝偻病患者中,低血清维生素D3水平与吞噬细胞活性降低有关[9],并且可通过补充1,25-(OH)2D3而逆转[10]。1,25-(OH)2D3可通过抑制活化B细胞的增殖并诱导其凋亡,稳定B细胞[11],也可抑制辅助T淋巴细胞的增殖[12]。气道上皮细胞可将骨化二醇活化为骨化三醇,后者能够抑制病毒感染后多聚免疫复合物诱导的趋化因子和细胞因子的产生,并维持抗病毒活性,对炎症反应起重要调节作用[13-14]。骨化三醇可以增加气道平滑肌24-羟化酶的表达,还可抑制血小板衍生生长因子诱导的气道平滑肌DNA合成,且呈剂量依赖性[15]。引用美国全国健康和营养调查数据,Keet等[16]发现维生素D3浓度与喘息症状和发生哮喘的风险呈负相关,维生素D3浓度每下降10 ng/ml,发生喘息的机会增加20%,发生哮喘的机会增加8%。研究还发现血清维生素D3浓度下降与肺功能下降、气道对乙酰甲胆碱反应性增加和激素治疗的反应性差相关[17-19]。
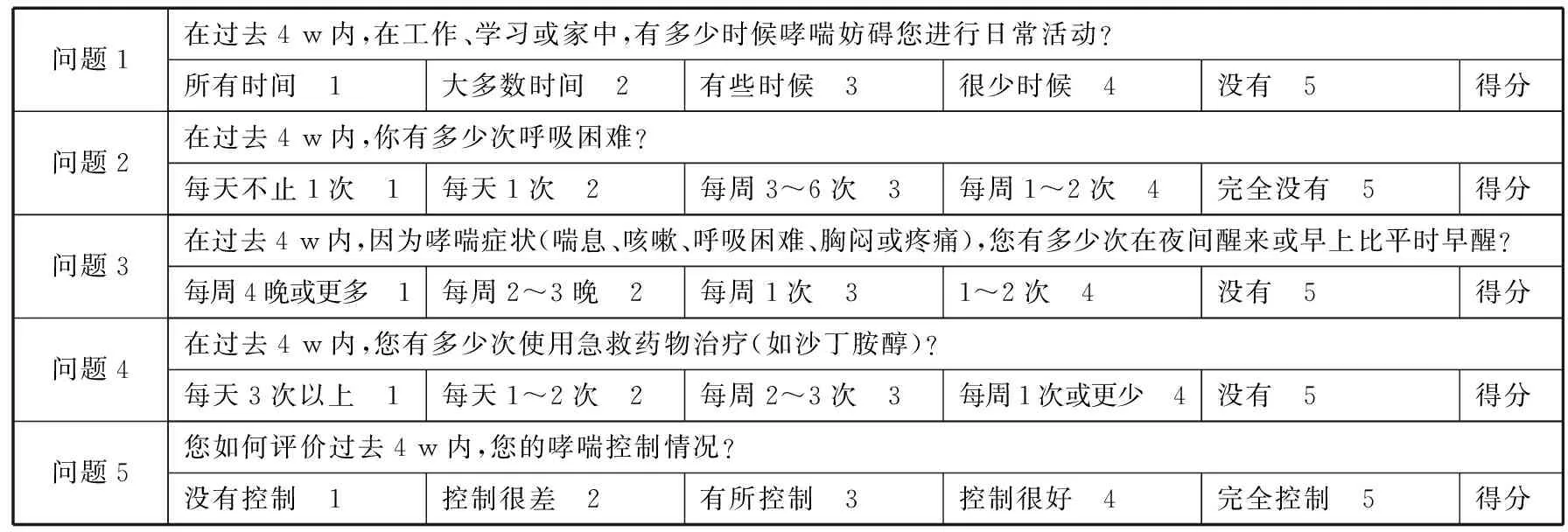
表1 哮喘控制测试评分
注:各题的分数相加得总分。25分:完全控制;20~24分:部分控制;<20分:未控制
本研究结果显示,给予沙美特罗替卡松(50 μg/250 μg)治疗3个月后,患者肺功能和ACT评分均得到改善,且改善程度在血清维生素D3浓度较高患者中更加明显。维生素D3对沙美特罗替卡松治疗的增效机制尚未明确。有研究表明,补充维生素D3可以通过抑制肺内炎性细胞因子,增加T细胞和树突细胞分泌白介素-10,减轻免疫反应性炎症[19-21]。动物实验显示,维生素D3可以改善哮喘大鼠气道高反应性,降低血清IgE水平,减少支气管肺泡灌洗液中嗜酸性粒细胞的浸润[22]。另有研究发现,维生素D3与地塞米松协同抑制哮喘大鼠气道炎症反应,其机制可能与降低哮喘大鼠血清中IgE水平、减少局部IL-4和IL-5等细胞因子有关[23]。补充活性形式的维生素D3,可以增强地塞米松对T细胞表达IL-10的刺激作用,并诱导调节性T细胞,以抑制Th2细胞因子的过多释放;在激素抵抗性患者,维生素D3可逆转调节性T细胞的分化障碍[24]。有学者还证实,氟替卡松和骨化三醇联合运用较任一单用能更明显抑制TNF-α和IFN-γ所致的RANTES分泌,骨化三醇可抑制氟替卡松诱导的趋化因子FKN的释放[25]。
综上,维生素D3水平与哮喘控制程度相关,补充维生素D3可能对提高哮喘控制水平有益。然而仍需要随机、对照、干预性临床试验来说明维生素D3与哮喘发病的因果关系,为哮喘治疗提供依据。
[1] Holt PG,Strickland DH.Interactions between innate and adaptive immunity in asthma pathogenesis:new perspectives from studies on acute exacerbations[J].J Allergy Clin Immunol,2010,125(5):963-972;quiz 973-974.
[2] Kumar RK,Yang M,Herbert C,et al.Interferon-gamma,pulmonary macro-phages and airway responsiveness in asthma[J].Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets,2012,11(4):292-297.
[3] Chishimba L,Thickett DR,Stockley RA,et al.The vitamin D axis in the lung:a key role for vitamin D-binding protein[J].Thorax,2010,65(5):456-462.
