不同土壤管理措施下土团聚体的大小分布及其稳定性
2014-04-01杨学云孙本华张树兰
李 婕, 杨学云, 孙本华, 张树兰
(西北农林科技大学,农业部西北植物营养与农业环境重点实验室, 陕西杨凌 712100)


1 材料与方法
1.1 试验地概况

1.2 试验设计

1.3 样品采集与分析
2011年冬小麦收获后,将各小区划分为3部分,每个处理采集3个重复。采取0—10,10—20,20—30 cm土层的原状土。将采集的原状土样在室内沿自然结构轻轻掰成小土块,过10 mm筛,自然风干,备用。


1.4 数据处理
各大小机械稳定性或水稳性团聚体的含量(%)=各大小机械稳定或水稳性团聚体质量(g)/土壤样品总质量(g)×100,土壤团聚体稳定性以团聚体破坏率(PAD)衡量,参照陈山[16]的方法计算,公式如下:
PAD(%) =(Wd-Ww)/Wd×100
式中:Wd为机械稳定团聚体中>0.25 mm团聚体所占的比例;Ww为水稳性团聚体中>0.25 mm团聚体所占的比例。
不同土壤管理措施对团聚体的影响采用单变量方差分析,当方差分析结果显著时,采用LSD法进行处理间平均值的多重比较,所有数据采用SPSS 16.0进行分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 不同土壤管理措施对土团聚体分布的影响




表1 不同土壤管理措施下机械稳定团聚体的组成(%)Table 1 The composition of dry aggregates under different soil management practices
注(Note): 同列数据后不同字母表示同一层土壤不同管理模式间差异达5%显著水平 Values followed by different letters in a column are significant among management practices in the same soil layer at the 5% level.

表2 不同土壤管理措施下水稳性团聚体的组成(%)Table 2 The composition of water stable aggregates under different soil management practices
注(Note): 同列数据后不同字母表示同一层土壤不同管理模式间差异达5%显著水平 Values followed by different letters in a column are significant among management practices in the same soil layer at the 5% level.
2.2 长期施肥对土团聚体分布的影响


表3 长期不同施肥下不同土层土壤机械稳定团聚体的组成(%)Table 3 The composition of dry aggregates of different soil layer under different fertilizations
注(Note): 同列数据后不同字母表示同一层土壤不同处理间差异达5%显著水平 Values followed by different letters in a column are significant among treatments in the same soil layer at the 5% level.





2.3 不同土壤管理措施团聚体破坏率差异
表5显示,长期不同土壤管理措施对团聚体破坏率有很大的影响。在0—10 cm土层,与作物体系相比,休闲和撂荒显著降低了团聚体破坏率,并且休闲和撂荒之间没有显著差异。10—20 cm土层,撂荒措施的团聚体破坏率显著低于作物体系和休闲, 休闲与作物体系相似。20—30 cm土层,休闲、 撂荒与作物体系相比,团聚体破坏率均没有显著差异。
从表6可以看出,长期不同施肥对土壤团聚体破坏率有一定影响。0—10 cm土层,与CK处理相比,M1NPK显著降低了团聚体破坏率,而其它处理团聚体破坏率没有明显变化。10—20 cm土层,除NPK处理较CK的团聚体破坏率显著提高外,其它处理的团聚体破坏率也没有显著变化。20—30 cm土层,除NK、 NP较CK处理显著增加团聚体破坏率外,其它处理的团聚体破坏率也没有明显的变化。
3 讨论
3.1 不同土壤管理措施对团聚体分布的影响
不同土壤管理措施对土壤机械稳定性或水稳性团聚体分布的影响主要限于表层和亚表层(0—10,10—20 cm)(表1,表2),这可能主要与耕作扰动以及植物根系主要集中在该区域有关。


表4 长期不同施肥下不同土层土壤水稳性团聚体的组成(%)Table 4 The composition of water stable aggregates of different soil layer under different fertilizations
注(Note): 同列数据后不同字母表示同一层土壤不同处理间差异达5%显著水平 Values followed by different letters in a column are significant among treatments in the same soil layer at the 5% level.

