A medical understanding on the wuxing theory in cell
2016-03-27XioDngsheng肖党生FngHui方辉SunWenji孙文佳PnHuiyun潘慧云ndLiShengjie郦圣捷
Xio Dngsheng(肖党生), Fng Hui(方辉), Sun Wenji(孙文佳), Pn Huiyun(潘慧云), nd Li Shengjie(郦圣捷)*,
a:VIP ward, the first Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310000, China
b:Department of Internal Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310000, China
A medical understanding on the wuxing theory in cell
Xiao Dangsheng(肖党生)a, Fang Hui(方辉)b, Sun Wenjia(孙文佳)b, Pan Huiyun(潘慧云)b, and Li Shengjie(郦圣捷)b*,
a:VIP ward, the first Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310000, China
b:Department of Internal Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310000, China
Yinyang theory and wuxing theory are the core parts in the Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and giving the accurate interpretation on these theories is one of directions for the modernization of TCM. In the cell, energy metabolism and gene expression are the fundamental processes which are regarded as yin and yang respectively. Furthermore, energy agents, oxygen, end metabolic products, energy releasing as well as genes are the five basic factors for maintaining the undergoing of all biochemistries in cell. Because these factors are the substrates of fi ve essential pathways for the survival of living cell and the abnormalities of any pathways will cause the death of cells, wuxing theory should be translated as five essential pathways in cell. These medical understandings on wuxing theory will not only give some novel viewpoints on the living cell but also promote the development of system biology in future.
Energy metabolism; Gene expression; Stable state; System biology; Yin-yang; Wuxing
INTRODUCTION
Traditional Chinese Medicine, which is regarded as an important components of complementary and alternative medicine CAM1,2, has some advantages in the treatment and prevention for certain diseases, such as cancer3, diabetes4, hyperlipidmia5and pains6. It is hoped that the modernization of TCM will be relied on the developments of systems biology7,8, evidence-based medicine9, precision medicine10,11and big data12. In west, some scholars had begun to accept the concept of yinyang13,14. Even so, there are many doubts on the theory of TCM15.
Giving the reasonable medical interpretations of yinyang theory and wuxing theory (the theory of fi ve elements) is perhaps a milestone for the modernization of TCM. Since 1975, many hypotheses about yinyang theory had been presented in the fi eld of molecule biology, endocrinology, immunology, cytology, oncology, etc16. However, these hypotheses did not provide the principles of TCM in the clinical application and afford few explanations on the wuxing theory as yet. In TCM, yinyang theory and wuxing theory are undividable while the contents of wuxing theory are much richer than that of yinyang theory, involving in the accurate definition of every element and the interpretation of the relationships among them which include inter-promotion, inter-restraint, over restraint and reverse restraint. Most researches on the wuxing theory are based on the paradigm of TCM while a few of researchers try to give their understandings about wuxing theory in the term of bimolecular.
In past, we have published our understanding on the wuxing theories in cell,in which we only af f ord some primary def i nition of wuxing theory17. Our recent researches had launched a novel understanding about wuxing theory in the oxidation of glucose18, which was a vital metabolic pathway in cell. According to this hypothesis, we realized some viewpoints on our understanding on wuxing theories in cell should be rectif i ed.
DISCUSSION
The fundamental metabolisms in cell
All metabolisms in cell are composed of a series of chemical reactions which can be abstracted into two fundamental pathways: energy metabolism and gene expression. Energy metabolism is a process for the oxidation of energy agents such as monosaccharide, amino acids, and fatty acids. The end products of this process are water, carbon dioxide, urea and other small organic molecules from which cell will get energy for its survival. Water, carbon dioxide and urea should be regarded as general end products (GEPs) for nearly all cells will produce these products by the oxidation of energy agents. Cell can alsoexcrete other organic molecular, such as neurotransmitters, steroid hormones, lactic acid, alcohol, proteins, and so on. These molecular should be regarded as specialized metabolic products (SMPs) which imply the specialized metabolism of a cell. Factually, cells will utility many intermediate products as substrates coming for the oxidation of energy agents for the synthesis of SMPs. The releasing of GEPs and SMPs will keep all metabolisms in cell undergoing continuously. It should not be denied that without synthesis of SMPs, a cell can survive with the absence of specialized functions while the inhabitation of oxidation of energy agents will cause the death of cells.
