嫁接机钢针顶起穴盘苗过程EDEM模拟验证及参数优化
2017-11-17高国华孙晓娜
高国华,王 凯,孙晓娜
嫁接机钢针顶起穴盘苗过程EDEM模拟验证及参数优化
高国华,王 凯,孙晓娜
(北京工业大学机械工程及应用电子技术学院,北京 100124)
针对该课题组自主开发研制的ZGM-7自动化穴盘苗嫁接机中出现的钢针顶起穴盘苗失败现象,该文在EDEM离散元分析软件中利用ECM粘结力弹塑性接触模型作为颗粒接触模型并建立多种不同材料属性的复杂颗粒模型来模拟真实的育苗基质,进而研究钢针与育苗基质的作用关系。并以顶起过程中的穴盘苗基质底面最大顶起高度作为指标参数,分析了不同钢针长度、不同钢针径粗、不同顶起速度条件下顶起穴盘苗的工作情况。利用响应曲面法设计并执行仿真和实际试验,仿真分析结果与试验结果得到了很好地验证,变化趋势基本一致,数值结果误差在0.7%~7.2%;钢针直径和顶起速度对指标参数影响显著,且存在显著的交互作用。以育苗基质底面竖直成功顶起的理论最大顶起高度144 mm为优化目标,利用Design_expert软件得到仿真优化参数结果:钢针直径2.28 mm,钢针长度12.28 mm,顶起速度0.09 m/s。仿真优化参数下进行试验,顶起机构顶起穴盘苗成功率高达95.3%,优化效果显著。该研究结果极大地提高了钢针顶起穴盘苗的运行效果,同时为钢针顶起离散基质等类似问题提供参考。
农业机械;嫁接;优化;EDEM;穴盘苗;钢针;顶起;响应曲面法
0 引 言
目前,发达国家设施园艺的人均种植面积超过1.00 hm2,相比之下中国0.07 hm2的水平显得尤为落后。因此,加速实现设施农业发展的机械化、现代化和高效化,推动中国农业生产效率的不断提高,已列入“十二五”发展计划的重点扶持部分[1]。在农业朝着机械化发展的过程中,大多数设施农业机械设计都会涉及到机械部件与育苗基质之间的作用关系,其作用效果的好坏通常也决定了机械化程度的高低。因而,设施农业机械部件与育苗基质之间作用关系的研究有着重要的意义。
本课题组自主开发研制的ZGM-7自动化穴盘苗嫁接机出现了钢针顶起穴盘苗失败现象,极大地降低了嫁接效率。因此,钢针与穴盘苗基质之间作用关系的研究就显得格外重要。该研究属于农业机械核心部件与育苗基质之间作用关系的研究。目前钢针和离散基质顶起的相关研究较少,类似相关研究也是以试验为主,但这种研究方法费时费力,且不容易得到理想结果。
近年来,国内外许多学者尝试着采用离散元法[2-3]进行相关研究。与有限元法相比,育苗基质不满足有限元法所基于的连续基质理论,而离散元法考虑了颗粒的物性参数及其分布等对颗粒流的影响,采用牛顿第二定律、动态松弛法和时步迭代求解每个颗粒的运动速度和位移,因而特别适合于求解育苗基质的非线性问题[4-5]。目前,离散单元法广泛应用于岩石力学[6-7]、物料运动[8-9]、农业机械优化[10-13]及土壤力学[14-19]等领域。