基于多水平模型的高血压患者住院费用及其影响因素分析
2020-09-06邓晓兰马维红夏行王禹
邓晓兰 马维红 夏行 王禹

摘要:目的 基于多水平模型分析高血壓患者住院费用及影响因素,为完善医疗保障措施提供参考。方法 选择2013~2016年某三级甲等综合医院收治的1942例高血压患者作为研究对象,收集患者临床资料,分析高血压患者住院天数及住院费用情况、住院费用构成情况,并采用单因素分析及多水平模型分析住院费用的影响因素,采用Pearson相关性分析住院费用与住院天数的关系。结果 2013~2016年,高血压患者的平均住院天数逐年减少,而住院费用总体呈上升趋势。住院总费用中排前4位的分别是西药费、影像学检查费、化验费和诊疗费,占比33.32%、18.14%、17.59%和10.79%,其中西药费占比呈下降趋势,而影像学检查费占比逐年上升。单因素分析显示,不同性别、主管医师级别间住院费用比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);不同住院时间、年龄、医疗付款方式、入院情况、高血压分类、手术情况、合并症情况、出院科室间住院费用比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Pearson相关性分析显示,住院天数与住院费用呈正相关(r=0.438,P=0.000);多水平模型分析显示,住院时间、出院科室、高血压分类、医疗付款方式、入院情况、手术情况、合并症比况、住院天数是住院费用的影响因素。结论 住院费用受多种因素影响,其中西药费、影像学检查费、化验费、诊疗费占比较高,并于住院天数呈正相关关系,而住院时间、出院科室、高血压分类、医疗付款方式、入院情况、手术情况、合并症情况、住院天数与住院费用密切相关,因此在诊疗过程中,合理安排检查和治疗,规范用药,积极治疗原发病及合并症,在保证有效治疗的前提下尽量减少住院天数,可降低患者的住院费用。
关键词:高血压,住院费用,影响因素
中图分类号:R544.1 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.15.019
文章编号:1006-1959(2020)15-0057-05
Abstract:Objective To analyze the hospitalization expenses and influencing factors of patients with hypertension based on a multilevel model, and provide a reference for improving medical security measures.Methods 1942 hypertension patients admitted to a tertiary general hospital from 2013 to 2016 were selected as the research objects. The clinical data of the patients were collected, and the hospitalization days, hospitalization expenses, and composition of hospitalization expenses were analyzed by single factor analysis. And a multilevel model was used to analyze the influencing factors of hospitalization expenses, and Pearson correlation was used to analyze the relationship between hospitalization expenses and hospitalization days. Results From 2013 to 2016, the average length of hospitalization for hypertensive patients decreased year by year, while the hospitalization expenses showed an overall upward trend. The top four in the total hospitalization costs are Western medicine, imaging examination fees, laboratory tests and diagnosis and treatment fees, accounting for 33.32%, 18.14%, 17.59% and 10.79%. The proportion of Western medicine expenses is decreasing, while imaging the proportion of tuition inspection fees has increased year by year. Univariate analysis showed that there was no statistically significant difference in hospitalization expenses between different genders and levels of physicians in charge (P>0.05); different length of stay, age, medical payment methods, admission status, hypertension classification, surgery status, and comorbidities,comparison of hospitalization expenses among discharge departments was statistically significant (P<0.05); Pearson correlation analysis showed that the length of stay was positively correlated with hospitalization expenses (r=0.438,P=0.000); multi-level model analysis showed that length of stay,discharge department, hypertension classification, medical payment method, admission status, surgical status, comorbidity ratio, and length of stay are the influencing factors of hospitalization expenses. Conclusion Hospitalization expenses are affected by many factors, among which western medicine fees, imaging examination fees, laboratory fees, and diagnosis and treatment fees account for a relatively high proportion, and are positively correlated with the number of days of hospitalization. The length of hospitalization, discharge department, hypertension classification, medical payment method,hospital admission, surgery, comorbidities, and length of stay are closely related to hospitalization expenses. Therefore, in the diagnosis and treatment process, reasonable arrangements for examination and treatment, standardized medication, and active treatment of the primary disease and comorbidities, as far as possible under the premise of ensuring effective treatment reducing the number of days in the hospital can reduce the expenses of hospitalization for patients.
