系统性红斑狼疮治疗领域文献的大数据分析
2019-01-06陈汉白赵之婧罗希莹熊豫麟
陈汉白 赵之婧 罗希莹 熊豫麟
摘要:目的 梳理PubMed醫学文献检索服务系统和Web of Science数据库中近40年来有关系统性红斑狼疮治疗领域文献的基本情况。方法 检索PubMed及Web of Science数据库中有关系统性红斑狼疮治疗领域的文献,检索时间1978年1月1日~2017年 12月31日。利用NoteExpress软件和GoPubMed分析文献的发表时间、刊载期刊、文献篇名、摘要、关键词、发文作者、发文作者单位、年文献量、期刊载文量、高频词、发文作者团队、发文国家和地区分布的特点。结果 共检索到文献10892篇,年文献量呈现稳步增长的趋势;文献分布在9943种期刊上,影响因子最高的期刊是New England Journal of Medicine;共有9667位作者发表相关文献,其中Hughes G发文60篇,位居第1,发文50篇以上的作者有3位,40篇以上的有7位;该领域形成了6个不同的团队,研究方向有所不同;全球共有110个国家和地区在关注该领域的研究,发文量中国大陆位居第4。结论 SLE治疗领域一直有研究团队持久关注,年文献量呈现稳步增长的变化,目前该领域形成了6个不同的研究团队,发文量中国大陆位居第4,说明我国科研实力显著增强,该疾病在亚洲人群中高发可能是形成研究热点的原因之一。
关键词:系统性红斑狼疮;大数据;文献计量学;PubMed;Web of Science
中图分类号:R593.24;G353.1 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2019.23.001
文章编号:1006-1959(2019)23-0001-07
Big Data Analysis of Literature in the Field of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Treatment
CHEN Han-bai1,ZHAO Zhi-jing2,LUO Xi-ying3,XIONG Yu-lin3
(1.Department of Foreign Languages,Kunming Medical University,Kunming 650500,Yunnan,China;
2.Department of Thyroid Breast Surgery,the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University,Kunming 650223,
Yunnan,China;
3.Library of Kunming Medical University,Kunming 650500,Yunnan,China)
Abstract:Objective To sort out the basic information about the literature on the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus in the PubMed medical literature retrieval service system and Web of Science database for nearly 40 years. Methods To search the literature on the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus in PubMed and Web of Science databases from January 1, 1978 to December 31, 2017. Use NoteExpress software and GoPubMed to analyze the publication time, published journals, document titles, abstracts, keywords, authors, authors, annual literature, journals, high-frequency words, authors, and countries. Characteristics of regional distribution.Results A total of 10,892 articles were retrieved, and the annual literature volume showed a steady growth trend; the literature was distributed in 9,943 journals, and the journal with the highest impact factor was New England journal of medicine; a total of 9,667 authors published relevant literature, of which Hughes G issued 60 articles. Ranked first, there are 3 authors who have published more than 50 articles, and 7 of 40 or more. There are 6 different teams in the field, and the research direction is different. 110 countries and regions around the world are paying attention to this. In the field of research, the number of publications in China is ranked fourth.Conclusion The SLE treatment field has always had a long-term attention from the research team, and the annual literature volume has shown steady growth. At present, there are 6 different research teams in the field, and the number of publications in China is ranked fourth, indicating that the scientific research strength of China is significantly enhanced. High incidence in Asian populations may also be one of the reasons for the formation of research hotspots.
