Solubility of Emodin in Alcohols*
2009-05-12Yangcheng吕阳成LINQuan林泉LUOGuangsheng骆广生andDAIYouyuan戴猷元
LÜ Yangcheng (吕阳成), LIN Quan (林泉), LUO Guangsheng (骆广生) and DAI Youyuan (戴猷元)
Solubility of Emodin in Alcohols*
LÜ Yangcheng (吕阳成)**, LIN Quan (林泉), LUO Guangsheng (骆广生) and DAI Youyuan (戴猷元)
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Emodin is a kind of anthraquiones with pharmaceutical activities. The solubilities of emodin in ethanol, 1-octanol, and ethanol+1-octanol at different temperatures were measured using an analytical method. The solubility of emodin in these solvents increased with an increase in temperature. With the temperature deviating from room temperature, the dependence of the solubility of emodin on temperature became a lot more remarkable. The solubility of emodin in ethanol was more sensitive to temperature than that in 1-octanol. The solubility data of emodin in the same species of solvent at different temperatures was correlated with an empirical equation. The calculated results agreed with the experimental data well.
solubility, emodin, ethanol, 1-octanol
1 INTRODUCTION
Emodin, as one kind of anthraquinone, is abundant with active components in Rhubarb,,and other herbs that are used widely around the world [1, 2]. The reported pharmacological and biological actions of emodin include purgation, anti-cancer, antibacterial, and enhancing the nucleotide excision repair of UV/cisplatin-induced DNA damage in human cells [3, 4].
Emodin is mainly obtained from herb extraction with different organic solvents or their mixtures. For pharmaceutical use, these constituents, with no pharmacological activity, need to be removed selectivelysolvent extraction and must follow purification steps. In herbs, emodin always coexists with other anthraquinone derivatives, for example, aloe-emodin, rhein, physcion, and chrysophanol [5]. Further biochemical, pharmaceutical, and clinical research on each component needs precise isolation methods such as, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), thin-layer chromatography (TLC), high-speed counter- current chromatography (HSCCC) [6]. All these separation processes involve the use of organic solvents. Therefore, it is important to have thermodynamic data for the solubility of emodin in various solvents in order to select a proper solvent or to simulate and design these separation processes.
Alcohols are solvents frequently used in the pharmaceutical industry. In the present study, the solubility of emodin in ethanol, 1-octanol, and ethanol+1-octanol has been measured using an analytical method. The effect of solvent composition and temperature on solubility is discussed. The solubility data is correlated with an empirical equation.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
2.1 Reagents and apparatus
Emodin (C15H10O5) was purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA), as a standard for HPLC, and was used without further purification. Other reagents were of analytical grade. Ethanol, 2-propanol, and 1-octanol were from the Beijing Chemical Reagent Co. Water was redistilled and ion-exchanged with a Millipore system (Bedford, MA, USA).
The emodin concentration in the solution was determined by an HP1050 high performance liquid chromatograph (HPLC). An HZS-H thermostat oscillator (Donglian, China) was used to control the dissolution temperature within ±0.1 K. An STA409 C/3/F thermoanalyzer (NETZSCH, Germany) was used to determine the melting point. The measured melting point of emodin was (531.28±0.5) K. Fig. 1 shows the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curve of emodin.
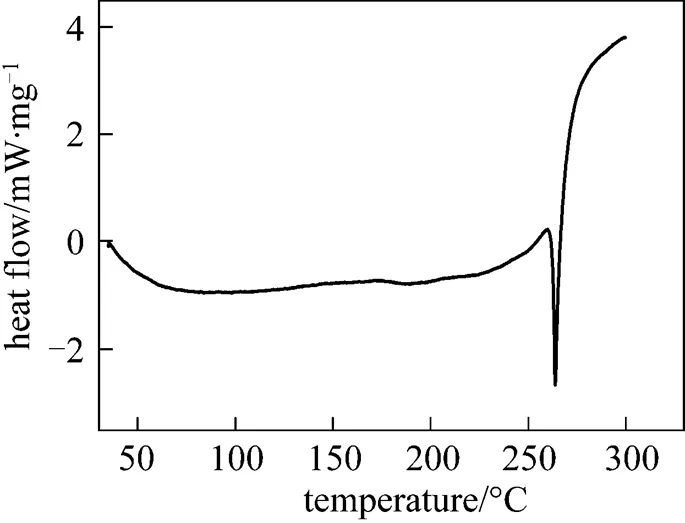
Figure 1 The DSC curve of emodin
2.2 Measurement procedure and sample analysis
An excess amount of solute (emodin) was added to the solvent in a sealed vial. The vial was fixed on a bracket located within the thermostat oscillator, in which the solid + liquid mixture was constantly oscillated at the desired temperature, for 12 h, to attain equilibrium. Subsequently the solution was allowed to settle for 2 h, and the upper portion was taken for analysis.
HPLC analysis was performed using an ODS C18column (4.6 mm×150 mm, 5 μm) by an external standard method. The mobile phase was methanol + water + phosphoric acid, with volume fraction 85︰15︰1. The HPLC conditions were set as follows: the wavelength of determination 278 nm; the column temperature 30ºC; the flow rate of the mobile phase was 1.0 ml·min-1. The uncertainty of measurement of the concentration of emodin was less than 2%.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION

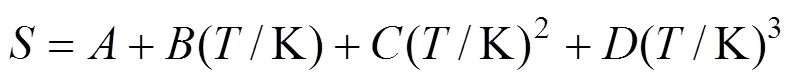
whereis the mole fraction solubility of emodin,is the absolute temperature, and,,andare the parameters. Calculated solubility values of emodin are also given in Tables 1 and 2. The values of parameters,,,and the root-mean-square deviations (rmsd) are listed in Table 3. The rmsd is defined as [7]