Key words:Hypertension,Hospitalization expenses,Influencing factors
高血压(hypertension)是最常见的慢性非传染性疾病,同时也是心脑血管疾病最主要的危险因素。有研究表明[1,2],高血压为伤残调整生命年(disability-adjusted life-years,DALYs)前3位的主要危险因素之一,2013年高血压导致了全球1040万人死亡。我国现有高血压患者2.45亿,成人高血压患病率为27.9%[3,4],高血压及其并发症产生的医疗费用给国家和个人带来了沉重的负担,研究表明[5],高血压是全球疾病负担的主要危险因素。本文旨在运用多水平模型的统计学方法对高血压患者的住院费用及其影响因素进行分析,为完善医疗保障措施提供参考,为控制医疗费用的上涨提供科学依据,现报道如下。
1对象与方法
1.1研究对象 回顾性分析2013年1月1日~2016年12月31日某三级甲等综合医院诊断为高血压的住院患者1942例作为研究对象。纳入标准:病案首页中第一诊断为高血压的原发性高血压病例。排除标准:①继发性高血压病例;②病案首页中第一诊断为高血压但资料不全的原发性高血压病例。
1.2方法
1.2.1数据收集 采用整群抽样和回顾性调查的方法收集资料,内容主要来自病案首页,包括姓名、性别、年龄、入院情况、住院时间、出院科室、出院诊断、手术情况、合并症情况、主管医师级别、住院总费用、各项费用明细及医疗付款方式等。
1.3统计学方法 采用Excel 2007进行原始数据录入,并进行数据整理、归纳,采用SPSS 18.0统计软件进行数据分析。将高血压患者住院费用进行正态性检验,不符合正态分布者将住院费用进行对数转换,数据仍不符合正态分布,采用秩和检验方法,运用Pearson相关性检验方法对住院费用和住院天数进行分析。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2.1高血压患者的基本情况 共收集高血压患者病例1942例,其中男性951例(48.97%),女性991例(51.03%);年龄15~97岁,中位数年龄为62岁。
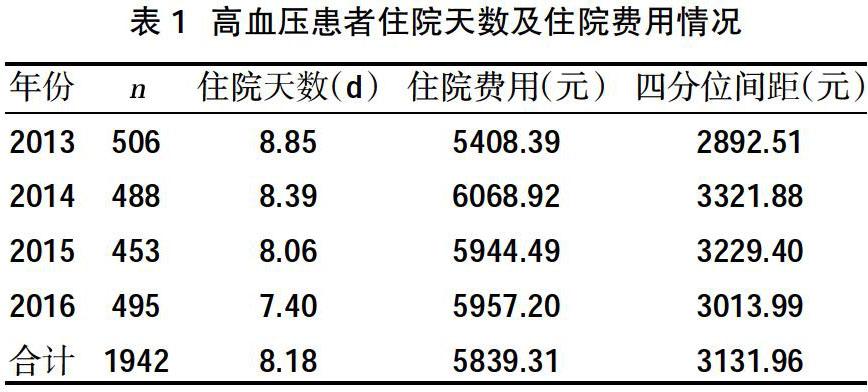
2.2高血压患者住院天数及住院费用情况 2013~2016年,高血压患者的平均住院天数逐年减少,而住院费用总体呈上升趋势,见表1。
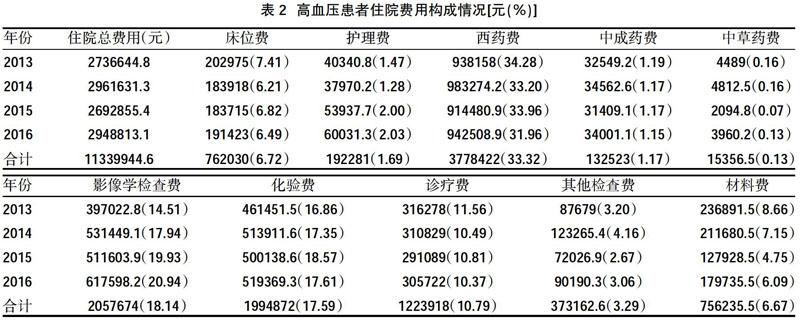
2.3高血压患者住院费用构成情况 住院总费用中排前4位的分别为西药费、影像学检查费、化验费和诊疗费,其中西药费占比呈下降趋势,而影像学检查费占比逐年上升,见表2。
2.4单因素分析住院费用的影响因素 不同性别、主管医师级别间住院费用比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);不同住院时间、年龄、医疗付款方式、入院情况、高血压分类、手术情况、合并症情况、出院科室间住院费用比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表3。
2.5 Pearson相关性分析住院费用与住院天数的关系 住院天数与住院费用呈正相关(r=0.438,P=0.000)。
3讨论
高血压是慢性疾病,目前尚不能根本治愈,需要长期服药治疗,因此,加强高血压的健康宣教、普及科学的健康知识、倡导健康的生活方式,并开展心血管疾病高危因素的初筛检查,对于早期发现高血压高危人群并降低高血压的发病率,减轻高血压的疾病负担具有重要意义[8]。
本研究结果显示,共收集高血压患者病例1942例,2013~2016年高血压患者住院费用总体呈上升趋势,2016年例均住院费用较2013年增加约500.00元,而平均住院天数逐年减少,由8.85 d降至7.40 d。在住院费用中,西药费占比最高,其次为影像学检查费和化验费,这3种费用之和占住院总费用近70%,是住院费用上涨的重要影响因素,而诊疗费、护理费等体现医务人员工作价值的费用占比较低,二者之和仅为住院总费用的12.48%,提示①提高诊疗费、护理费等医疗服务费用,一方面可以更好地体现医务人员的工作价值,另一方面也可以调整住院费用的构成,使其更加合理;②合理规范地用药,加强药品流通环节的监管,降低虚高的药价,有助于控制住院费用的增长;③如今的互联网科技十分发达,可通过建立医院互联网系统,建立健康档案,实现资源共享,让医生在接诊患者时更全面地了解患者的基本情况,减少重复的检查或化验,降低检查费或化验费,进而减少住院费用[9]。