表5 不同土壤管理措施下土壤团聚体破坏率(%)Table 5 The values of PAD under different soil management practices
注(Note): PAD—Percentage of soil aggregate disruption. 同列数据后不同字母表示同一层土壤不同管理模式间差异达5%显著水平 Values followed by different letters in a column are significant among management practices in the same soil layer at the 5% level.
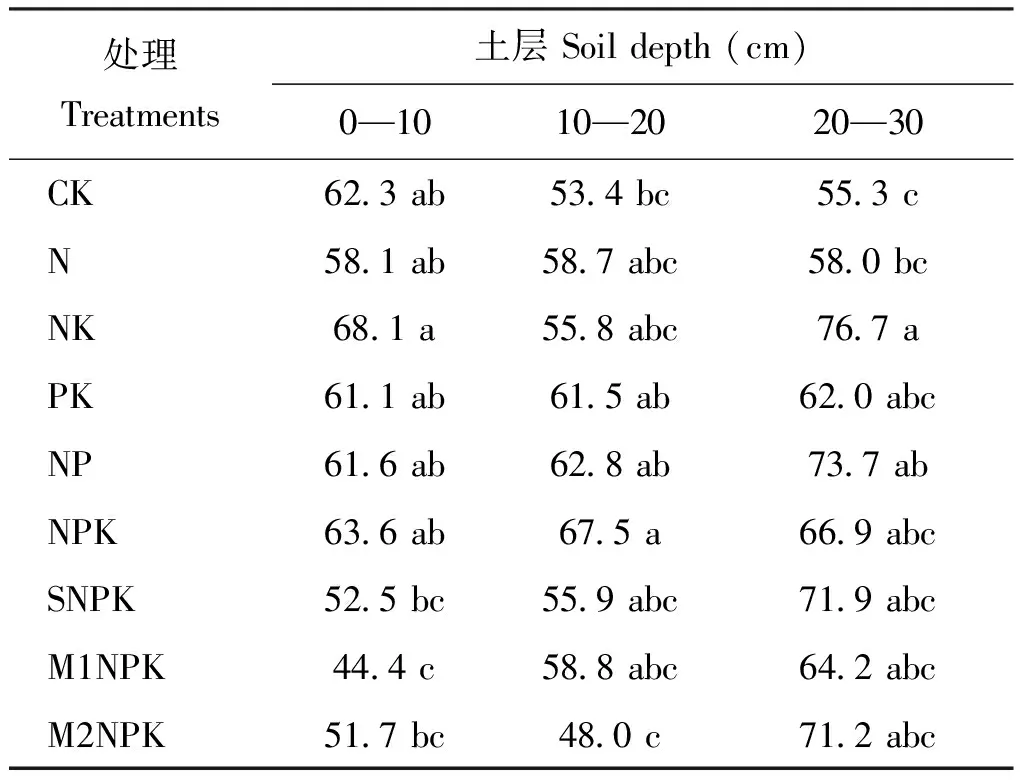
表6 长期不同施肥处理下土壤团聚体破坏率(%)Table 6 The values of PAD under different fertilizations
注(Note): PAD—Percentage of soil aggregate disruption. 同列数据后不同字母表示同一层土壤不同处理间差异达5%显著水平 Values followed by different letters in a column are significant among treatments in the same soil layer at the 5% level.
3.2 长期施肥对团聚体分布的影响

4 结论

参考文献:
[1] Pirmoradian N, Sepaskhah A R, Hajabbasi M A. Application of fractal theory to quantify soil aggregate stability as influenced by tillage treatments[J]. Biosyst. Eng., 2005, 90 (2): 227-234.
[2] Six J, Bossuyt H, Degryze S, Denef K. A history of research on the link between (micro) aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics[J]. Soil Till. Res., 2004, 79: 7-31.
[3] 高飞, 贾志宽, 韩清芳, 等. 有机肥不同施用量对宁南土壤团聚体粒级分布和稳定性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2010, 28(3): 100-106.
Gao F, Jia Z K, Han Q Fetal. Effects of different fertilizer treatments on distribution and stability of soil aggregates in the semiarid area of south Ningxia[J]. Agric.Res. Arid Areas, 2010, 28(3): 100-106.
[4] 戴珏, 胡君利, 林先贵, 等. 免耕对潮土不同粒级团聚体有机碳含量及微生物碳代谢活性的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2010, 47(5): 923-929.
Dai J, Hu J L, Lin X Getal. Effects of non-tillage on content of organic carbon and microbial carbolic metabolism of soil aggregates in a Fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2010, 47(5): 923-929.
[5] 刘恩科, 赵秉强, 梅旭荣, 等. 不同施肥处理对土壤水稳定性团聚体及有机碳分布的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(4): 1035-1041.
Liu E K, Zhao B Q, Mei X Retal. Distribution of water-stable aggregates and organic carbon of arable soils affected by different fertilizer application[J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2010, 30(4): 1035-1041.
[6] 霍琳, 武天云, 蔺海明, 等. 长期施肥对黄土高原旱地黑垆土水稳性团聚体的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(3): 545-550.
Huo L, Wu T Y, Lin H Metal. Effects of long-term fertilization on water-stable aggregates in calcic kastanozem of Loess Plateau[J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2008, 19 (3): 545- 550.
[7] 汪景宽, 冷延慧, 于树, 等. 不同施肥处理下棕壤有机碳库对团聚体稳定性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2009, 40(1): 77-80.
Wang J K, Leng Y H, Yu Setal. Effect of SOC pool on aggregate stability in brown earth under different fertilizations[J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2009, 40(1): 77-80.
[8] 苗淑杰, 周连仁, 乔云发, 等. 长期施肥对黑土有机碳矿化和团聚体碳分布的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2009, 46(6): 1068-1075.
Miao S J, Zhou L R, Qiao Y Fetal. Organic carbon mineralization and carbon distribution in aggregates as affected by long-term fertilization in black soil[J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2009, 46(6): 1068-1075.
[9] 周萍, 潘根兴. 长期不同施肥对黄泥土水稳性团聚体颗粒态有机碳的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2007, 38(2): 256-261.
Zhou P, Pan G X. Effect of different long-term fertilization treatments on particulate organic carbon in water-stable aggregates of a paddy soil[J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2007, 38(2): 256-261.