[4] Chambers ES,Hawrylowicz CM.The impact of vitamin D on regulatory T cells[J].Curr Allergy Asthma Rep,2011,11(1):29-36.
[5] Herr C,Greulich T,Koczulla RA,et al.The role of vitamin D in pulmonary disease:COPD,asthma,infection,and cancer[J].Respir Res,2011,12:31.
[6] Mak G,Hanania NA.Vitamin D and asthma[J].Curr Opin Pulm Med,2011,17(1):1-5.
[7] Sandhu MS,Casale TB.The role of vitamin D in asthma[J].Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol,2010,105(3):191-199;quiz 200-2,217.
[8] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会.支气管哮喘防治指南(2008)[J].中国实用乡村医生杂志,2011,18(12):28-36.
[9] Stroder J,Kasal P.Evaluation of phagocytosis in rickets[J].Acta Paediatr Scand,1970,59(3):288-292.
[10] Bar-Shavit Z,Noff D,Edelstein S,et al.1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3and the regulation of macrophage function[J].Calcif Tissue Int,1981,33(6):673-676.
[11] Chen S,Sims GP,Chen XX,et al.Modulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3on human B cell differentiation[J].J Immunol,2007,179(3):1634-1647.
[12] Lemire JM,Adams JS,Kermani-Arab V,et al.1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3suppresses human T helper/inducer lymphocyte activity in vitro[J].J Immunol,1985,134(5):3032-3035.
[13] Hansdottir S,Monick MM,Hinde SL,et al.Respiratory epithelial cells convert inactive vitamin D to its active form:potential effects on host defense[J].J Immunol,2008,181(10):7090-7099.
[14] Hansdottir S,Monick MM,Lovan N,et al.Vitamin D decreases respiratory syncytial virus induction of NF-kappaB-linked chemokines and cytokines in airway epithelium while maintaining the antiviral state[J].J Immunol,2010,184(2):965-974.