在离散单元法仿真农业基质颗粒方面,张金波在深松铲减阻耐磨仿真理论与技术中,采用离散元法和PFC-2D软件对深松铲与土壤基质的接触进行了二维模拟分析,分析计算了土壤基质颗粒与深松铲的接触力,从定性方面分析了结果与土槽试验、田间试验的结果基本一致[20]。于建群等采用离散元法研究土壤基质开沟器的工作过程及工作阻力,仿真与试验的相对误差在10%~20%,由此证明用离散元法分析开沟器工作过程和阻力的基本可行性,但并未细致考虑土壤的成分复杂性[21]。Obermayr等也对推土板与无粘结颗粒间的作用进行了离散单元法研究,以期对今后更复杂的研究有所帮助[22]。综上可知,大多数学者均是以成分相对简单的土壤基质或其他基质为研究对象,很少研究成分复杂且有较强粘性的育苗基质动态行为,以优化农业中与育苗基质发生作用的核心部件。
本文在EDEM(enhanced discrete element method)软件中应用ECM(elasto-plastic cohesion model)[23-25]粘结力弹塑性接触模型作为颗粒接触模型并建立不同材料属性的复杂育苗基质颗粒模型仿真分析钢针顶起穴盘苗工作过程,并将仿真结果和试验结果进行对比,验证仿真数据有效性,为后续钢针与育苗基质作用关系的研究提供参考。
1 离散元仿真建模
1.1 问题描述
ZGM-7自动化穴盘苗嫁接机中的顶起机构(如图1所示)主要实现的功能是顶起带有育苗基质的穴盘苗并旋转苗木子叶方向。顶起机构主要结构有:气缸安装板1、气缸2、旋转电机3、底板4、顶杆5、钢针6。气缸2固定在气缸安装板1上,并与底板4螺栓连接。旋转电机3固定在底板4上,并与顶杆5螺栓连接。钢针6固定在顶杆5上端。气缸2推出带动安装在顶杆5上的钢针6向上运动并顶起带有育苗基质的穴盘苗,再通过旋转电机3旋转苗木子叶方向。
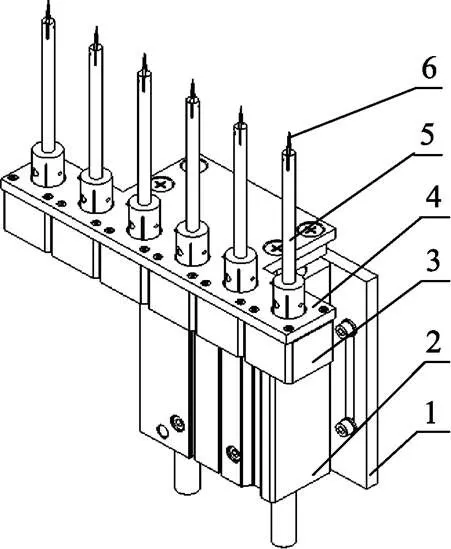
1. 气缸安装板 2. 气缸 3. 旋转电机 4. 底板 5. 顶杆 6. 钢针
按照预期设计要求,需要钢针竖直顶起带有育苗基质的苗木一段距离。但在实际运行时出现了顶起失败现象:顶歪和顶掉(如图2所示)。根据调试过程分析,将失败现象的原因归结于设备参数调制未佳。本文将利用离散元仿真和试验相结合的方式研究不同参数对于钢针顶起穴盘苗过程的作用关系。

1.顶歪的穴盘苗 2. 顶掉的穴盘苗
1.2 机构模型
考虑到实际试验中苗木部分对于顶起过程的影响很小且很难利用离散元法来仿真,因此,只对育苗基质进行离散单元建模和分析,并将苗木根系对育苗基质的紧固力通过提高育苗基质颗粒的粘结性来体现。图1中的顶起机构可同时顶起6株穴盘苗,可极大地提高嫁接效率。本文为提高仿真效率,以单株穴盘苗顶起过程进行研究,并建立如图3所示的机构简化模型。图中,穴盘单元格为上底半径19 mm、下底半径10 mm、高44 mm的圆台型育苗基质槽,且下底面中心有一个半径为5 mm的孔。机构简化模型利用SolidWorks 2014软件绘制,以.igs格式导入EDEM软件。
