Improvement of Intercept Probability Algorithm for Anti-ship Missile Based on Search Theory
2011-07-25WANGXingang汪新刚XIEXiaofang谢晓方LIXue李雪
WANG Xin-gang(汪新刚),XIE Xiao-fang(谢晓方),LI Xue(李雪)
(1.Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University,Yantai 264001,Shandong,China;2.Unit No.91183,Qingdao 266000,Shandong,China)
Introduction
The medium and long range anti-ship missiles have become primary offensive weapons and play very important roles in modern naval warfare.As they have to calculate and make decision before launching,the decision-making systems are widely used.For them,the high intercept probability is one of the most important performances,and also the basement of penetration and hit probabilities.
1 Traditional Intercept Probability and Its Problems
The intercept probability can be divided into longitudinal and lateral intercept probabilities.The intercept can be defined as a covering of the radar beam to the target.The radar’s intercept probability determines upon its own performance and is close to 1,and is assumed as 1 in this paper.If the start time of the missile’s radar is selected properly,its beam will cover the target’s longitudinal scattering area,the missile’s longitudinal intercept probability can be assumed as 1.
For the lateral intercept probability,if the missile’s left deviation limit of auto-control destination makes the target lie inside the right limit of the missile’s radar beam,and vice versa,it can intercept the target.The traditional intercept probability can be given as
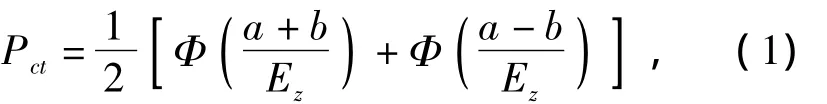
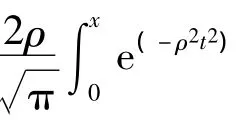
Only the distribution density function of missile auto-control destination is considered in the above formula,while the target region distribution shape and density function are not taken into account.
Generally,assume that the ideal missile trajectory passes through the centre of the target region.But,in some shooting modes,such as regional rough shooting,there is always a difference between the target coordinates and aiming point.
2 Principle of Search Theory and Missile Intercept Analysis for Linear Region
2.1 Principle of Search Theory
If the target’s prior densityg(a)in regionAis known,according to the search theory,we have

The intercept probabilityPcan be written as

wherePdAis the detection probability of the target in region dA.
For the seeker,the prior densityg(b)is known,in regionB,the distribution function can be taken as 1.The detection probability of targetPcan be expressed as
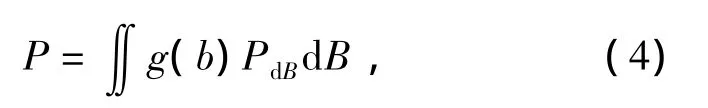
wherePdBis the probability of acquiring target when the target is in the region dB.
2.2 Missile Intercept Probability Analysis for Linear Region
In Fig.1,O0is the theoretical start point of missile radar.

Fig.1 Fall point distribution of missile in course of intercepting target
The radar can detect the most left side of the target region when the missile locates at the pointOKwhich is the most right side of error ellipse centered atO0.
O1is the theoretical shutdown point of missile radar.The radar can detect the most right side of target region when the missile locates at the pointOGwhich is the most left side of error ellipse centered atO1.
The missile will distribute in the regionK1,K2,K3,K4,K5,K6,when it detects the target.The distribution alongXis uniform and normal alongZaxis.

Fig.2 Intercept situation on linear region
As shown in Fig.2,the probability that the missile falls into range[-3σ,3σ]alongZaxis will be 99.7%,and it can be taken as 1.In the figure,ais the half width of radar scan andf(ZB)is the PDF alongZBaxis.
Combined Eq.(3 -4),the intercept probability for missile in regionA0A1and target inB0B1can be expressed as

3 Interception Probability in Different Target Distributions
The present point shooting is a main shooting mode for the anti-ship missile.In this mode,the original target position is known,but its course and speed are unknown.
The target region comprises two parts,the detection error of investigative platform,which distributes normally,and the error caused by the target motion,which distributes uniformly.
3.1 Model of Target Region
Analyzed the errors,the distance from target region boundary to the center can be written as

whereeis the medium error of detection error,rm(t)the targetmotion error,ρthe normalconstant 0.476 936.
The target motion error changes in the course of missile detecting target continuously.
For the missile flying in straight line,the minimum flight time from launch point to the most left point of target region ist0.

whereLis the linear distance between launch point to target present point,vmthe missile velocity,vdthe target velocity,T0the delay time,d0the radar scan range.
For the route-programmable missile,if its flight path and direction are determined,Eq.(7)is also true.
The vertical distance from the target region boundary swept by radar to ideal missile trajectory can be expressed as

wheret1is the flight time after the missile enters the target region.