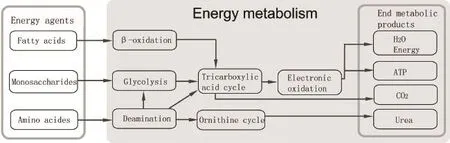
Figure 1. Energy metabolism in cell
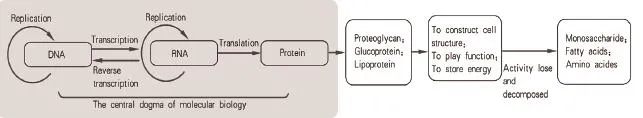
Figure 2. The gene expression in cell
The other pathway is the gene expression. In cell, all metabolisms are carried out in a mild condition with the proteins or proteases playing the vital roles. It is well known that synthesis of proteins is directed by genes according to the centre doma. After being synthesized, these proteins will play their functions, such as catalyzing biochemical reactions, or playing the special physiological functions, or organizing the sharp of cell and subcellular organelles. Completing these functions, these proteins will lose its activity and then be decomposed into amino acids for energy metabolism. This is the whole process of gene expression. At the time that proteins lose their activity and begin to be decomposed, a cycle of gene expression gets the termination and a new cycle of gene expression will be generated to produce new proteins for the replacement of the old one.
Energy agents (monosaccharide, amino acids, and fatty acids) are the initial substrates both for energy metabolism and gene expression. When these agents enter cell, they will be assigned to these tow processes. Entering energy metabolism, energy agents will be oxidized directly into end products. This is named as the short metabolic pathway which is the same as energy metabolism. At same time, some energy agents can also be fi rstly involved in DNA replication, RNA transcription and synthesis of proteins, glycoproteins, proteoglycans and lipoproteins as well which will be used for constructing cell’s structure, catalyzing biochemical reactions and completing other functions. Finishing these functions, proteins, DNA and RNA will be decomposed into monomers for energy metabolism. This is named as the long metabolic pathway. Being connected with the long and short metabolic pathways, all of metabolisms in cell construct a loop. According to this loop, we will fi nd at the case that the quantity of energy agents involving in gene expression is as much as that from decomposition of DNA, RNA and protein, newly synthesized proteins will just replace in-active ones and the cells will show their functional and structural stability. This is regarded as the stable-state of cells, in which all energy agents will be oxidize into fi nal products with no accumulation in cells. The stable-state of cells is the result of the intrinsic balance between gene expression and energy metabolism. By analyzing this state, a novel understanding on wuxing theory can be presented here.
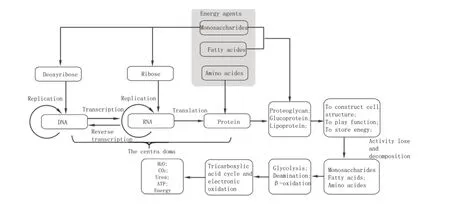
Figure 3. Long metabolic pathway in cell
Wuxing theory will provide interpretation of relationships among the fi ve factors that af f ect the stable-state of cells
Our hypothesis on the wuxing theory in the oxidation of glucose had shown that fi ve factors were the basic ones for the undergoing of glucose oxidation: glucose, oxygen, catalyst, energy, and the end products. By analyzing the stable-state of a cell, all metabolisms can be abstracted into the oxidation of energy agents when a cell is in stable-state and there are just five factors which would affect the state of cell, which are energy agents, oxygen, energy dissipation (signal transduction system), the releasing of end products and gene expression (or the synthesis of proteins). Energy agents and oxygen are the substrates for metabolism while self-renewals of proteins depend on the gene expression. The releasing of end products will keep the chemical reaction undergoing continuously. During the oxidation of energy agents, amount of energy are released, most of which are dissipated as heat and part of which are used by signal transduction system in cell to keep all metabolisms in a harmony.
The essentials of wuxing theory include the def i nitions of fi ve elements and the relationships among them. If the five factors, which have ef f ects on the stable-state of a cell, are classed into wuxing theory, the relationships among the fi ve factors and fi ve elements are just like following: the releasing of end products being regarded as waterTCM; gene expression (or the synthesis of protein) being regarded as woodTCM; energy dissipation being regarded as fi reTCM; energy agents (reductant) being regarded as earthTCM; oxygen (oxidizing agent) being regarded as metalTCM. This classification will afford some helps for the interpretation of the five factors. However, we were still wandering that five elements could not stand for the content of wuxing theory while that fi ve metabolic pathways should be more accurate to express the essence of wuxing theory. In ancient China, it is a general grammar that a noun can be directly used as a verb, which implies that a noun will be used to describe a process rather than an object while the object plays the dominant role in the process. Perhaps, this is the key thinking pattern in traditional Chinese culture which has profound ef f ects on the origination and development of TCM. According to this thinking pattern, fi ve elements in wuxing theory can not only be regard as fi ve objects such as water, earth, metal, fire and wood, but also should be regarded as fi ve processes in which the fi ve elements play the dominant roles respectively. Maybe, this is the essence of wuxing theory.