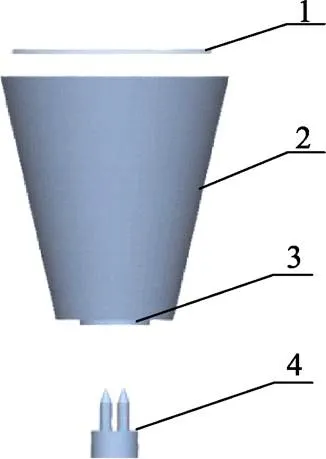
1. 颗粒生成表面 2. 穴盘单元格 3. 模拟地面 4. 钢针
1.3 基质颗粒模型
建立准确的育苗基质颗粒模型是保证仿真结果有效性的基础。为穴盘苗提供营养成分的育苗基质是北京鸿信达育苗基质,其主要由珍珠岩、泥炭和玉米皮按照1∶8∶1的成分组成。颗粒模型外型的建立根据颗粒实际外型建模,现有研究表明,泥炭颗粒的基本结构主要包括块状颗粒、核状颗粒、柱状颗粒[26]。珍珠岩、玉米皮的基本结构分别为球状和片状。因此,建立相应的颗粒模型如图4所示。其中模型中球形直径为1 mm。设置六种颗粒模型接触参数如下,泥炭颗粒接触表面能20 J/m2,颗粒接触弹塑比0.6;珍珠岩颗粒接触表面能12 J/m2,颗粒接触弹塑比0.9;玉米皮颗粒接触表面能8 J/m2,颗粒接触弹塑比0.8。颗粒接触表面能反映的是颗粒的粘性水平,数值越大,粘性越强;颗粒接触弹塑比反映的是颗粒的接触弹塑性水平。0为完全弹性,1为完全塑性[27-28]。
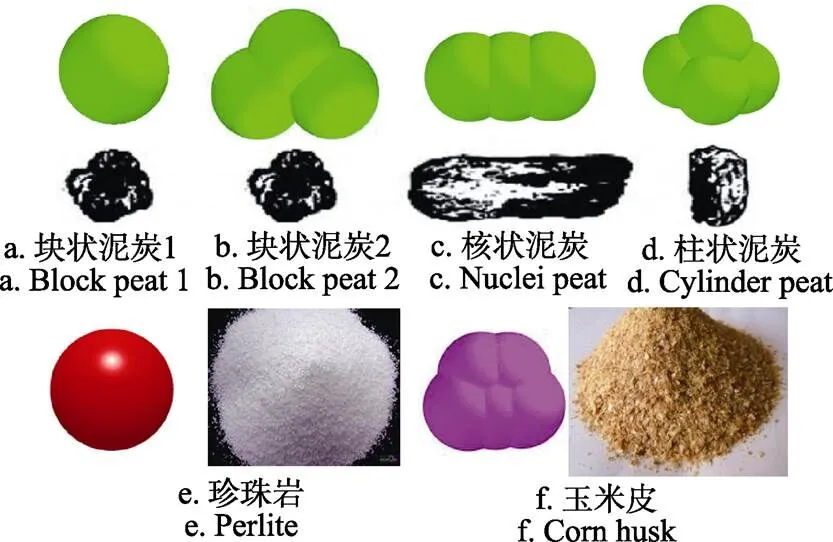

图4 育苗基质成分颗粒模型
1.4 仿真参数设置
对育苗基质进行基本物理性能试验(环刀法测量密度、直剪试验和三轴试验等),获得如表1的仿真参数。育苗基质颗粒接触模型采用北京海基科技发展有限责任公司提供的ECM粘结力弹塑性接触模型,版本号V2_2014。在EDEM前处理器模块依次进行接触力学模型、仿真参数、育苗基质颗粒模型、几何模型和颗粒工厂等的设置。在EDEM求解器模块设置仿真步长1´10–5s、数据保存间隔时间0.01 s等。仿真开始时生成育苗基质颗粒,待颗粒沉降稳定后,顶起钢针开始运动,直至仿真结束,最后在EDEM后处理工具模块进行仿真结果的分析和导出。现有研究表明,泥炭中颗粒大小呈正态分布。为提高仿真育苗基质与实际育苗基质的一致程度,并考虑EDEM运算仿真效率,设置6种育苗基质颗粒大小分别呈正态分布,平均值为1 mm,标准差为0.1。EDEM模型中,对应于图4a~4f中颗粒的数量分别为360、360、360、360、180、180。
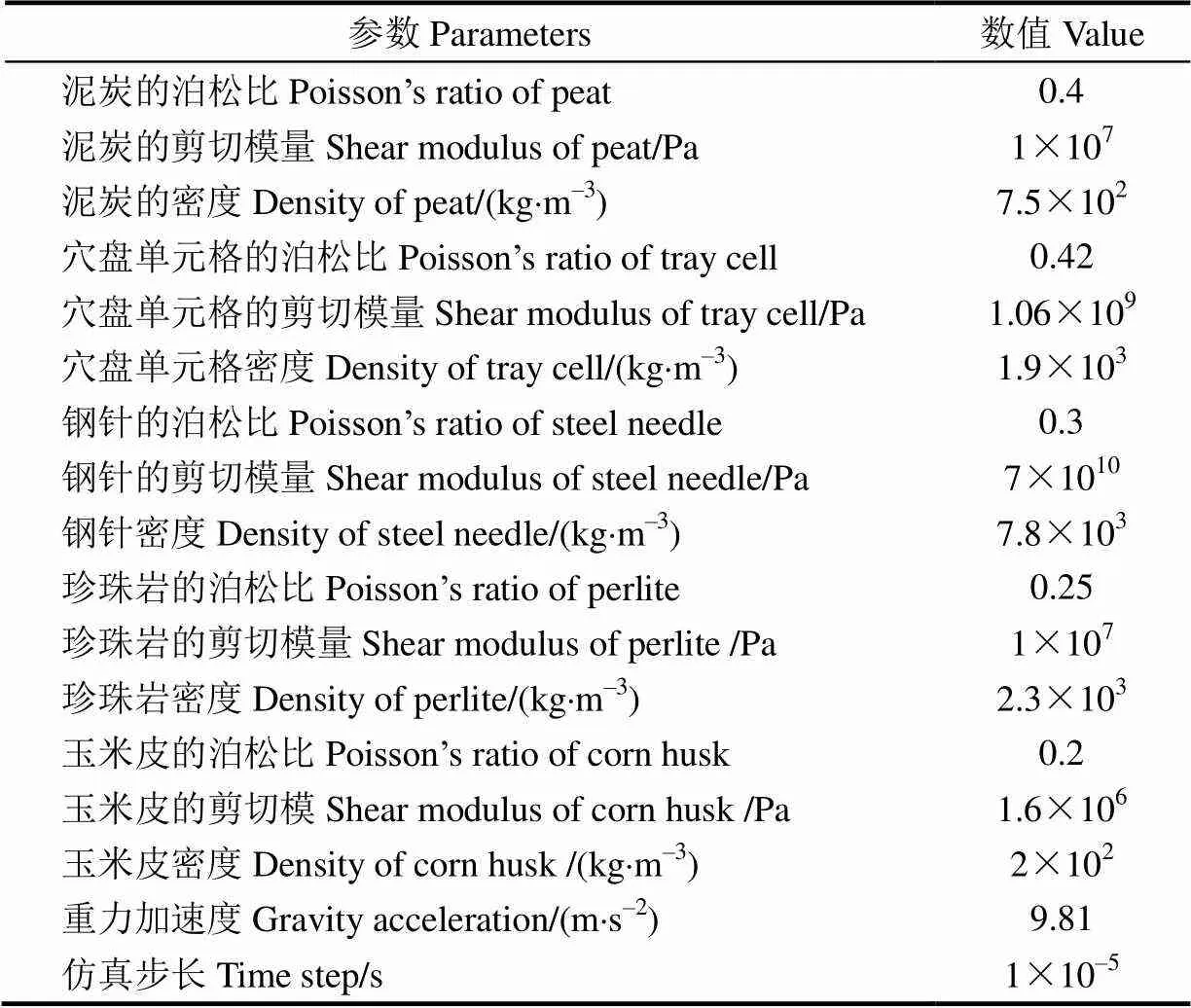
表1 离散单元仿真的参数
2 仿真及试验设计
2.1 参数范围选择
通过多次实地调试,总结影响穴盘苗顶起效果好坏的主要参数如下:
1)钢针直径
为了保证顶起穴盘苗的稳定性,顶起机构采用2根钢针同时顶起的方式。钢针直径的大小是钢针插入育苗基质过程中重要的影响因素之一。经试验验证,若钢针直径小于1 mm,则钢针容易损坏;若钢针直径大于3 mm,则钢针很难完全插入育苗基质。经过试验测定,钢针直径选择取值范围1~3 mm。