Fig.3 Target region
As shown in Fig.3,the target region Ⅱ is formed by the target maximum velocity andⅠby tactical economical velocity.
Taken the ideal missile trajectory asXaxis,its vertical direction asZaxis,the target present point as the origin of coordinates,a Cartesian coordinate system can be built.
In simulation,the distance from launch point to target is 180 km,delay time 30 min,missile velocity 240 m/s,detect error 1 km.
The target region is a symmetrical figure and its top half is shown in Fig.3.The region Ⅱ is formed by the target’s maximum velocity of 30 knots.
The missile fight time from launch point to the point on which the missile can detectC11is 8.399 min,fromC11toC15is 306.9 s,fromC11toOis 143.574 7 s,fromC11toC14is 153.441 8 s.
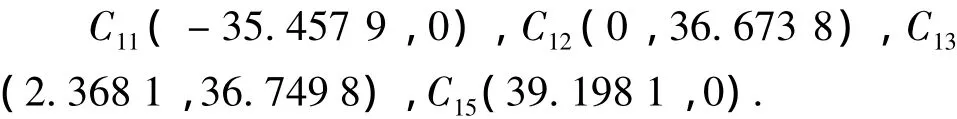
Target regionⅠis formed by the tactical economical velocity of 20 knots.
C21-C25are coordinates of region ⅠatXaxis.C21(-23.554 1,0),C22(0,25.563 8),C23(1.055 0,23.540 7),C25(39.198 1,0).
3.2 Targets Distributing on RegionⅡBoundary Uniformly
The investigation platforms may be detected by the target ship when it works,the target will be alerted,increase battle grade and evade in maximum speed.The target will distribute on the boundary of regionⅡuniformly.
R(T0+t0)is the distance from anyone point on boundary to theX-axis,the intercept probability for this point can be given as
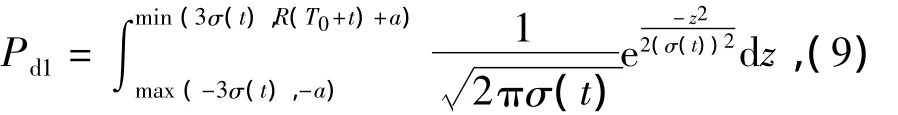
whereθ∈(0,π)is the intercept probability for the whole regionⅡboundary

3.3 Target Distributing Between BoundaryⅠand BoundaryⅡUniformly
Commonly,the target always navigates in tactical cruise speed.During investigation and missile interception,it may find the coming missile,increase battle grade and navigate in its maximum speed.If the missile is launched in present point shooting mode,the target will distribute between boundariesⅠandⅡU-niformly.
FromC11toC21,the intercept probabilityPM1of the missile’s radar for linear regionM0M2normal toZaxis can be expressed as
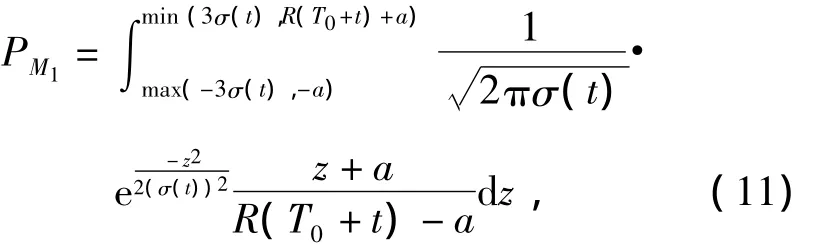
whereT0is the delay time,tthe missile’s flight time from launch point to the point that the missile’s radar can detectM0M2,3σ(t)the missile’s lateral flight error from launch point to the point that the missile’s radar can detectM0M2.
The intercept probabilityPM2of the radar for the random regionM0M2normal toXaxis fromC21toC25can be written as

if 3σ(t)<r(T0+t)-a,thenPM2=0.The intercept probabilityPM3of the radar for the random regionM0M2normal toZaxis fromC25toC15can be expressed as