If this understanding on wuxing theory is right, we can get some conclusions by abstracting all metabolisms in cell. In cell, there are the fi ve metabolic pathways as following: supplement of energy agents, oxidation of energy agents, releasing of energy, releasing of end products and the synthesis of proteins while the five factors are the substrates of the five pathways respectively. When all pathways are normal, the cell will be in a stable state. On the other hand, in cell, any pathway can never undergo independently without the supporting of others. It is more signif i cant that the relationships among fi ve pathways are nonlinear that element A will have inf l uence on element B instead that pathway A will cause pathway B, which can be describedaccording to the wuxing theory. Factually, our current viewpoint is that wuxing theory should be interpreted into five metabolic pathways which were as following: supplement of energy agents, oxidation of energy agents, releasing of end products and energy, synthesis of proteins (gene expression). The ideal understanding of the relationships among the fi ve metabolic pathways and the wuxing theory were as following: the releasing of end products being regarded as waterTCM; gene expression (or the synthesis of protein) being regarded as woodTCM; energy dissipation being regarded as fireTCM; supplement of energy agents (monosaccharide, amino acids, and fatty acids) being regarded as earthTCM; oxidation of energy agents being regarded as metalTCM. The pathways for the supplement of energy agents
Energy agents are the major substrates for the pathway the supplement of energy agents. Energy agents, including monosaccharides, fatty acids and amino acids which are the substrates for all metabolisms in cell, can pass the membrane while nearly all biomacromolecular such as proteins, polysaccharide, must be decomposed into these energy agents for entering the cell. So, the whole pathway of supplement of energy include following steps.
The first steps: the appearance of energy agents outside the cell. This step is also the initial step for both fundamental metabolisms in cell.
The second step is that energy agents enter cell, in which not all energy agents can enter the cell for the cell only absorbs the energy agent that it required for its metabolism for example that many cancer cells has glutamine transporters to get glutamine for the glutaminolysis pathway19,20. It is a reasonable hypothesis that by regulating the activity of transporters in the membranes, cell will obtain the required energy agents for its metabolism21. This can be regarded as fi reTCMpromoting earthTCM.
After entering the cell, there are three general pathways for the energy agent. The fi rst way is to be oxidized into end-products, which should be regarded as earthTCMpromoting metalTCM. The second pathway is to surge the synthesis of proteins, glycoproteins, lipoproteins, DNA, RNA, polysaccharides, which should be regarded as woodTCMretaining earthTCM. The third is stored as energy carriers. Factually, macromolecular in cell, most of which are the end-product of gene expression, can also be regarded as the pattern of energy storages which should be also regarded as woodTCMretaining earthTCM. On the other hand, macromolecular and energy agents are soluble which will inhabit the releasing of water and this should also be regarded as earthTCMretaining waterTCM.
The pathway of oxidation in cell
Oxygen is the major substrate for the pathway of oxidation in cell. Oxidation is a general chemistry in cell while nearly all organic molecular can be oxidized. In cell, all metabolisms can be divided in two parts: anaerobic oxidation and aerobic oxidation. Typical aerobic oxidations occur in mitochondria including three carboxylic acid cycle and electron transfer with water and carbon dioxidation as end products while oxygen, as one of substrates, will attend these biochemistries. In mitochondria, there is no reverse reaction about election oxidation, which destines the oxidation of energy agents. In fact, there are more anaerobic oxidations in cell, for example: decomposition of biomacromolecular, glycolysis, β-oxidation of fatty acids, and so on in which oxygen cannot attend these biochemistries directly. For anaerobic microorganisms, there are no tricarboxylic acid cycle and electron oxidation in cell, which cannot deny the appearance of anaerobic oxidation in cells. The oxidation pathway in cell is multistep biochemistries, while the whole pathway was as following.
The fi rst step: the decomposition of bio-macromolecular. This step should be regarded as metalTCMretaining woodTCMwith the energy agents as the end products of this step. The oxidation of the energy agents was regarded as earthTCMpromoting metalTCM.