[15] Damera G,Fogle HW,Lim P,et al.Vitamin D inhibits growth of human airway smooth muscle cells through growth factor-induced phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein and checkpoint kinase 1[J].Br J Pharmacol,2009,158(6):1429-1441.
[16] Keet CA,McCormack MC,Peng RD,et al.Age- and atopydepen-dent effects of vitamin D on wheeze and asthma[J].J Allergy Clin Immunol,2011,128(2):414-416.e5.
[17] Black PN,Scragg R.Relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and pulmonary function in the third national health and nutrition examination survey[J].Chest,2005,128(6):3792-3798.
[18] Li F,Peng M,Jiang L,et al.Vitamin D deficiency is associated with decreased lung function in Chinese adults with asthma[J].Respiration,2011,81(6):469-475.
[19] Sutherland ER,Goleva E,Jackson LP,et al.Vitamin D levels,lung function,and steroid response in adult asthma[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2010,181(7):699-704.
[20] Sandhu MS,Casale TB.The role of vitamin D in asthma[J].Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol,2010,105(3):191-199;quiz 200-2,217.
[21] Parikh SJ,Edelman M,Uwaifo GI,et al.The relationship between obesity and serum 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D concentrations in healthy adults[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2004,89(3):1196-1199.
[22] Taher YA,van Esch BC,Hofman GA,et al.1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3potentiates the beneficial effects of allergen immunotherapy in a mouse model of allergic asthma:role for IL-10 and TGF-beta[J].J Immunol,2008,180(8):5211-5221.
[23] 马雅心,戚好文.维生素D3联合地塞米松对哮喘大鼠的治疗作用及机制[J].第四军医大学学报,2008,29(15):1407-1409.
[24] Urry Z,Xystrakis E,Richards DF,et al.Ligation of TLR9 induced on human IL-10-secreting Tregs by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3abrogates regulatory function[J].J Clin Invest,2009,119(2):387-398.
[25] Banerjee A,Damera G,Bhandare R,et al.Vitamin D and glucocor-ticoids differentially modulate chemokine expression in human airway smooth muscle cells[J].Br J Pharmacol,2008,155(1):84-92.
Correlation between serum 25(OH)D3level and asthma control degree in adult patients with asthma
Ren Fangping,Liu Lingli,Yang Juanli,Wu Changgui
Department of Respiratory Disease,Xijing Hospital of the Fourth Military Medical University,Xi'an,Shanxi,710032,China
Objective To explore the correlation between serum 25(OH)D3level and improvement degrees of pulmonary function before and after the treatment in adult patients with asthma.Methods 95 patients diagnosed as moderate asthma were selected.Their concentration of serum 25(OH)D3was detected.They
inhalation with salmeterolticasone(50 μg /250 μg)(1 inhalation every 12 hours)for 3 months.Their basic pulmonary functions before and after the treatment were detected,such as the percentage of the forced expiratory volume at the first second in the predicted value(FEV1% pred)and the forced vital capacity(FEF25%-75%).The asthma control test(ACT)scores before and after the treatment were recorded.The correlations between serum 25(OH)D3concentration and the improvements in FEV1%pred,FEF25%-75%,and ACT sores were analyzed.Results Among the 95 cases,32 ones did not receive the follow-up on time;23 ones did not receive the treatment according to the physician's order;and 40 ones received the follow-up to the end of the study.There was positive correlation between serum 25(OH)D3concentration and the increases of FEV1% pred,FEF25%-75%,and ACT scores(P<0.01).Conclusion There is a positive correlation between serum 25(OH)D3concentration and the therapeutic reaction in adult patients with asthma.
asthma;25-hydroxyvitamin D3;pulmonary function;ACT score;correlation
710032 西安,第四军医大学西京医院呼吸内科
吴昌归,E-mail:changgui@fmmu.edu.cn
R 562.25
A
1004-0188(2014)02-0138-03
10.3969/j.issn.1004-0188.2014.02.008
2013-12-20)