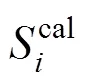

Table 1 Mole fraction solubility xw of emodin in pure solvents
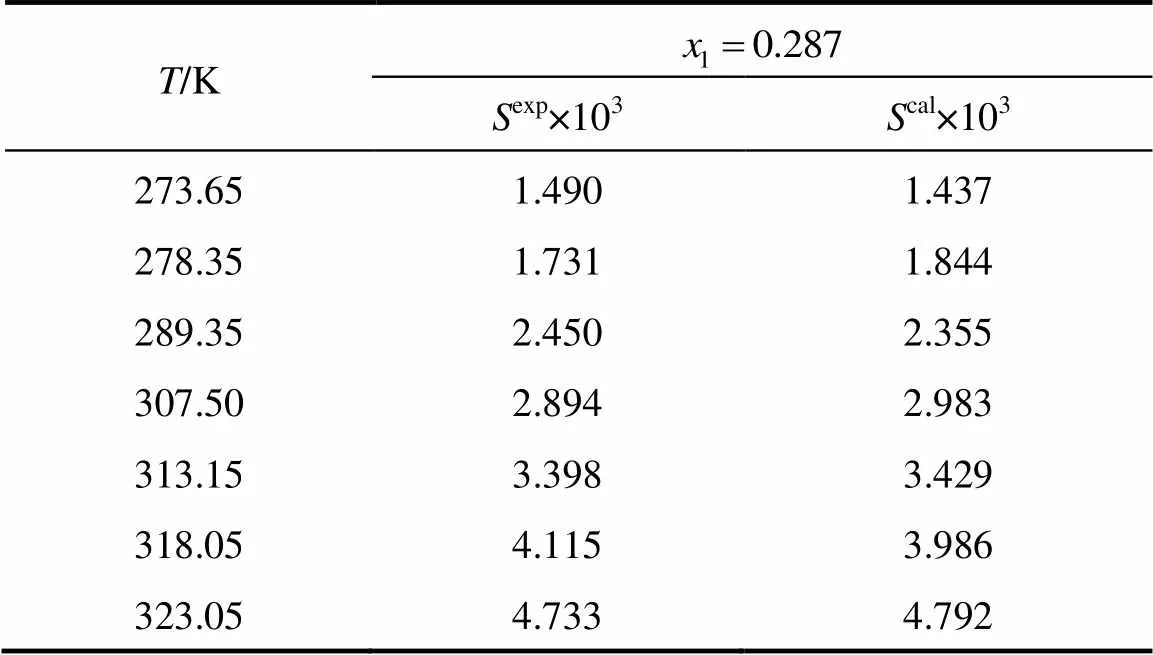
Table 2 Mole fraction solubility of emodin in ethanol (1)+1-octanol (2)


Table 3 Parameters of Eq. (1) for emodin in different solvents
4 CONCLUSIONS
The solubilities of emodin in ethanol, 1-octanol, and ethanol+1-octanol at different temperatures were measured using the analytical method. The solubility of emodin in these solvents increased with an increase in temperature. With the temperature deviating from room temperature, the dependence of the solubility of emodin on temperature became a lot more remarkable. The solubility of emodin in ethanol was more sensitive to temperature than that in 1-octanol. The solubility data of emodin in all these solvents at different temperatures was correlated with an empirical equation. The calculated results agreed well with the experimental data.
1 Tian, K., Zhang, H.G., Chen, X.G., Hu, Z.D., “Determination of five anthraquinones in medicinal plants by capillary zone electrophoresis with β-cyclodextrin addition”,.., 1123, 134-137 (2006).
2 Koyama, J., Morita, I., Kobayashi, N., “Simultaneous determination of anthraquinones in rhubarb by high-performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis”,.., 1145, 183-189(2007).
3 Wang, L.P., Zhang, Z.P., Ye, B.X., “Study on the electrochemical behaviour of the anticancer herbal drug emodin”,., 51, 5961-5965 (2006).
4 Lu, H.M., Ni, W.D, Liang, Y.Z., Man, R.L., “Supercritical CO2extraction of emodin and physcion from polygonum cuspidatum and subsequent isolation by semipreparative chromatography”,..., 29, 2136-2143 (2006).
5 Singh, N.P., Gupta, A.P., Sinha, A.K., Ahuja, P.S., “High-performance thin layer chromatography method for quantitativedetermination of four major anthraquinone derivatives in”,.., 1077, 202-206 (2005).
6 Zhang, H.X., Liu, M.C., “Separation procedures for the pharmacologically active components of rhubarb”,.., 812, 175-181 (2004).
7 Hao, H.X., Hou, B.H., Wang, J.K., Zhang, M.J., “Solubility of erythritol in different solvents”,..., 50, 1454-1456 (2005).
2008-04-23,
2008-12-01.
the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20406008).
** To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: luyc@tsinghua.edu.cn
杂志排行
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Design and Performance Analysis of Micro Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells*
- Isolation of Cordyceps ophioglossoides L2 from Fruit Body and Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for Its Mycelial Growth*
- Efficient and Comprehensive Utilization of Hemicellulose in the Corn Stover*
- Simulating Surface Aeration Systems at Different Scale of Mixing Time*
- Kinetics of Reaction-Crystallization of Struvite in the Continuous Draft Tube Magma Type Crystallizers—Influence of Different Internal Hydrodynamics
- Preparation and Characterization of Tungsten-substituted Molybdophosphoric Acids and Catalytic Cyclodehydration of 1,4-Butanediol to Tetrahydrofuran*