The core step of oxidation in aerobic cell is the carboxylic acid cycle and electron transfer in mitochondria, which is the irreversible reaction cell. In the anaerobic microorganisms, there was still some irreversible reaction in cells which should be regarded as core step of oxidation, for example: the synthesis of lactic acid in lactobacilli. The core steps designated the oxidation of energy agents.
The end-products for the oxidation of energy agents are water, carbon dioxide, which was regarded as metalTCMpromoting waterTCM. During the oxidation of energy agents, a lot of energy will be released, which should be regarded as fireTCMretaining metalTCM.
The pathway for the releasing of end-products
The major substrate for the pathway of end-products releasing are water, carbon dioxide and urea. Some products just like proteins, neurotransmitters, steroid hormone and other organic molecular can also be excreted by cells, which should be regarded as specialized end-products for these molecular stands for the specialized function of a cell.
The basic principle of the chemistry is that releasing of end-products will be beneficial for the undergoing of chemical reaction. So, the releasing of all metabolic products will help the undergoing of biochemistries in cell. The pathways for releasing of end products are listed as following.
The core step for the releasing of end products is the excretion of water. Water, the smallest molecule with its stability, was not only the end product of oxidation which is regarded as metalTCMpromoting waterTCM, but also the product for synthesis of protein, DNA, RNA and so on, which should be regarded as waterTCMpromoting woodTCM. So, releasing of water will be benef i cial for most reactions in cell. It has been pointed out that water was the main energy carrier for the releasing of energy, which should be regarded as waterTCMretaining fireTCM. When specialized endproducts are released by cell, they will also take the energy out of cell in the pattern of chemical energy, which should also be regarded as waterTCMretaining fi reTCM.
The water is also a vital dissolvent and can dissolve most of energy agents, which should be regarded as earthTCMretaining waterTCM.
The pathway for genes expression
Genes are the substrates for the pathway of gene expression. It is well known that without catalysts, most of bio-chemistries cannot be carried out in cell. In cell, most of catalysts are proteins or proteases and can be renewed by gene expression, which never occur in vitro. The central dogma is the core part of the pathway for gene expression. Synthesis of DNAs, RNAs and proteins is condensation reaction with water as one of the product of these bio-reactions. So, the releasing of the water will be benef i cial for these reactions which should be regarded as waterTCMpromoting woodTCM.
During the synthesis of these bio-macromolecular, energy agents are the substrates for these reactions, which should be regarded as woodTCMretaining earthTCM.
Any behaviors of cell are composed of a series of reaction with the proteins as catalysts. After being synthesized, the proteins will play their function as catalysts, which should be regarded as woodTCMpromoting fi reTCM, for any reaction will be involved in the releasing of energy as chemical energy or/and heat.
Finishing their function, RNAs and proteins will lose their activity and began to be decomposed, which should be regarded as metalTCMretaining the woodTCMfor the decomposition of these bio-mcramolecular are anaerobic oxidation.
It should not be ignored that the primary function of DNA is to carry and store the hereditary information and hydrogen binding plays a vital role in this function of DNA. In the case that hydrogen bindings of double helix were destroyed, DNA will be unwounded for the replication or transcription instead of storing or repairing the hereditary information. Water in cell is the just agents for destroying the hydrogen bindings so that the releasing of water will be beneficial for DNA keeping in double helix structure with some disadvantages of replication or transcription which should be regarded as waterTCMpromoting woodTCM. In short, releasing of water perhaps is a double-edged sword for DNA playing its function.
The releasing of energy
What are the patterns for the releasing of energy in cell? This is an interesting question. Our studies discovered the patterns of energy releasing as following. Firstly, the releasing of metabolic products will take the energy out of cell. There are two kinds of metabolic products in cell: SMPs and EMPs. Proteins, polysaccharide, RNA, small organic molecular (neurotransmitters, steroid hormone and so on) are specialized metabolic products which can be oxidized for releasing energy. So, the releasing of these molecular implied that the energy in cell will be released as chemical energy which should be regarded as waterTCMretaining fireTCM. Water, carbon dioxide and urea are the end metabolic products. The releasing of these molecular will carry the energy as heat which is also regard as waterTCMretaining fi reTCM.