Key words:Systemic lupus erythematosus;Big data;Bibliometrics;PubMed;Web of Science
系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)是一种病因未明的,全身多系统受损的慢性自身免疫性疾病。以自身抗体的产生和免疫复合物的沉积为主要病理特征,形成的免疫复合物沉积在各组织,导致皮肤、关节、肾脏、肺部、神经系统、浆膜和其他器官的损伤,其临床表现多样,如皮肤的蝶形红斑、皮肤血管炎、关节痛、关节炎、关节畸形、肾炎、肾病综合征等。有些患者症状反复出现,严重影响生活质量,病情严重者会累积肾脏、脑部,甚至出现狼疮危象,如果不给予适当治疗病情会加速进展,甚至死亡。SLE在世界范围内均有出现,全球平均患病率为12/10万~39/10万,亚洲人及黑人患病率高于白种人。该疾病有明显的性别倾向,累及男女之比为1∶7~1∶9,发病年龄以20~40岁为主[1]。我国患病率为30.13/10万~70.41/10万,在全世界的种族中,汉族人SLE发病率位居第2。临床治疗SLE多为缓解症状,尚无根治手段,其标准治疗药物包括糖皮质激素和免疫抑制剂。糖皮质激素具有强大的抗炎作用和免疫抑制作用,是治疗SLE 的基础药,与免疫抑制剂联合应用能更快缓解病情和巩固疗效[2]。在世界范围内开展SLE治疗研究的团队较多[3],本文采用大数据分析方法,从文献计量学的角度对该领域研究情况进行分析,总结近40年有关SLE治疗领域研究的基本情况,现报道如下。
1资料与方法
1.1资料来源 文献来源于PubMed医学文献检索服务系统和Web of Science数据库。在PubMed中,使用主题词“Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic”,搭配副主题词“therapy”进行检索;在Web of Science中选择Science Citation Index(SCI)和SCI-Expanded 两个数据库,使用关键词“Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, therapy, treat,treatment ”检索,检索时间选择1978年1月1日~2017年12月31日。
1.2纳入和排除标准 纳入标准:仅纳入期刊上刊载的临床和基础研究、病例报告、综述等正式发表的文献。排除标准:①评论、短篇报道及信件等其它类型的文献;②信息不全的文献,如缺少作者信息、期刊信息等。
1.3方法 利用NoteExpress文献管理软件和德国德累斯顿技术大学开发的大数据分析工具GoPubMed,对文献的发表时间、刊载期刊、文献篇名、摘要、关键词、发文作者、发文作者单位、年文献量、期刊载文量、高频词、发文作者团队、发文国家和地区分布等指标进行分析。
2结果
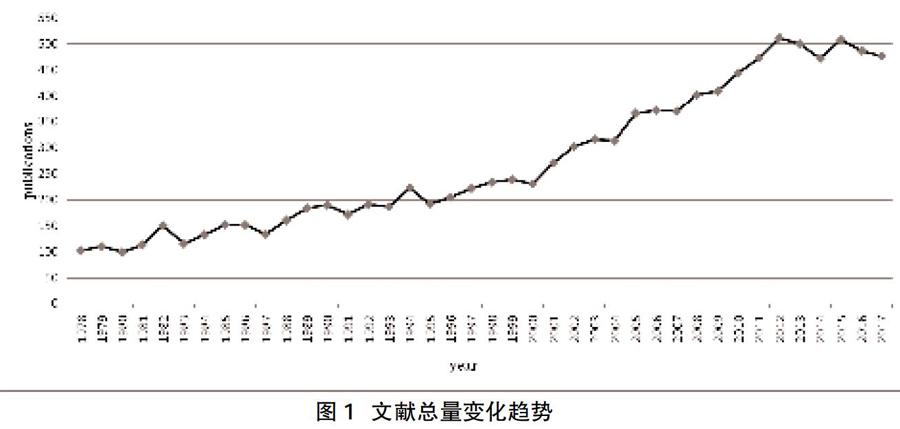
2.1年文献量 共检索文献10892篇,1978~2017年有关SLE治疗领域的文献量呈现稳步增长的变化,其中2000年以后增长较为迅速。年文献量从1978年的103篇,增长到2017年的 477篇,见图1。