2)钢针长度
钢针长度决定了钢针插入育苗基质的最大深度。穴盘苗基质高度与穴盘单元格高度基本一致为44 mm。经试验验证,若钢针长度小于5 mm,则钢针顶起育苗基质不稳固;若钢针长度大于15 mm,则容易损坏穴盘苗的根系。经过试验测定,钢针长度选择取值范围5~15 mm。
3)顶起速度
顶起速度决定了顶起过程的平稳程度。经试验验证,若顶起速度小于0.04 m/s,则钢针不容易插入育苗基质;若顶起速度大于0.12 m/s,则钢针容易顶掉育苗基质。经过试验测定,顶起速度选择取值范围0.04~0.12 m/s。
2.2 仿真方案
本文选用响应曲面试验方法中的BBD设计方法(box-benhnken design)进行仿真方案设计,并对顶起机构顶起穴盘苗的影响因素进行优化。响应曲面法是一个建立过程模型,以及对过程进行优化的系统方法,很适用于本文连续因素变量的研究[29-32]。不同的参数条件都可能造成育苗基质的顶掉和顶歪现象,但在育苗基质顶起的过程中,育苗基质底面所能达到的最大高度是不同的。以操作平台水平面高度作为零高度面,考虑气缸运动行程和气缸安装位置等后,育苗基质竖直成功顶起的理论高度是144 mm。当基质发生歪斜,以基质底面中心点高度作为测量点。考虑到每次钢针成功竖直顶起高度不会恰巧在144 mm,设定可接受范围误差在±0.5 mm之间。当顶起最大高度小于可接受范围,表明育苗基质在顶起过程中提前掉落了;当顶起最大高度大于可接受范围时,表明钢针没有完全插入育苗基质或钢针顶歪了育苗基质。当顶起最大高度在可接受范围内时,表明钢针竖直成功顶起育苗基质。因此,本文以顶起过程中的育苗基质底面最大顶起高度作为指标参数,来区分不同参数条件对于育苗基质的顶起效果。利用软件Design-expert依据水平因素编码表(如表2所示)进行仿真方案设计。
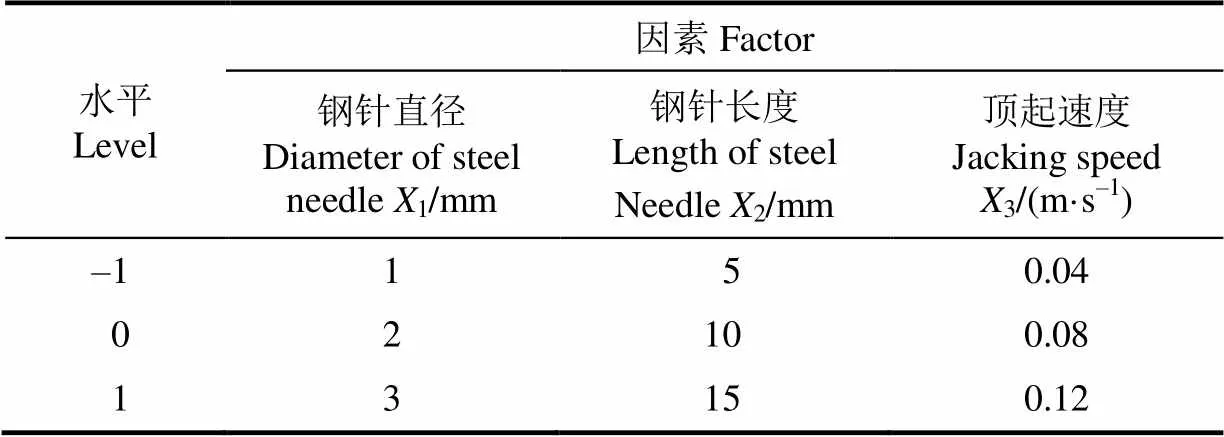
表2 因素水平编码 Table 2 Factors levels coding
2.3 实际试验
为验证仿真数据的可信度,对顶起机构顶起穴盘苗进行了与仿真方案相同的实际试验,选用顶起过程中育苗基质底面的最大顶起高度作为不同参数条件对顶起穴盘苗运行效果的指标参数。
试验地点北京市京鹏环球科技股份有限公司,顶起机构顶起穴盘苗试验测试平台如图5所示,利用ZGM-7自动化穴盘苗嫁接机中的顶起机构,并通过安装不同的钢针和气缸调流阀控速的方式进行试验参数调控,顶起过程中最大顶起高度的测量通过AOS高速相机AOS-Q-MIZE捕捉以及相应处理软件AIS获得。试验现场的育苗基质湿度为20.3%。每组试验重复5次,每次同时试验6株穴盘苗,剔除个别明显差异结果,最后以最大顶起高度的平均值作为该组参数的结果。
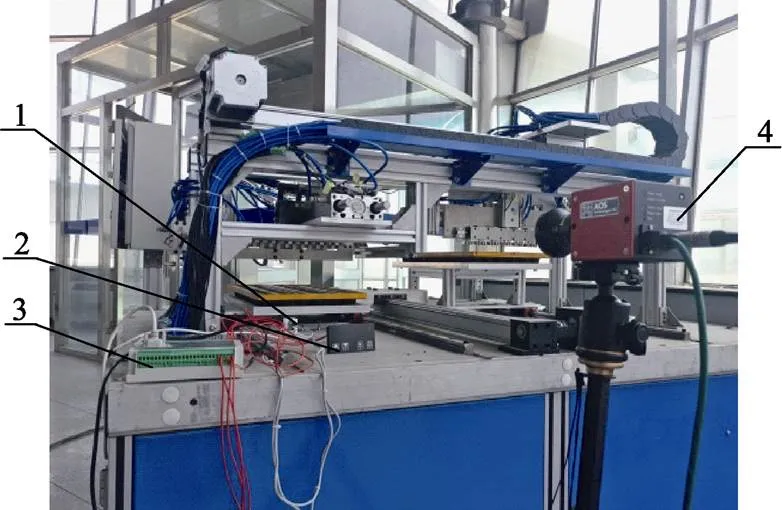
1. 传感器 2. 数显仪表 3. 测速系统 4. 高速相机