Secondly, cell will also use ATP to synthesize the biomacromolecilar such as RNA, DNA and proteins during which the energy will be released or transformed. This pattern of energy releasing should also be regard as woodTCMpromoting fireTCM, which is always appearing in anabolism.
The released energy by oxidation of energy agents can be divided into two parts, most of which will be discharged as heat and carried by water. This is regarded as waterTCMretaining fireTCM. No more than 40% energy released by oxidation of energy agent is used for synthesis of ATP. Parts of ATP are used for anabolism, which is regarded as woodTCMpromoting fi reTCM. The other is used to phosphorylation of proteins. When a protein is phosphorylated, its activity will be altered and then take a chain reaction so as to bring transformation of metabolism and gene expression in cell, which is named as sign transduction in cell. In cell, a lot of specialized proteins, which can be phosphorylated and then dephosphporylated, constructed a signal pathway for eucaryote cell to detect and respond to external and internalstimuli. Some major signaling pathways include MAPK/ERK pathway22, cAMP-dependent pathway23, IP3/DAG pathway24, and so on. Although the signaling pathways are the hot points for researchers and attracting the attention of researchers, it is ignored that signal transduction is a pattern of energy releasing. When a protein is phosphorylated, an ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP and Pi which will be added to the amino acid residue of a protein covalently and then the Pi will be removed by phosphatase. During this process, the energy carried by ATP is released with the fl uctuation of protein activity. So, by the pattern of releasing little energy by phosphorylation of proteins, cell carries out the regulation of metabolism and gene expression so as to respond to the external and internal stimuli and survive in different conditions. Our viewpoint is that the signal pathways should also be regarded as fi reTCM.
Our another hypothesis is that signal pathways can also regulate the activity of membrane proteins so as to help the cell obtain the required energy agents, which should be regarded as fi reTCMpromoting earthTCM.
How do cells die?
In cell, all biochemistries can be classified into the five metabolic pathways while a slight change of chemistry will take many alterations of these metabolic pathways which can be concluded by the interrelations of the five pathways. However, the interrelations of the fi ve pathways are very complicated and we only discovered a part of them. So, the behaviors of cell are the cooperation of the fi ve pathways with one pathway playing its dominant role. In case that the fi ve pathways keep in normality, the behaviors of a cell will stay in stable state. Any changes of these pathways will break the stable state and cell will reach another stable state.
Death is unavoidable for cells. In our body, billions of cells will die every day and the same number of cells will be also born. How do cell die is another hot point for researchers. Cooperation of the fi ve pathways will keep cells in stable state and they will be responsible for cell’s mortality as well once any pathway reach the extremely abnormality or is inhibited completely. Energy agents, oxygen, end products, genes and energy are the substrates of five pathways respectively and any changes of these five factors will take the alteration of the pathways. So, extreme alterations of the fi ve factors or the fi ve pathways are the patterns for a cell go to death. These are the essential viewpoints of yinyang theory and wuxing theory which will also provide some new viewpoints on the death of cell.
Energy agents
Without the supplement of energy agent, the pathway for supplement of energy agents will be blocked and the cells starve to death25. Over-supplement of energy agents implies that the pathway for supplement of energy agents is in a state of extreme saturation which will make cell die from over-nutrition. Every metabolism must share the specialized spaces for its undergoing. For example, the occurrence of glycolysis, deamination and beta oxidation is in cytoplasm with the tricaroxylic acid cycle and elecion oxidation in mitochondrion while replication, transcription as well as synthesis and modification of proteins appear in nucleus and ribosomal respectively. In the case that too many energy agents enter cell, they must be stored as fats, proteins and polysaccharides which will share some spaces of a cell. Therefore, the more space for storage of energy suppliers, the less space for metabolism. This will lead to the decreasing of energy metabolism and /or gene expression. Once there is no space for these metabolisms, cells will go to die.
Oxygen
For some anaerobic microorganism, they can only survive in the condition of hypoxia for there are some proteins which are sensitive to oxygen. Under the condition that they are with oxygen, these proteins will be oxidized and lose their activity and the cell will also die of absence of protein. As for most of aerobic cell, both hypoxia and over-supplement of oxygen can cause the death of cells. Without oxygen26, the tricaroxylic acid cycle and elecion oxidation in mitochondrion will be blocked and cell will die from the absence of energy27. In cell, nearly all organic molecular can be oxidized, including macromolecules such as DNA, RNA and proteins. Oversupply of oxygen will not only oxidize energy suppliers, but also accelerate the oxidation of those macromolecular in cell, which will decrease the renewal of protein. Without new synthesized proteins, both energy metabolism and gene out will decrease to termination and death for cell will be inevitable.