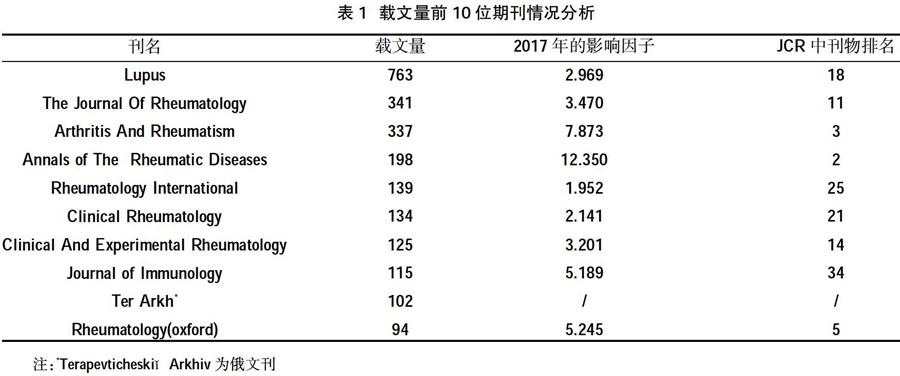
2.2期刊载文量 10892篇文献分布在9943种期刊上,其中排名前10位的期刊载文量占总量的21.56%,根据美国科学信息研究所2017年版《期刊引用报告》(JCR)的期刊分类,除Journal of Immunology属于免疫学期刊外,其余9种都属于风湿病学刊物,JCR中风湿病学刊物共有32种,其中排名第2的是Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases,IF值为12.350,共刊载SLE治疗领域文献198篇,见表1。
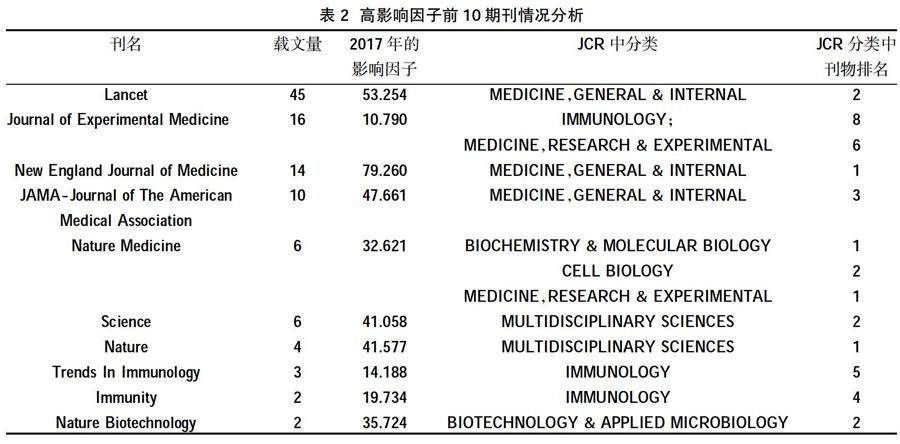
9943种期刊中,根据2017年IF值排名前10位期刊的载文情况排名见表2,其载文量占总量的1.09%。10种期刊分属于JCR期刊分类中的7个类别,最多隶属在3个学科之下,其中影响因子最高的是New England Journal of Medicine,IF值79.260,在JCR的MEDICINE,GENERAL & INTERNAL期刊类别中排名第1位,共刊载SLE治疗领域文献14篇。
2.3高频词 根据文献标题和摘要、关键词中包涵的名词性术语,出现频率最高的20个主题词或关键词见图2。
2.4作者发文情况 共有9667名作者发表了有关SLE治疗领域的文献,其中Hughes G发文60篇,位居第1,发文50篇以上的有3位,40篇以上的有7位。根据这些作者合作的情况,共形成了6个主要的研究团队,见表3。
2.5发文国家和地区情况 全球共有110個国家和地区在关注SLE治疗领域的研究,见图3;其中排名前20位的国家和地区发文量占总量的55.00%,见图4。其中美国发文总量1978篇,领先其它国家和地区,位居第1,中国大陆位居第4。在排名前20位的国家和地区中,亚洲国家和地区有7个,分别是日本、中国大陆、以色列、中国台湾、中国香港、印度、韩国,发文总量占前20位的国家和地区发文总量的26.90%。
3讨论
3.1年文献量与期刊载文量 文献量的多少从一定程度上反映该研究的发展水平。因该疾病还存在一些难点和疑点,如病因至今尚未明确,SLE患者尚不能根治等问题,所以SLE治疗领域一直有研究团队持久关注,文献量呈现稳步增长的变化。本研究列出了载文量最多的10个期刊,并根据JCR排名,总结了期刊的发文特点,对于需要了解该领域的研究热点、新兴技术等信息,可以持续关注这些期刊。另外本研究还总结了该领域影响因子排名前10 的期刊,可以看到其在JCR所属类别中排名也非常高,说明领域出现了许多质量非常高的文献,有较高的学术价值。
3.2高频词 从高频词中可以发现SLE疾病自身的许多特点。如该疾病有明显的性别倾向,女性患者明显多于男性,“女性”这个词在图2的词表中出现了6362次,位居第3,“男性”出现了3570次,位居第6。本次研究显示,“Lupus Nephritis”和“Nephritis”2个高频词分别排名第9位和第10位,原因在于SLE可導致机体的多系统损害,其中肾脏病变最为常见,SLE患者肾活检肾受累几乎为100%,其中45%~85%的患者有肾损害的临床表现,且是危及远期生存质量的关键因素。