Liu J, Wang Y Q, Wang Yetal. Evolution of physical properties in Lou soil with long-term fertilization[J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2004, 35(5): 542-545.
[11] 祁迎春, 王益权, 刘军. 关中地区土壤团聚体组成特征及稳定性研究[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2011, (5): 66-69.
Qi Y C, Wang Y Q, Liu J. The study on the composition and stability of soil aggregates in Guanzhong area[J]. Shaanxi Agric. Sci., 2011, (5): 66-69.
[12] 王勇, 姬强, 刘帅, 等. 耕作措施对土壤水稳性团聚体及有机碳分布的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(7): 1365-1373.
Wang Y, Ji Q, Liu Setal. Effects of tillage practices on water-stable aggregation and aggregate-associated organic C in soils[J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2012, 31(7): 1365-1373.
[13] 孙汉印, 姬强, 王勇, 等. 不同秸秆还田模式下水稳性团聚体有机碳的分布及其氧化稳定性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(2): 369-376.
Sun H Y, Ji Q, Wang Yetal. The distribution of water-stable aggregate -associated organic carbon and its oxidation stability under different straw returning modes[J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2012, 31(2): 369-376.
[14] 中国科学院南京土壤研究所. 土壤理化分析[M].上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1978.
Nanjing Soil Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Physical and chemical analysis of soil[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1978.
[15] Yoder R E. A direct method of aggregate analysis of soils and a study of the physical nature of erosion losses[J]. Agron. J., 1936, 28: 337-351.
[16] 陈山, 杨峰, 林杉, 等. 土地利用方式对红壤团聚体稳定性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2012, 26(5): 211-216.
Chen S, Yang F, Lin Setal. Impact of land use patterns on stability of soil aggregates in red soil region of south China[J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2012, 26(5): 211-216.
[17] Bronick C J, Lal R. Soil structure and management: a review[J]. Geoderma, 2005, 124: 3-22.
[18] Boix-Fayos C, Calvo-Cases A, Imeson A C, Soriano-Soto M D. Influence of soil properties on the aggregation of some Mediterranean soils and the use of aggregate size and stability as land degradation indicators[J]. Catena, 2001, 44(1): 47-67.
[19] Bouajila A, Gallali T. Soil organic carbon fractions and aggregate stability in carbonated and no carbonated soils in Tunisia[J]. J. Agron., 2008, 7: 127-137.
[20] Virto I, Gartzia-Bengoetxea N. Fernandez-Ugalde O. Role of organic matter and carbonates in soil aggregation estimated using laser diffractometry[J]. Pedosphere, 2011, 21(5): 566-572.

Wang L L, Zhang S L, Yang X Y. Soil carbon storage affected by long-term land use and fertilization regimes in manural loess soil[J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2013, 19(2): 404-412.
[22] Yang X, Ren W, Sun B, Zhang S. Effects of contrasting soil management regimes on total and labile soil organic carbon fractions in a loess soil in China[J]. Geoderma, 2012, 177-178: 49-56.
[23] Jastrow J D, Miller R M, Lussenhop J. Contributions of interacting biological mechanisms to soil aggregate stabilization in restored prairie[J]. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30: 905- 916.
[24] 杨茹萍, 郭贤仕, 吕军峰, 等. 不同耕作和种植模式对土壤团聚体分布及稳定性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(1): 252-256.
Yang R P, Guo S X, Lü J Fetal. Distribution and stability of soil aggregate as affected by different patterns of tillage and cropping[J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2010, 24(1): 252-256.
[25] 冷延慧, 汪景宽, 李双异. 长期施肥对黑土团聚体分布和碳储量变化的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2008, 27(12): 2171-2177.
Leng Y H, Wang J K, Li S Y. Effects of long-term fertilization on aggregates size distribution and carbon stock in black soil[J]. Chin. J. Ecol., 2008, 27(12): 2171-2177.
Ge W J, Chang Y L, Liu J Metal. Potassium balance and pool as influenced by long-term fertilization under continuous winter wheat-summer maize cropping system in a manural loess soil[J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2012, 18(3): 629-636.

Li Z J, Li P R, Shi Y G, Zhang S L. Effects of long-term fertilization mangement regimes on availability of soil micronutrients element[J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2010, 16(6): 1456-1463.