3 仿真及试验结果
离散元仿真和试验结果见表3。仿真中的育苗基质顶起失败现象如图6所示,基本符合实际失败现象。

表3 仿真与试验结果
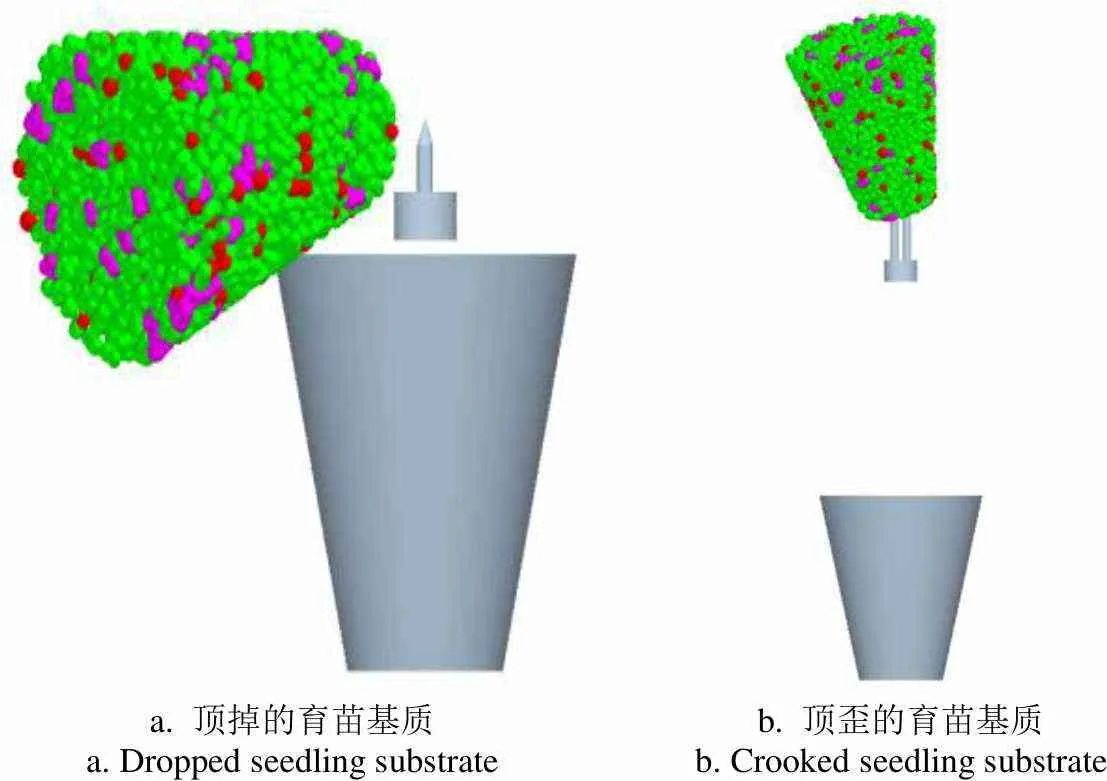
a. 顶掉的育苗基质 a. Dropped seedling substrateb. 顶歪的育苗基质 b. Crooked seedling substrate
图6 仿真中顶起穴盘苗失败现象
Fig.6 Failure phenomenon of jacking tray-seedling in simulation
利用数据处理软件Design-expert Version 8.0对仿真数据进行分析。仿真数据的方差分析如表4所示,该模型的<0.05,说明该模型显著;失拟项的>0.05,说明模型失拟性不显著,具有很好的拟合性。在此模型中,各因素对穴盘苗最大顶起高度的影响依次为钢针直径>顶起速度>钢针长度。钢针直径和顶起速度交互项的值为0.0317<0.05,说明钢针直径和顶起速度存在显著的交互作用。
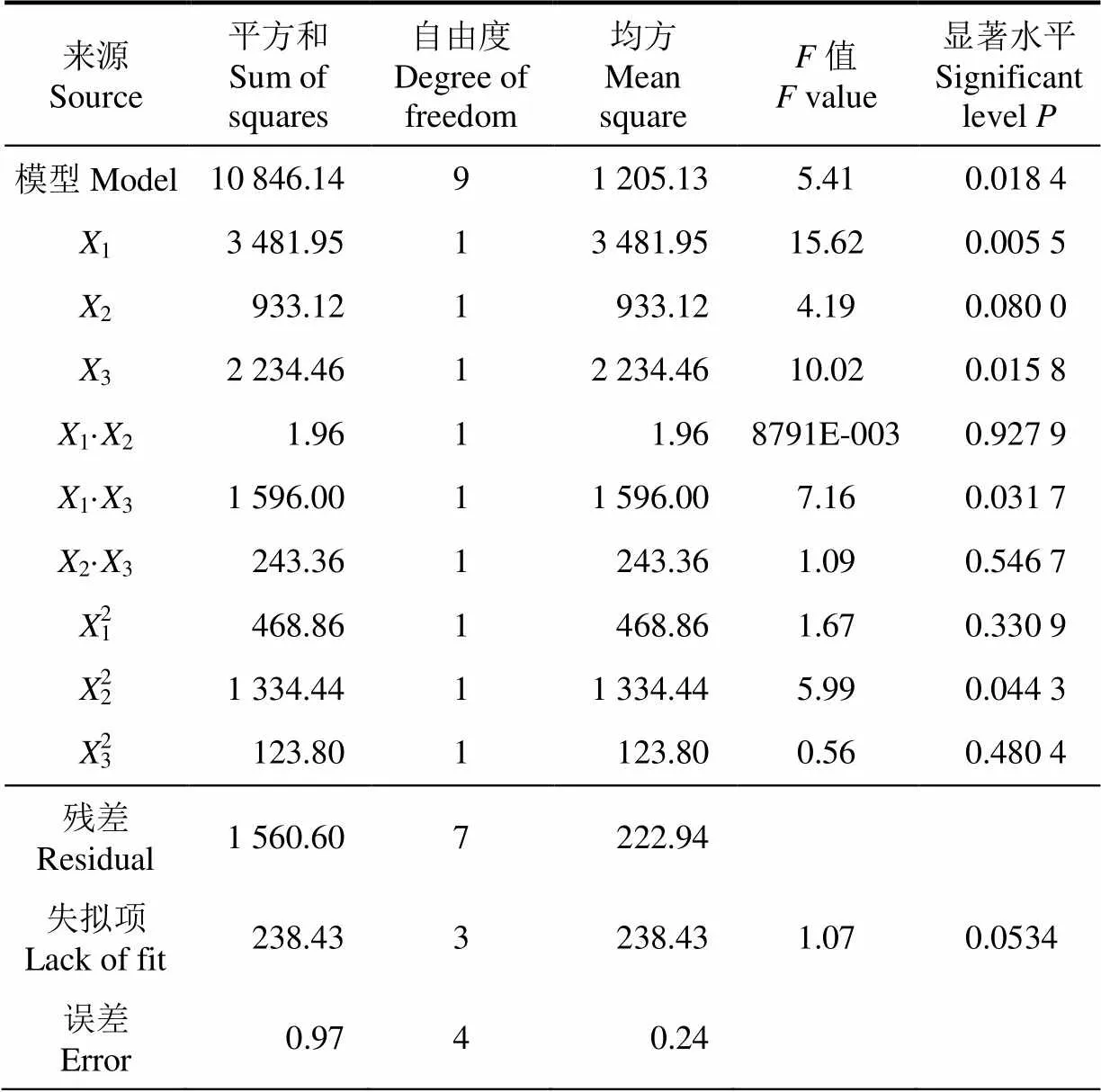
表4 最大顶起高度的回归模型方差分析
4 结果与分析
4.1 结果分析
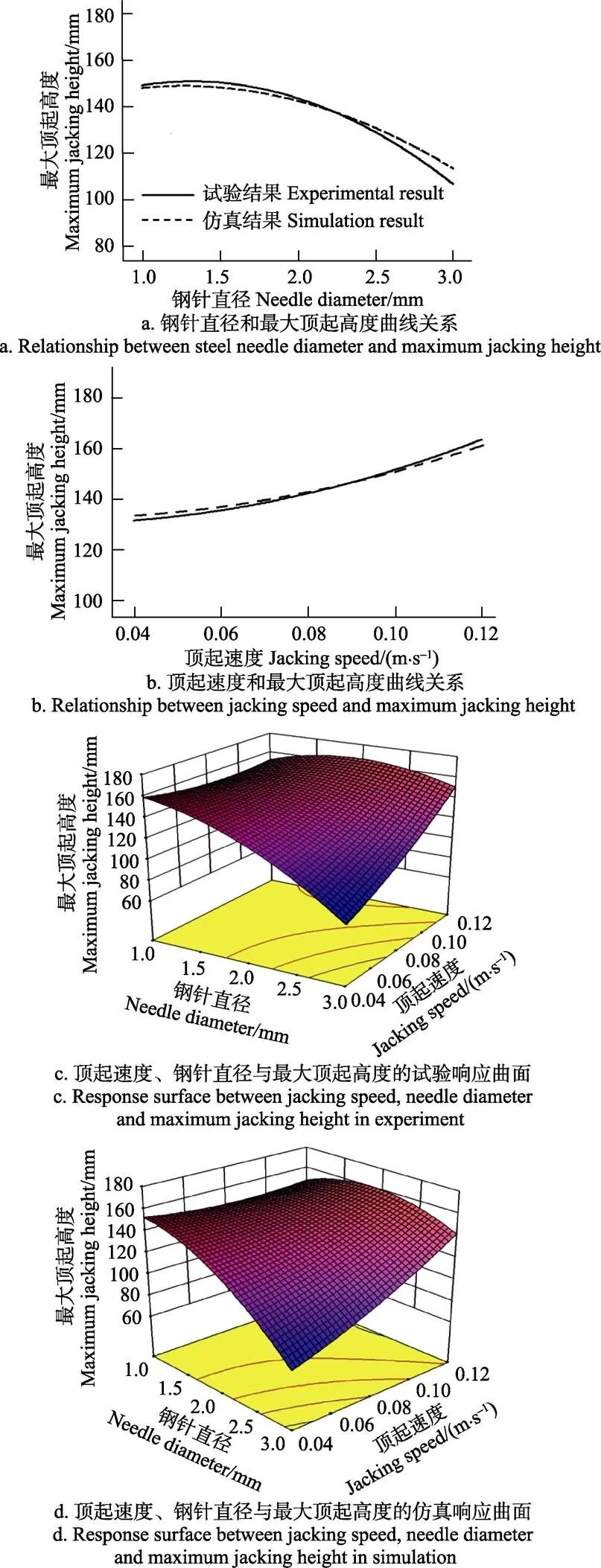
对比分析仿真结果与试验结果,发现误差在0.7%~7.2%之间。较大误差仅存在于顶歪和顶掉等明显失败现象中,主要是因为试验育苗基质中存在苗株根系阻碍钢针插入,加速了育苗基质提前掉落和顶歪。另外,仿真结果和试验结果均表明钢针直径和顶起速度对育苗基质底面的最大顶起高度影响显著,且钢针直径、顶起速度存在显著的交互作用,利用软件Design-expert绘制显著因素与育苗基质底部最大顶起高度关系图(如图7所示)。
钢针直径对育苗基质底面最大顶起高度的仿真和试验影响曲线如图7a所示。在钢针直径试验水平范围内可以得出:随着钢针直径的增加,最大顶起高度先缓慢单调递增,再单调递减。顶起速度对穴盘苗底部最大顶起高度的仿真和试验影响曲线如图7b所示。在顶起速度试验水平范围内可以得出:随着顶起速度的增加,最大顶起高度单调递增。钢针直径、顶起速度的试验和仿真响应曲面图如图7c、7d所示,两者均表明:钢针直径、顶起速度的交互作用显著。钢针直径较小时,最大顶起高度随顶起速度的增大逐渐减小;钢针直径较大时,最大顶起高度随顶起速度的增大逐渐增大;钢针顶起速度较小时,最大顶起高度随钢针直径的增大逐渐减小;钢针顶起速度较大时,最大顶起高度随钢针直径的增大,先逐渐增大再减小。
4.2 参数优化
利用Design_expert软件的优化功能,以期育苗基质竖直成功顶起理论最大高度144 mm,其他因素参数在试验水平范围内为标准对仿真结果进行优化,得到一组最优解:钢针直径2.28 mm,钢针长度12.28 mm,顶起速度0.09 m/s。将最优解代入到实际机构中,150株穴盘苗顶起高度在误差接受范围内有143株,顶起成功率95.3%。优化参数下的顶起效果如图8所示,顶起效果优化明显。