3.3作者发文情况 本研究发现了一些真正致力于SLE治疗领域的研究人员,这些研究人员根据各自不同的研究领域,共形成了6个不同的团队。
第1团队主要研究抗磷脂综合征:抗磷脂综合征或抗磷脂抗体综合征(APS或APLS)是一种由反复发作的动脉或静脉血栓、异常妊娠和持续阳性的抗磷脂抗体(APL)引起的疾病。APS可继发于SLE或其他自身免疫性疾病,但也可单独发生(如原发性APS)。无论是原发性APS还是继发性APS,临床表现和实验室检测均无差异。临床表现从无症状APL阳性(无血栓史或异常妊娠史)到恶性APS(数天内发生广泛血栓),程度不一。在极少数情况下,患者可同时或者在短时间内出现多处血栓形成,引起多脏器的缺血和坏死,被称为“灾难性抗磷脂综合征”(重症抗磷脂综合征)。这种情况一旦发生,患者死亡率极高。通过阅读文献,发现该团队主要研究APS与SLE的关系[4-10],特别是采用流行病学方法研究APS相关SLE的检测、治疗和预防[6-8]。
第2团队主要研究羟氯喹(HCQ)的疗效与安全性:HCQ在1955年被FDA批准用于所有类型SLE患者的长期治疗。研究显示,孕妇使用HCQ后,娩出胎儿的先天畸形发生率并未明显升高,因此可以推荐HCQ作为治疗SLE的基础用药。目前学界普遍认为HCQ用于治疗SLE孕妇安全性较高。第2团队主要评估患者服用HCQ的依从性[11]及其预测疾病的作用[12-14]、HCQ的毒副作用[15]及其治疗SLE孕妇的安全性、有效性[16-18]。
第3团队主要研究使用环磷酰胺治疗狼疮性肾炎(LN)。LN是SLE最常见和严重的临床表现,肾脏损害的严重程度与SLE的预后密切相关,肾脏受累和进行性肾脏损害是SLE死亡的主要原因。随着皮质类固醇和环磷酰胺的应用,狼疮性肾炎患者的生存率有了显著提高,因此,联合应用这些药物成为该疾病的标准治疗方法。随着患者存活率的提高,狼疮性肾炎治疗的目标转向寻找能够长期改善患者肾脏功能,并将治疗毒性降至最低的治疗方法。第3团队不仅观察环磷酰胺对LN的治疗效果[19],还研究了环磷酰胺联合甲基强的松龙治疗LN的方案[20,21]。
第4团队先后研究了B细胞耗竭治疗[22-28]、B细胞代谢[29-32]以及利妥昔单抗[33-35]和依帕珠单抗的治疗效果[36]。B淋巴细胞简称B细胞,来源于骨髓的多能干细胞,具有提呈可溶性抗原,产生抗体介导体液免疫应答,参与免疫调节的功能,也是引发自身免疫性疾病的细胞之一。B细胞受到刺激后就开始活化,活化以后的B细胞在生长因子的干预下增殖或凋亡。B细胞活化因子(BAFF)又称B淋巴细胞刺激因子(BLyS),负责B细胞的发育和存活,促进成熟和分化。研究发现,在SLE患者中,BAFF过度表达,导致B细胞过度增生,产生大量的自身抗体,并与体内相应的自身抗原结合形成免疫复合物,沉积在皮肤、关节、小血管、肾小球等部位。贝利单抗是一种BLyS特异性抑制剂,可阻断BLyS与B细胞的结合,抑制B细胞的生存,降低SLE自身免疫性损伤。该药于2011年3月被美国食品和药物管理局批准为SLE的标准治疗药物。