As the target distributes in the circular region uniformly,according to Eq.(3),the intercept probabilityP1of the missile for the target fromC11toC21can be given as
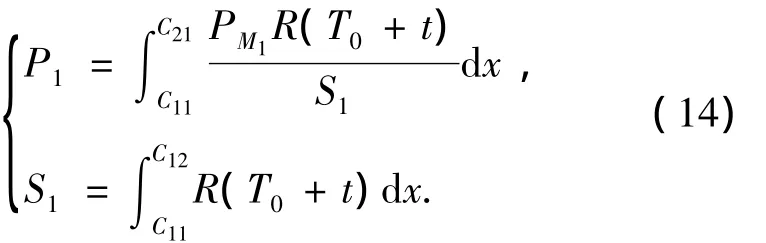
The intercept probabilityP2of the missile for the target fromC21toC25can be written as
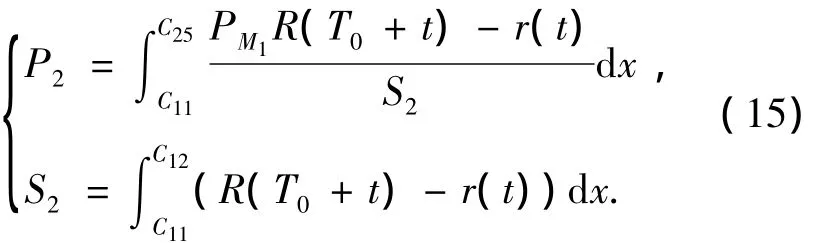
The intercept probabilityP3of the missile for the target fromC25toC15can be expressed as
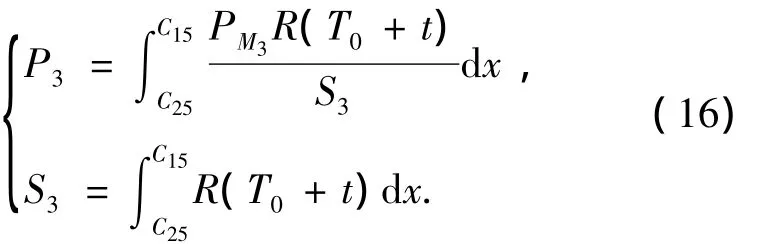
Then,the intercept probability of the missile for the target in the whole region can be written as

3.4 Targets Distributing in RegionⅡUniformly
If the target’s maximum speed is known only,it is considered that the target distributes in regionⅡuniformly.But in fact,the target always moves in higher speed and hardly stays at the present point.Thus,the uniform distribution will be the rarely case in battle.
The intercept probabilityPMof the radar for the target in the linear regionM0M2normal toXaxis can be expressed as
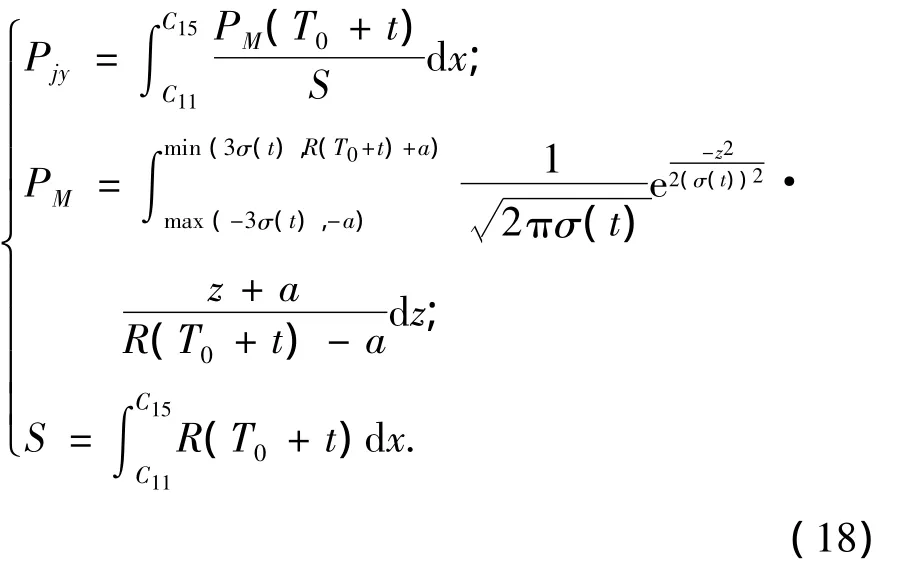
3.5 Intercept Probability in Difference between Present Point and Aiming Point
As shown in Fig.4,Ois the present point,andO2is the aiming point,build up the coordinate systemX1O1Z1.