注:图a中钢针长度10 mm顶起速度0.08 m/s;图b中钢针长度10 mm,钢针直径2 mm;图c、d中钢针长度10 mm。
根据仿真结果和实际试验结果对比分析,两者误差较小、规律基本一致,且根据仿真数据的优化结果取得了显著效果。研究可为今后钢针与育苗基质作用关系的研究提供参考。
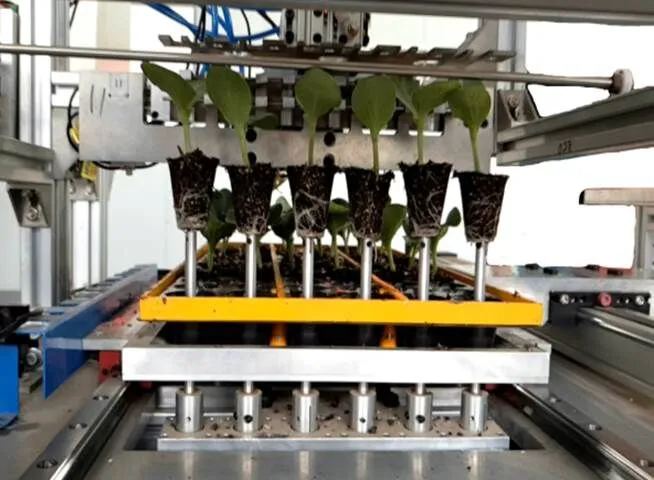

图8 优化参数后的顶起效果图
5 结 论
本文采用ECM粘结力弹塑性颗粒接触模型作为育苗基质的颗粒接触模型并建立多种不同材料属性的育苗基质颗粒来模拟接近真实的育苗基质环境,进而研究钢针顶起穴盘苗工作过程,取得了较好的仿真效果,这种方法可被应用于其他类似复杂环境。
1)采用离散元软件对钢针顶起穴盘苗的工作过程进行仿真研究,并通过实际试验验证。仿真结果和试验结果的误差在0.7%~7.2%之间且规律基本一致。各因素对穴盘苗最大顶起高度的影响顺序由大到小依次为钢针直径、顶起速度、钢针长度,其中钢针直径和顶起速度存在显著的交互作用。
2)运用Design_expert软件对仿真数据分析,以穴盘苗基质底面理论最大顶起高度144 mm为指标参数,确定最优参数:钢针直径2.28 mm,钢针长度12.28 mm,顶起速度0.09 m/s,顶起成功率95.3%,顶起优化效果显著。研究结果可为今后钢针与育苗基质作用关系的研究提供参考。
[1] 王恒一,邹雪剑,王涛. 我国设施农业机械发展现状及趋势分析[J]. 农业科技与装备,2015,2(248):61-62. Wang Hengyi, Zou Xuejian, Wang Tao. Status and trend analysis of facility agricultural machinery development in china[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment, 2015, 2(248): 61-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] Cundall P A. A computer model for simulating progressive large scale movements in blocky system In: Muller Led[J]. Proceedings of Symposium of International Society of Rock Mechanics. Rotterdam; A. A. Balkema, 1971(1): 8-12.
