腹腔镜胃癌根治术患者术后肺部感染与影响因素分析
2021-08-18朱根英吴辰魏云海徐永灿
朱根英 吴辰 魏云海 徐永灿

[关键词] 腹腔镜;胃癌根治术;肺部感染;影响因素
[中图分类号] R735.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)19-0007-03
Analysis on postoperative pulmonary infection and influencing factors in the patients undergoing laparoscopic radical gastrectomy of gastric cancer
ZHU Genying WU Chen WEI Yunhai XU Yongcan
Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery,Huzhou Central Hospital in Zhejiang Province,Affiliated Hospital of Huzhou Normal University, Huzhou 313000, China
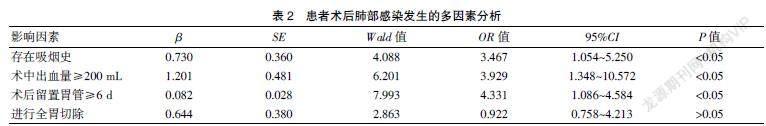
[Abstract] Objective To explore postoperative lung infection and influencing factors in the patients undergoing laparoscopic radical gastrectomy of gastric cancer. Methods A total of 186 patients who underwent laparoscopic radical gastrectomy of gastric cancer in our hospital from January 2018 to December 2018 were selected as the research subjects.The basic data of all gastric cancer patients were investigated and statistically analyzed. A single factor and multi-factor analysis were also carried out on those data. Results 19 of all patients had lung infections, with the infection incidence rate of 10.2%. Among them, the incidence rate of pulmonary infections in the patients with a history of smoking,gastric tube indwelling time ≥6 days, intraoperative blood loss ≥200 mL, and experience of total gastrectomy were higher than the patients with no past history of smoking, postoperative gastric tube indwelling time <6 days, intraoperative blood loss<200 mL and no experience of total gastrectomy(P<0.05); a past smoking history,bleeding volume ≥200 mL, and postoperative gastric tube indwelling time≥6 days were all independent risk factors for postoperative lung infections in the patients undergoing gastrectomy of gastric cancer(P<0.05). Conclusion A past smoking history, intraoperative blood loss ≥200 mL,and postoperative gastric tube indwelling time≥6 days are independent risk factors for lung infections after laparoscopic radical gastrectomy of gastric cancer. A detailed understanding of the patient′s physical condition and targeted guidance before surgery can help avoid or reduce the incidence of postoperative lung infections.
[Key words] Laparoscopy; Radical gastrectomy of lung cancer; Lung infection; Influencing factors
目前,胃癌是臨床中较为常见的恶性肿瘤,根治性手术切除仍是对该类患者进行治愈的唯一手段[1]。与传统的开腹手术比较,腔镜手术的安全性及临床效果均相对较好,并具有微创特征[2]。近年来,随着手术技术的进步及围手术期处理的改善,胃癌根治术后患者并发症发生率明显降低,但肺部感染仍较为常见,致使患者住院时间延长,医疗费用增加,病情严重者呼吸功能衰竭或者死亡,对其生活质量产生严重影响[3-4]。因此,通过对肺部感染的危险因素进行有效分析,有助于采取有效预防措施促进患者病情恢复[5]。本研究分析腔镜胃癌根治术患者的临床资料,并对其术后发生肺部感染的危险因素进行探讨,现报道如下。