第5团队采用多中心起始队列观察SLE患者的多项指标,如代谢综合征[37,38]、心境障碍等[39-46]疾病。起始队列由系统性狼疮国际合作诊所(SLICC)小组负责,是促进SLE问题的前瞻性多中心研究。该项目自2000~2009年从北美、欧洲和亚洲11个国家的30个中心选择研究对象,患者必须满足美国风湿病学会(ACR)的SLE分级标准才能入组。所有患者自确诊之日起15个月内进行登记[40],之后开始参与队列研究,该团队利用国际多中心大数据研究的数据,研究结果更加准确可靠、有价值。
第6团队主要研究肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNFα)阻滞剂的疗效与安全性[47-54],TNFα由活化的巨噬细胞产生,在许多病理状态下产生增多,包括败血症、恶性肿瘤、慢性炎性和SLE疾病。TNF阻滞剂(阿达木单抗、英夫利昔单抗、依那西普)可特异性地与TNF-α结合,并阻断其与TNF受体的相互作用,减少自身免疫性疾病的炎症反应。TNF阻滞剂目前已用于各种风湿性疾病,如类风湿关节炎、少年特发性关节炎、银屑病关节炎、强直性脊柱炎等。但有些患者会出现严重的副作用,最常报告的不良反应是感染(如鼻咽炎、上呼吸道感染和鼻窦炎)、注射部位反应(红斑、瘙痒、出血、疼痛或肿胀)、头痛和骨骼肌肉疼痛。
3.4发文国家和地区情况 目前全球共有110个国家和地区关注SLE相关的研究,说明SLE在世界范围内均有出现。其中排名前20位的国家和地区都是研究的活跃地区,其科研水平和论文质量能代表该研究的水平。另外每个地区研究的方向不一,这与不同地区人群的发病情况、疾病的表现和研究者关注视角不同有关。中国大陆发文数位居第4,说明近年来我国科研实力显著增强,另外该疾病在亚洲人群中高发,在全世界的种族中,汉族人群SLE发病率位居第2,严重威胁人类健康,因此关注的研究团队较多,发表文献也多。
对SLE治疗相关论文的文献计量学分析,可以了解其发展脉络。近年来,随着分子生物学的发展和对SLE发病机制的深入研究,通过改善免疫系统治疗SLE的药物发挥出了巨大的潜力,本研究发现的6个团队中有2个团队都在做此方面的研究。相信随着SLE分子水平的进一步发展,相关研究会进入一个新的时代,相关药物在SLE的治疗中将会有更加广阔的应用前景。
参考文献:
[1]张静,张蓓蓓,蔡辉.系统性红斑狼疮发病机制和生物学标志物的研究进展[J].现代医学,2017,45(6):887-890.
[2]周立偲,田浤,高向东,等.生物技术药物治疗系统性红斑狼疮的研究进展[J].药学与临床研究,2014(3):251-256.
[3]姜桐桐,史鐵英,王林.基于关键词共现的健康坚韧性国外研究分析[J].中国健康教育,2017,33(12):1121-1125.
[4]Perez-Sanchez C,Barbarroja N,Messineo S,et al.Gene profiling reveals specific molecular pathways in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in antiphospholipid syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome with lupus[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2015,74(7):1441-1449.