So, both hypoxia and over-supplement of oxygen will take abnormality of oxidation in cell and cell will die from hypoxia or oxygen toxicity.
Gene expression
Gene expression is the only way for the renewal of protein incell which will also responsible for the survival of living cells. In the middle of last century, experimental evidences conform that without the nucleus, in which initial steps of gene expression occur, cells cannot avoid the fate of death although they can live for a short time, just like red blood cell. So, it is acceptable that without gene expression, cell will die from the insufficiency of protein renewal. Furthermore, gene expression is the pathway of self-repairing against the damage of cell structure. Under the condition that a cell cannot self-repair by gene expression against structural damages, the cell cannot avoid the fate of death which is called as necrosis.
Energy releasing
Energy carried by energy agents must be releasing in the pattern of heat carried by water and chemical energy carried by exocrine proteins and other organic substances. The abnormality of energy releasing will also cause the death of cells. Heat is the energy to maintain the motion of all molecular and activity of protein in cell. In the case the too much heat is released, the motion of molecular and activity of protein will get decreased and the metabolism as well as renewal of proteins in cell will be slowed so that cell will be go to die or be frozen. In the case that heat cannot be released, they will be accumulated in cell to increase the motion of molecular so as to destroy the intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonds, ionic linkages, hydrophobia bonds, Vander Waals forces, which maintain not only the unique three-dimensional shape of each protein molecule but also the structure of cell. Without the normal structure, the only fate for cell is death.
Activation of signal conduction is one of the pattern for energy releasing and activation of certain pathways will take death to cell which is called as apoptosis or the process of programmed cell death, just like the TNF-induced model28and the Fas-Fas ligand-mediated model29.
Releasing of GEPs and SMPs
Accumulation of GEPS will inhibit the metabolism in cell. Accumulation of water will take the water intoxication which will lead cell to death while the same results will also occur with the accumulation of carbon dioxide, urea. The over-releasing of water will take the hydropenia to cell which will also inhibit the chemistry in cell and cell will die from shortage of water. No evidence conforms that over-releasing of carbon dioxide, urea will take the death of cell.
All metabolisms can be divided into two groups: general metabolism with the GEPs as end products and specialized metabolisms with SMPs as end products. The specialized behaviors and functions of a cell are always based on the specialized metabolisms while general metabolism in cell will afford energy and intermediate products for specialized metabolisms. Without specialized metabolism, a cell can survive. On the contrary, without general metabolism, cell will die from the deficiency of energy. SMPs are the end products of specialized metabolisms. So, when too many SMPs are released, the specialized metabolisms will play the dominant role in cell and more intermediate products will enter the specialized metabolism with the inhabitation of general metabolisms, which may cause the death of cells.
PERSPECTIVE
Although some researchers hope that the development of system biology highlights the new direction for the modernization of TCM7,8, few researchers presented their understanding on the yinyang theory and wuxing theory in the principle of system biology. In recent years, there are two principle streams within systems biology: 1) Pragmatic systems biology30, which emphasized the utilization of large-scale molecular analysis and computer technology,such as genomics, proteomics and metabonomics, with the hopes to fi nd new biomarks for diagnose and news targets for treatment; 2) Theoretic system biology31, which will take radical changes for theoretic and methodological approaches in biological researches.
System biology is still under discussion32,33. Many models are presented for explaining theoretically the principles of system34,35and some biological models are also published for clinical applications36. From these documents, we can get some general idea about biosystem. As for a cell, it could be regarded as an open biosystem with a variety of biochemistries so as to get the energy and materials from surrounding and release metabolic products to its environment34. Cell can also produce organelles by self-organizing while the growth and division should be regarded as autopoiesis35. Except for these, there are few ideas on a cell in the sight of theoretic system biology. What are the general principles of biosystem? What are the basic mechanisms for the operation of a living biosystem? How to give a novel classification about organelles in cell in the principle of system biology? How to give an explanation about the selforganization of organelles? How to give a clinical assessment for a patient in the principles of system biology? How to takesome new viewpoints about disease and alternative treatment for patients? The lists of similar questions can go on while giving the scientif i c answers about these questions are always wandering the development of system biology.