Fig.4 Intercept situation in difference between present point and aiming point
3.5.1 Target Distributing Between RegionⅠandⅡUniformly
The target usually navigates in the tactical speed,they will sail in its maximum speed in evading or trial voyage,and the cruise duration will not exceed 60 min.If it keeps lower alert grade and navigates in the tactical speed,it distributes between regionⅠ andⅡuniformly.
The lines normal to theXaxis and passing pointC11andC12divide the target region in Fig.4 into three parts,1,2 and 3.The lineB21B22normal toXaxis intersects region Ⅰ at pointsB11andB12.
The parameterdis the distance from the target’s present point to the missile’s aiming point.
Firstly,according to Eq.(4),the intercept probabilityPBof the missile for the target uniformly distributing in the linear regionB21B22inside the region 1 can be written as
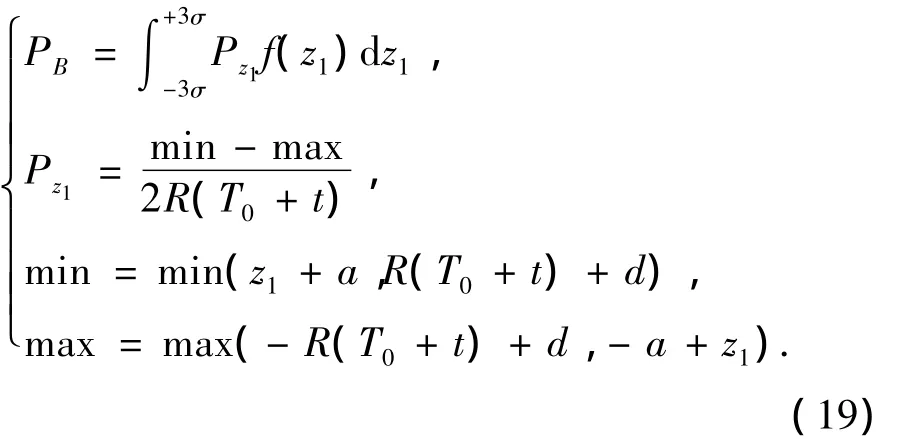
The intercept probabilityP1of the missile for the target in the region 1,according to Eq.(3)can be written as

Secondly,The intercept probabilityPBof the missile for the target in the linear regionB21B22inside the region 2,according to Eq.(4),can be expressed as

The intercept probabilityP2of the missile for the target in the region 2,according to Eq.(3),can be given as

Thirdly,the intercept probabilityP3of the missile from the target in the regionB21B22inside the region 3 can be similarly expressed.
If the target distributes between regionⅠandⅡuniformly,the intercept probabilityPjy2can be written as

3.5.2 Target Distributing on Region Ⅱ Boundary U-niformly
If the target keeps higher alert grade,it will detect the abnormal when the investigation platform working and the target will evade in higher speed.The target will distribute in boundaryⅡ uniformly.
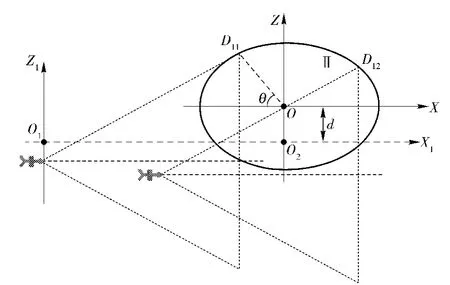
Fig.5 Intercept probabilityfor target distributing on boundary uniformly
The radio of boundary length detected by missile radar to the whole circumference is the intercept probability,the model is similar to Eq.(9)and Eq.(10),no further derivation is necessary.
4 Simulation Results and Analyses
The simulation parameters are the target velocity of 28 knots,target indication error of 3 km,missile range of 300 km,missile velocity of 200 m/s,radar sweep half-width of 30 km,radar range of 40 km,σ(t)=0.1t2,and the distance between missile and target is 200 km.
Fig.6 shows the simulation results,wherePctis the traditional intercept probability,Pbjis the intercept probability under the condition that the target distributes on boundaryⅡ uniformly,Pzjis the intercept probability under the condition that the target distributes in region betweenⅠ andⅡ uniformly,Pjyis the intercept probability under the condition that the target distributes in regionⅡ uniformly.
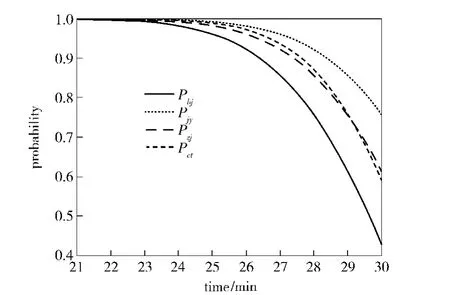
Fig.6 Simulation results of relation between delay time and intercept probability
If the delay time is short,wherever the missile is at any point of auto-control destination,the missile’s radar can cover the whole target region,and the target distribution has no effect to intercept probability.
The longitudinal and lateral width of target region will all increase with the delay time increasing.Compared withPjy,the variation ofPctis more acute,because the traditional intercept probability only takes the longitudinal width variation into account.The variation ofPbjis the most acute,because of the target evading influence.
Fig.7 shows the simulation results under the condition that there is a difference between the present point and the aiming point.
Assume that the target tactical velocity is 22 knots and the target distribute on boundary uniformly.Parameterdis the distance between the present point and aiming point.