[3] Cundall P A. The Measurement and Analysis of Acceleration Inrock Slopers[D]. London: Imperial College London (University of London), 1971.
[4] 邓佳玉,胡军,李庆达,等. 基于EDEM离散元法的深松铲仿真与试验研究[J]. 中国农机化学报,2016,37(4):
13-18. Deng Jiayu, Hu Jun, Li Qingda, et al. Simulation and experimental study on subsoiler based on EDEM discrete element method[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2016, 37(4): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Cundall P A. UDEC-a generalized distinct element program for modeling jointed rock[R]. Report PCA R-1-80, Peter Cundall Associates. European Research Office, US Army Corps of Engineers. 1980.
[6] 周先齐,卫亚钮,钮新强,等. 离散单元法研究进展机器医用综述[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(增刊):408-417. Zhou Xianqi, Wei Yaniu, Xiu Xinqiang, et al. A review of distinct element method researching progress and application[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(Supp): 408-417. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 徐寅,陈胜宏. 基于离散单元法的滑坡堆积及其涌浪设计[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(9):2850-2856. Xu Yin, Cheng Shenghong. Calculation of heap shape of landslide and its surge based on discrete element method [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(9): 2850-2856. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 石林榕,吴建民,赵武云,等. 基于CFD-EDEM耦合的小区玉米帘式滚筒干燥箱数值模拟[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2014,32(6):273-278. Shi Linrong, Wu Jianmin, Zhao Wuyun, et al. The numerical simulation for corn curtain roller drying box based on CFD-EDEM coupling[J]. Agriculture Resear-ch in the Arid Areas, 2014, 32(6): 273-278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 周德义,马成林,左春柽,等. 散粒农业物料孔口出流成拱的离散元仿真[J]. 农业工程学报,1996,12(2):186-189. Zhou Deyi, Ma Chenglin, Zuo Chuncheng, et al. Discrete element simulation for arch flowing of agricultural particle material in outlet[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1996, 12(2): 186-189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李洪昌,李耀明,唐忠,等.基于EDEM的振动筛分数值模拟与分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(5):117-121. Li Hongchang, Li Yaoming, Tang Zhong, et al. Numerical simulation and analysis of vibration screening based on EDEM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(5): 117-121. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 廖庆喜,张鹏玲,廖宜涛,等.基于EDEM的离心式排种器排钟性能数值模拟[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(2):109-114. Liao Qingxi, Zhang Pengling, Liao Yitao, et al. Numerical simulation on seeding performance of centrifugal rape-seed metering device based on EDEM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(2): 109-114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 陈进,周韩,赵湛,等.基于EDEM的振动种盘中水稻种群运动规律研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2011,42(10):79-83. Chen Jin, Zhou Han, Zhao Zhan, et al. Analysis of rice seeds motion on vibrating plate using EDEM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(10): 79-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 石林榕,吴建民,赵武云,等.基于离散单元法的水平圆盘式精量排钟器排种仿真实验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(8):40-48. Shi Linrong, Wu Jianmin, Zhao Wuyun, et al. Simulation test for metering process of horizontal disc precision metering device based on discrete element method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(8): 40-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 徐泳,李红艳,黄文彬.耕作土壤动力学的三维离散元模型和仿真方案策划[J]. 农业工程学报,2003,19(2):34-38. Xu Yong, Li Hongyan, Huang Wenbin. Modeling and method logical strategy of discrete element method simulation for tillage soil dynamics[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2003, 19(2): 34-38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 张锐,李剑桥,李因武. 离散单元法在土壤机械特性动态仿真中的应用进展[J]. 农业工程学报,2003,19(1):16-19. Zhang Rui, Li Jianqiao, Li Yinwu. Development of simulation on mechanical dynamic behavior of soil by distinct element method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2003, 19(1): 16-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李艳洁,吴腾,林剑辉. 基于离散单元法的贯入圆锥对沙土颗粒运动特性分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(24):55-61. Li Yanjie, Wu Teng, Lin Jianhui. Influence of penetrating cone on motion characteristics of sandy soil particle using discrete element method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(24): 55-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李艳洁,徐泳. 土壤试样单轴亚索试验与离散元法模拟对比研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2009,14(4):103-108. Li Yanjie, Xu Yong. Comparison study between the soil uniaxial compression test and the discrete element simualtion[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 14(4): 103-108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李艳洁,刘翼晨,林剑辉,等. 圆锥指数仪贯入沙土过程的三维离散元法模拟[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(7):63-68. Li Yanjie, Liu Yichen, Lin Jianhui, et al. 3D DEM simulations of the cone penetration tests in sandy soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(7): 63-68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 翟力欣,姬长英. 基于离散单元法的土壤力学接触模型的建立[J]. 江西农业学报,2008,20(9):108-111. Zhai Lixin, Ji Changying. Foundation of dynamic soil model based on distinct element method[J]. Acta Agriculture Jiangxi, 2008, 20(9): 108-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 张金波. 深松铲减阻耐磨仿真理论与技术[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2014. Zhang Jinbo. Bionic Drag Reduction and Wear-resistant Theory and Techniques of Subsoiler[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2014.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 于建群,钱立彬,于文静,等. 开沟器工作阻力的离散元法仿真分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2009,40(6):53-57. Yu Jianqun, Qian Libin, Yu Wenjing, et al. DEM Analysis of the resistances applied on furrow openers[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2009, 40(6): 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] Obermayr M, Dressler K, Vrettos C, et al. Prediction of draft forces in cohesionless soil with the Discrete Element Method[J]. Journal of Terramechaics, 2011, 48(5): 347-358.