本研究结果表明,住院天数与住院费用呈正相关(r=0.438,P=0.000),即住院天数越长,住院费用越高。住院天数延长,床位费、护理费、诊疗费等费用随之增加,进而引起住院总费用相应的上涨。因此,在保证治疗效果的情况下,缩短平均住院天数,可减少患者重复感染或院内感染的机会,降低患者的医疗费用,减轻患者的经济负担,同时,也有助于促使医院提高医疗效率,更充分有效地利用医疗资源。不同医疗付款方式的患者,住院费用各有不同,其中公费医疗的患者住院费用最高,商业医疗保险者次之,二者的住院费用高于其他付款方式的患者,其原因可能是这些患者的住院费用可以由国家或者商业医疗保险报销,不需考慮经济情况,故而在住院时会相对多做一些检查或用一些较贵的药物,从而使得公费医疗及商业医疗保险的患者住院费用高于其他患者。合并症也是住院费用的影响因素之一,有合并症的患者,病情相对复杂,在治疗过程中,还需兼顾其他疾病,且住院时间也相对延长,住院费用高于无合并症的患者,且合并症越多,住院费用越高。因此,在高血压的治疗中,需向患者强调高血压并发症的严重性,督促患者规律服用降压药,按照诊疗规范治疗,提高患者的依从性,减少并发症的发生,降低并发症的致残率和致死率,进而减轻高血压的疾病负担。入院情况对住院费用有一定影响,当患者病情较为复杂时,患者的检查费及化验费用有所增加,疾病确诊时间延长,进而引起住院天数延长,住院费用随之增加;当患者病情危重时,所用药物也相对较好、较贵,而住院天数也会延长,故住院费用增加。而进行手术的患者住院费用高于无手术者,可能与其需要更多的医疗服务,导致检查费、药费、材料费等较普通患者升高有关。不同高血压分类的患者住院费用有一定差别,其中以高血压危象的患者费用最高,当出现高血压危象时,患者病情复杂且危重,治疗难度相对增加,故住院费用较高。不同出院科室的患者住院费用各有不同,以中医科的住院费用最低,可能与中医药治疗的成本相对较低有关。
综上所述,住院费用受多种因素影响,其中西药费、影像学检查费、化验费、诊疗费占比较高,并与住院天数呈正相关关系,而住院时间、出院科室、高血压分类、医疗付款方式、入院情况、手术情况、合并症情况、住院天数与住院费用密切相关,因此在诊疗过程中,合理安排检查和治疗,规范用药,积极治疗原发病及合并症,在保证有效治疗的前提下尽量减少住院天数,可降低患者的住院费用。
参考文献:
[1]GBD 2013 Risk Factors Collaborators,Forouzanfar MH,Alexander L,et al.Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013[J].Lancet,2015,386(10010):2287-2323.
[2]GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators.Global,regional,and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural,environmental and occupational,and metabolic risks or clusters of risks,1990-2016:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016[J].Lancet,2017,390(10100):1345-1422.
[3]胡盛寿,高润霖,刘力生,等.《中国心血管病报告2018》概要[J].中国循环杂志,2019,34(3):209-220.
[4]Wang Z,Chen Z,Zhang L,et al.Status of hypertension in China: results from the China Hypertension Survey,2012-2015[J].Circulation,2018,137(22):2344-2356.
[5]Lim SS,Vos T,Flaxman AD,et al.A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions,1990–2010:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010[J].Lancet,2012(380):2224-2260.
[6]孫振球,徐勇勇,医学统计学[M].第4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2014:352-368.
[7]石磊,向其凤,鲁筠.多水平模型及其在经济分析中的应用[J].数学建模及其应用,2016,5(1):3-8,27.
[8]国务院办公厅.中国防治慢性病中长期规划(2017-2025年)[EB/OL].http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-02/14/content_5167886.htm
[9]叶俊,刘琴,陈坤福.基于健康档案的区域医疗信息平台建设与应用[J].中国医疗设备,2018,33(7):131-134.
收稿日期:2020-04-21;修回日期:2020-05-21
编辑/杜帆