In recent year, by utilization of large-scale molecular analysis and computer technology, some researchers hoped to find biomarkes for the diagnosis of TCM or to discover the principles for applications of Chinese medicinal herb7. There are little progresses in modernization of TCM theory, which would perhaps bring some radical changes of theoretic system biology, even the theoretic biology while giving the reasonable definitions on wuxing theory and yinyang theory in term of cytology are the initial steps. The essential characteristic of TCM is its viewing the human body as a whole system. Yinxing theory and wuxing theory is the fundamental theory in TCM, which is used to construct a virtual model for clinical applications. However, there are few articles to describe this virtual model in the term of molecular biology. Now, our understanding on wuxing theory discovers this virtual model, which can advance the development of system biology. So, we are convinced that the interrelationships between the energy metabolism and gene expression are the primary force for the self-organization and autopoiesis of a living creature while wuxing theory provied some novel viewpoints on the operation of living creature. Furthermore, we can also give a bold conclusion that the whole process of gene expression is the key dif f erence of living creature from the unanimated substance. By altering the five pathways, any factor will take some influences on the behaviors of a cell while the cell will change its stable state by alteration of one or more pathway instead of several targets.
In short, there are a variety of principles, methods and herbal medicines in the paradigm of TCM for the therapy of diseases. Modernization of TCM theory will help us choose the reasonable treatment for the patients while our understandings on wuxing theory will promote some advancement in this field. However, these are still more researches that should be carried out in the future.
REFERENCES
1 Cheung F. Modern TCM: Enter the clinic. Nature, 2011, 480(7378): S94-95.
2 Xutian S, Cao D, Wozniak J, Junion J, Boisvert J. Comprehension of the unique characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine. Am J Chin Med, 2012,40(2): 231-244.
3 Sha O, Niu J, Ng TB, Cho EY, Fu X, Jiang W. Anti-tumor action of trichosanthin, a type 1 ribosome-inactivating protein, employed in traditional Chinese medicine: a mini review. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,2013,71(6): 1387-1393.
4 Tong XL, Dong L, Chen L, Zhen Z. Treatment of diabetes using traditional Chinese medicine: past, present and future. Am J Chin Med, 2012, 40(5): 877-886.
5 Xu DY, Shu J, Huang QY, et al. Evaluation of the lipid lowering ability, anti-inflammatory effects and clinical safety of intensive therapy with Zhibitai, a Chinese traditional medicine. Atherosclerosis,2010,211(1):237-241.
6 Berman BM, Langevin HM, Witt CM, Dubner R. Acupuncture for chronic low back pain. N Engl J Med, 2010,363(5): 454-461.
7 Ji Q, Zhu F, Liu X, Li Q, Su SB. Recent Advance in Applications of Proteomics Technologies on Traditional Chinese Medicine Research. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,2015:983139.
8 Wang P, Wang Q, Yang B, Zhao S, Kuang H. The Progress of Metabolomics Study in Traditional Chinese Medicine Research. Am J Chin Med,2015(43):1281-1310.
9 Spence W, Li N. An exploration of Traditional Chinese Medicine practitioners’ perceptions of Evidence Based Medicine. Complement Ther Clin Pract,2013,19(2):63-68.
10 Zhou X, Li Y, Peng Y, et al. Clinical phenotype network: the underlying mechanism for personalized diagnosis and treatment of traditional Chinese medicine. Front Med,2014, 8(3):337-346.
11 Jafari S, Abdollahi M, Saeidnia S. Personalized medicine: a conf l uence of traditional and contemporary medicine. Altern Ther Health Med,2014,20(5): 31-40.
12 Liu B. Utilizing big data to build personalized technology and system of diagnosis and treatment in traditional Chinese medicine. Front Med,2014,8(3):272-278.
13 Pradere JP, Dapito DH, Schwabe RF. The Yin and Yang of Toll-like receptors in cancer. Oncogene,2014,33(27): 3485-3495.
14 Godson C, Perretti M. Novel pathways in the yin-yang of immunomodulation. Curr Opin Pharmacol,2013,13(4): 543-546.
15 Lehmann H. A Westerner’s question about traditional Chinese medicine: are the Yinyang concept and the Wuxing concept of equal philosophical and medical rank. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao, 2012(10):237-248.
16 Sheng X. Application and review of yinyang theory in modern. Global Traditional Chinese Medicine,2011,4(2): 120-124.
17 Xiao DS,Yang YM, Yu GY. The Relationship among The Organelles and The Implication of Yin-yang and Wuxing in Chinese Traditional Medicine. Journal of Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2008(3): 293-295.