[23] Subhash SC, Morrissey JP, Sun J, et al. Micromechanical analysis of cohesive granular materials using the discrete element method withan adhesive elasto-plastic contact model[J]. Granular Matter, 2014, 16: 383-400.
[24] Tsuji T, Nakagawa Y, Matsumoto N. 3-D DEM simulation of cohesive soil-pushing behavior by bulldoz-er blade[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2012, 49: 37-47.
[25] Obermayr M, Vrettos C, Eberhard P, et al. A discrete element model and its experimental validation for the prediction of draft forces in cohesive soil[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2014, 53: 91-104.
[26] 王燕. 基于离散单元法的深松铲结构与松土效果研究[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学,2014. Wang Yan. Simultion Analysis of Structure and Effect of the Subsoiler Based on DEM[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] Thakur S C, Morrissey J P, Sun J, et al. Micromechanical analysis of cohesive granular materials using the discrete element method with an adhesive elasto-plastic contact model[J]. Granular Matter, 2014, 16(3): 383-400.
[28] 玉亚. 土壤接触角及土壤表面能量特征的研究[D]. 西安:西安建筑科技大学,2007. Yu Ya. A Study on Soil Contact Angle and Soil Surface Free Energy Properties[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 周福君,芦杰,杜佳兴. 玉米钵苗移栽机圆盘式栽植机构参数优化及试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(1):18-24. Zhou Fujun, Lu Jie, Du Jiaxing. Parameters optimization and experiment of corn-paper transplanting machine with seedling disk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(1): 18-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 田素博,杨继峰,王瑞丽,等. 蔬菜嫁接机嫁接夹振动排序装置工作参数优化试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(6):9-16. Tian Subo, Yang Jifeng, Wang Ruili, et al. Optimization experiment of operating parameters on vibration sorting-clip device for vegetable grafting machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(6): 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 高国华,冯天翔,李福. 盆栽红掌移栽手爪设计与工作参数优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(17):34-42. Gao Guohua, Feng Tianxiang, Li Fu. Design and optimization of operating parameters for potted anthodium transplant manipulator[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(17): 34-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 贾洪雷,赵佳乐,郭明卓,等. 双凹面摇杆式排种器设计与性能试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,45(1):60-65. Jia Honglei, Zhao Jiale, Guo Mingzhuo, et al. Design and performance experiment on double-concave surface rocker type seed metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 45(1): 60-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
高国华,王 凯,孙晓娜.嫁接机钢针顶起穴盘苗过程EDEM模拟验证及参数优化 [J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(21):29-35. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.21.003 http: //www.tcsae.org
Gao Guohua, Wang Kai, Sun Xiaona. Verification for EDEM simulation of process of jacking tray-seedling by steel needle in grafting machine and parameter optimization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(21): 29-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.21.003 http: //www.tcsae.org
Verification for EDEM simulation of process of jacking tray-seedling by steel needle in grafting machine and parameter optimization
Gao Guohua, Wang Kai, Sun Xiaona
(100124,)
The jacking mechanism of ZGM-7 automatic tray-seedling grafting machine developed by our research group has failure problems in the process of jacking seedling by needle. For solving those failure problems, the software EDEM (enhanced discrete/distinct element method) is used in the research of the process of jacking seedling by needle in this paper. The Edinburgh elastic-plastic cohesion model (ECM) is chosen as particle contact model and a variety of complex particle models with various material properties are established to simulate the realistic seedling substrate in the software EDEM. Furthermore, the relationship between the mechanism and the seedling substrate is studied in simulation. It takes the maximum jacking height of the bottom of seedling substrate as index parameter and analyzes the principles how the different factors, including needle diameter, needle length and jacking speed, influence the process of jacking seedling by needle. The simulation and experimental tests are designed and performed by response surface methodology. The actual experimental result is consistent with the simulation result. The both results show that needle diameter and jacking speed have a significant influence on the maximum jacking height of the bottom of seedling substrate, and the interaction between needle diameter and jacking speed is significant. The maximum jacking height of the bottom of seedling substrate increases monotonically and then slowly decreases monotonically with the increasing of needle diameter in the test level. The maximum jacking height of the bottom of seedling substrate increases monotonically with the increasing of jacking speed in the test level. The maximum jacking height of the bottom of seedling substrate increases with the increasing of jacking speed, when the needle diameter is large. The maximum jacking height of the bottom of seedling substrate decreases with the increasing of the needle diameter, when the jacking speed is small. The maximum jacking height of the bottom of seedling substrate gradually increases and then decreases with the increasing of the diameter of steel needle, when the jacking speed is large. The error between simulation and experiment result is only 0.7%-7.2%. Among those errors, larger errors only exist in phenomenon of dropping and crooking seedling substrate. The realistic seedling substrate has a root system, which prevents the insertion of needle. Thus, the seedling substrate is easier to be dropped and crooked early. However, the error when vertically jacking seedling substrate is less than 2.1% in simulation and experiment. The successful maximum jacking height of the bottom of seedling substrate is 144 mm, which is proposed as the optimization target. The software Design-Expert is used to optimize the simulation results within test level. The optimal parameters of the simulation result are needle diameter of 2.28 mm, needle length of 12.28 mm and jacking speed of 0.09 mm/s. The simulation optimization parameters are applied to the actual mechanism. It’s found that the effect of simulation optimization is significant and the success rate of jacking seedlings is 95.3%. This study greatly improves the operation effect of jacking mechanism of ZGM-7 automatic plug-seedling grafting machine, and it provides reference for the similar problems like jacking up the discrete matrix by needle. Meantime, the reliability of simulation results has been proved in this paper. So, the experimental results can be replaced by simulation results, which will reduce actual test workload significantly and shorten the equipment development cycle obviously. The method in this paper achieves a good simulation effect, which can be applied to other similar complicated environments.
agricultural machinery; grafting; optimization; enhanced discrete element method; seedling; needle; jacking; response surface methodology
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.21.003
S223.9
A
1002-6819(2017)-21-0029-07
2017-07-12
2017-10-20
国家自然科学基金(51675011)—盆花移栽机筑模成穴机构多因素作用优化设计方法研究。
高国华,男,河北大城人,博士,教授,主要研究方向为机械设计及理论。Email:ggh6768@126.com