Fig.7 Simulation result in difference between present and aiming point
Selecting the present point as the aiming point,the missile can get the highest intercept probability if the delay time is less than 31.1 min.Pbj(d=1.44 km)is maximal if the delay timeT0∈(31.1,32.9),whilePbj(d=2.35 km)is maximal ifT0∈(32.9,35.4),andPbj(d=3.77 km)corresponds withT0∈(35.4,37.0).
In fact,for each delay time,the deviationdcorresponding to the maximum intercept probability can be obtained.
The above analyses show that the aiming point different from present point will result in higher intercept probability under some conditions.
From the probability theory,it can be seen that,in missile salvo,taking the point corresponding to the maximum intercept probability at both sides of the present point as the aiming point,the effect will be better than that of the present point.Thus,this model may serve as the aiming point analysis model in missile salvo,if the target evades.
5 Conclusions
Based on the traditional anti-ship intercept probability model,a new intercept probability model is derived in this paper,according to the search theory,target distribution and missile radar scan features.The simulation results show its correctness and practical applicability.It improves the traditional algorithm,solves the problems of intercept probability for the different target distributions,and provides a theoretical basis of the intercept probability analysis and selection of aiming point for medium and long rang anti-ship missiles in actual combat.
For the other shooting modes of future point and bearing only,and so on,the new intercept probability models can be constructed by using above method also.
[1]Parashak P M III.The effects of quality and timeliness of targeting information on submarine employment of long range anti-ship cruise missiles[D].California:Naval Postgraduate School,2005.
[2]Jablon A,Agrawal A.Optimal number of array faces for active phased array radars[J].IEEE Trans on AES,2006,42(1):351 -360.
[3]WANG Guang-hui,WANG Rui-qi,ZHU Xing-bang.A-nalysis of beyond-line-of-sight anti-ship missile’s hit probability[J].Journal of Projectiles,Rockets,Missiles and Guidance.2008,28(2):33-34.(in Chinese)
[4]WANG Lin,LI Shou-xiu.Research on the analysis and calculation of acquisition probability of homing radar in anti-ship missile[J].Tactical Missile Technology,2007,(3):12-15.(in Chinese)
[5]XU Jian-ping,TANG Guo-jian.Research on the acquiring probability of anti-ship missile[J].Tactical Missile Technology,2008,(6):45-48.(in Chinese)
[6]ZHAO Jian-jun,WANG Guang-hui.Error spreading of auto-control terminal point of anti-ship missiles[J].Fire Command and Control,2003,(10):15 -18.(in Chinese)
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Defence Technology的其它文章
- Research on the Application of Explosive Network in the Shaped Charge Warhead
- Research on the Fracture Mechanism of Scored Liner Under Explosive Loading
- Research on Complex Refraction Indices of Expanded Graphite
- Variable-mass Thermodynamics Calculation Model for Gas-operated Automatic Weapon
- Test and Analysis for Spraying Ammonia in Diesel Engine
- Modeling and Simulation of Aerial Dispersion on Piston Dispersal Mechanism