18 Fang H, Li SJ,Zhu QH, Pan HY, Xiao DS. A novel understanding about oxidation of glucose in term of wuxing TCM theory. World Journal of Integrated traditional and western Medicine,2016(2):31-36.
19 Bröer A, Rahimi F, Bröer S. Deletion of Amino Acid Transporter ASCT2 (SLC1A5) Reveals an Essential Role for Transporters SNAT1 (SLC38A1) and SNAT2 (SLC38A2) to Sustain Glutaminolysis in Cancer Cells. J Biol Chem,2016,291(25):13194-13205.
20 Jin L, Alesi GN, Kang S. Glutaminolysis as a target for cancer therapy. Oncogene,2016,35(28): 3619-3625.
21 César-Razquin A, Snijder B, Frappier-Brinton T, Isserlin R, Gyimesi G, Bai X, et al. A Call for Systematic Research on Solute Carriers. Cell,2015(162):478-487.
22 Burotto M, Chiou VL, Lee JM, Kohn EC. The MAPK pathway across dif f erent malignancies: a new perspective. Cancer,2014,120(22):3446-3456.
23 Kleppe R, Krakstad C, Selheim F, Kopperud R, Døskeland SO. The cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathway as therapeutic target: possibilities and pitfalls. Curr Top Med Chem,2011,11(11):1393-1405.
24 Ayala-Peña VB, Scolaro LA, Santillán GE. ATP and UTP stimulate bone morphogenetic protein-2, -4 and -5 gene expression and mineralization by rat primary osteoblasts involving PI3K/AKT pathway. Exp Cell Res, 2013,319(13): 2028-2036.
25 Lashinger LM, O’Flanagan CH, Dunlap SM, Rasmussen AJ, Sweeney S, Guo JY, et al. Starving cancer from the outside and inside: separate and combined ef f ects of calorie restriction and autophagy inhibition on Ras-driven tumors. Cancer Metab,2016(4):18.
26 Gdynia G, Sauer SW, Kopitz J, et al. The HMGB1 protein induces a metabolic type of tumour cell death by blocking aerobic respiration. Nat Commun,2016(7):10764.
27 Jardim-Messeder D, Moreira-Pacheco F. 3-Bromopyruvic Acid Inhibits Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Glutaminolysis in HepG2 Cells. Anticancer Res,2016,36(5):2233-2241.
28 Brenner D, Blaser H, Mak TW. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: live or let die. Nat Rev Immunol, 2015,15(6):362-374.
29 Calmon-Hamaty F, Audo R, Combe B, Morel J, Hahne M. Targeting the Fas/FasL system in Rheumatoid Arthritis therapy: Promising or risky. Cytokine, 2015,75(2): 228-233.
30 Melham T. Modelling, abstraction, and computation in systems biology: A view from computer science. Prog Biophys Mol Biol,2013,111(2-3):129-136.
31 Bard J, Melham T, Noble D. Epilogue: Some conceptual foundations of systems biology. Prog Biophys Mol Biol, 2013,111(2-3):147-149.
32 Gatherer D. So what do we really mean when we say that systems biology is holistic. BMC Syst Biol,2010(4):22.
33 Joyner MJ, Pedersen BK. Ten questions about systems biology. J Physiol, 2011(589):1017-1030.
34 Bose B. Systems biology: a biologist's viewpoint. Prog Biophys Mol Biol,2013(113):358-368.
35 Razeto-Barry P. Autopoiesis 40 years later. A review and a reformulation. Orig Life Evol Biosph, 2012(42):543-567.
36 Voit EO. A systems-theoretical framework for health and disease: inf l ammation and preconditioning from an abstract modeling point of view. Math Biosci,2009(217):11-18.
(Accepted: June 12, 2016)
Funding:This study was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China :microRNA-194在非酒精性脂肪肝发病机制中的作用的研究(81300302)
*Corresponding author: Email: dou900@163.com;Mobile phone:+86-571-87236102
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- A randomized, controlled trial of Shutangluo fang in treating painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Meta-analysis about Western Medicine combined with activating blood drugs on modulating blood glucose and lipids in diabetic patients
- Clinical ef f ects of acupoints moxibustion therapy on postsurgical gastroparesis syndrome after resection of esophageal cardia cancer
- Analysis of the features of TCM and western medicine in the diagnosis and treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism characteristics
- INSTRUCTION FOR AUTHORS