[5]Cuadrado MJ,Bertolaccini ML,Seed PT,et al.Low-dose aspirin vs low-dose aspirin plus low-intensity warfarin in thromboprophylaxis:a prospective,multicentre,randomized,open, controlled trial in patients positive for antiphospholipid antibodies(ALIWAPAS)[J].Rheumatology (Oxford),2014,53(2):275-284.
[6]Sciascia S,Cuadrado MJ,Sanna G,et al.Thrombotic risk assessment in systemic lupus erythematosus:validation of the global antiphospholipid syndrome score in a prospective cohort[J].Arthritis Care Res(Hoboken),2014,66(12):1915-1920.
[7]Sciascia S,Sanna G,Murru V,et al.Validation of a commercially available kit to detect anti-phosphatidylserine/prothrombin antibodies in a cohort of systemic lupus erythematosus patients[J].Thromb Res,2014,133(3):451-454.
[8]Bertolaccini ML,Sciascia S,Sanna G,et al.Antiphosphatidylserine/prothrombin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus[J].J Rheumatol,2013,40(9):1620.
[9]Matta BN,Uthman I,Taher AT,et al.The current standing of diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome associated with systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Expert Rev Clin Immunol,2013,9(7):659-668.
[10]Nayfe R,Uthman I,Aoun J,et al.Seronegative antiphospholipid syndrome[J].Rheumatology (Oxford),2013,52(8):1358-1367.
[11]Costedoat-Chalumeau N,Amoura Z,Hulot JS,et al.Very low blood hydroxychloroquine concentration as an objective marker of poor adherence to treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Annals of the rheumatic diseases,2007,66(6):821-824.
[12]Costedoat-Chalumeau N,Amoura Z,Hulot JS,et al.Low blood concentration of hydroxychloroquine is a marker for and predictor of disease exacerbations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Arthritis and rheumatism,2006,54(10):3284-3290.
[13]Costedoat-Chalumeau N,Le Guern V,Piette J C.Routine Hydroxychloroquine Blood Concentration Measurement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Reaches Adulthood[J].J Rheumatol,2015,42(11):1997-1999.
[14]Costedoat-Chalumeau N,Galicier L,Aumaitre O,et al.Hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a French multicentre controlled trial(PLUS Study)[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2013,72(11):1786-1792.
[15]Costedoat-Chalumeau N,Hulot JS,Amoura Z,et al.Heart conduction disorders related to antimalarials toxicity:an analysis of electrocardiograms in 85 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine for connective tissue diseases[J].Rheumatology(Oxford),2007,46(5):808-810.
[16]Costedoat-Chalumeau N,Amoura Z,Le Thi Huong D,et al.Pleading to maintain hydroxychloroquine throughout Lupus pregnancies[J].Rev Med Interne,2005,26(6):467-469.
[17]Costedoat-Chalumeau N,Amoura Z,Huong DL,et al.Safety of hydroxychloroquine in pregnant patients with connective tissue diseases.Review of the literature[J].Autoimmunity Reviews,2005,4(2):111-115.
[18]Costedoat-Chalumeau N,Amoura Z,Duhaut P,et al.Safety of hydroxychloroquine in pregnant patients with connective tissue diseases:a study of one hundred thirty-three cases compared with a control group[J].Arthritis and Rheumatism,2003,48(11):3207-3211.
[19]Steinberg AD,Gourley M.Cyclophosphamide in lupus nephritis[J].The Journal of Rheumatology,1995,22(10):1812-1815.
[20]Illei GG,Takada K,Parkin D,et al.Renal flares are common in patients with severe proliferative lupus nephritis treated with pulse immunosuppressive therapy:long-term followup of a cohort of 145 patients participating in randomized controlled studies[J].Arthritis and Rheumatism,2002,46(4):995-1002.
[21]Illei GG,Austin HA,Crane M,et al.Combination therapy with pulse cyclophosphamide plus pulse methylprednisolone improves long-term renal outcome without adding toxicity in patients with lupus nephritis[J].Annals of Internal Medicine,2001,135(4):248-257.
[22]Isenberg DA.Treating patients with lupus with B-cell depletion[J].Lupus,2008,17(5):400-404.
[23]Cambridge G,Isenberg DA,Edwards JC,et al.B cell depletion therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus:relationships among serum B lymphocyte stimulator levels,autoantibody profile and clinical response[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2008,67(7):1011-1016.
[24]Ioannou Y,Lambrianides A,Cambridge G,et al.B cell depletion therapy for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus results in a significant drop in anticardiolipin antibody titres[J].Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases,2008,67(3):425-426.
[25]Ng KP,Cambridge G,Leandro MJ,et al.B cell depletion therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: long-term follow-up and predictors of response[J].Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases,2007,66(9):1259-1262.
[38]Parker B,Urowitz MB,Gladman DD,et al.Clinical associations of the metabolic syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: data from an international inception cohort[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2013,72(8):1308-1314.
[39]Hanly JG,Urowitz MB,Su L,et al.Mood Disorders in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus:Results From an International Inception Cohort Study[J].Arthritis Rheumatol,2015,67(7):1837-1847.
[40]Little J,Parker B,Lunt M,et al.Glucocorticoid use and factors associated with variability in this use in the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics Inception Cohort[J].Rheumatology(Oxford),2018,57(4):677-687.
[41]Hanly JG,O'Keeffe AG,Su L,et al.The frequency and outcome of lupus nephritis:results from an international inception cohort study[J].Rheumatology(Oxford),2016,55(2):252-262.
[42]Hanly JG,Su L,Urowitz MB,et al.A Longitudinal Analysis of Outcomes of Lupus Nephritis in an International Inception Cohort Using a Multistate Model Approach[J].Arthritis Rheumatol,2016,68(8):1932-1944.
[43]Bourré-Tessier J,Urowitz MB,Clarke AE,et al.Electrocardiographic findings in systemic lupus erythematosus:data from an international inception cohort[J].Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken),2015,67(1):128-135.
[44]Bruce IN,O'Keeffe AG,Farewell V,et al.Factors associated with damage accrual in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus:results from the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC)Inception Cohort[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2015,74(9):1706-1713.
[45]Urowitz MB,Gladman DD,Ibanez D,et al.American College of Rheumatology criteria at inception, and accrual over 5 years in the SLICC inception cohort[J].J Rheumatol,2014,41(5):875-880.
[46]Hanly JG,Urowitz MB,O'Keeffe AG,et al.Headache in systemic lupus erythematosus:results from a prospective,international inception cohort study[J].Arthritis Rheum,2013,65(11):2887-2897.
[47]Aringer M,Smolen JS.Therapeutic blockade of TNF in patients with SLE-promising or crazy[J].Autoimmunity Reviews,2012,11(5):321-325.
[48]Aringer M,Smolen JS.Efficacy and safety of TNF-blocker therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Expert Opinion on Drug Safety,2008,7(4):411-419.
[49]Aringer M,Feierl E,Smolen J.Cytokine blockade-a promising therapeutic option in SLE[J].Zeitschriftfür Rheumatologie,2008,67(4):315-317.
[50]Aringer M,Smolen JS.The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Arthritis Research&Therapy,2008,10(1):202.
[51]Aringer M,Steiner G,Graninger WB,et al.Effects of short-term infliximab therapy on autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Arthritis and Rheumatism,2007,56(1):274-279.
[52]Smolen J,Steiner G,Aringer M.Anti-cytokine therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Lupus,2005,4(3):189-191.
[53]Aringer M,Graninger WB,Steiner G,et al.Safety and efficacy of tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade in systemic lupus erythematosus:an open-label study[J].Arthritis and Rheumatism,2004,50(10):3161-3169.
[54]Aringer M,Smolen JS.Tumour necrosis factor and other proinflammatory cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus:a rationale for therapeutic intervention[J].Lupus,2004,13(5):344-347.
收稿日期:2019-9-19;修回日期:2019-10-14
編辑/钱洪飞
