汉高新一代专利芯片粘接剂:流控芯片粘接技术智能控制胶层倒角
2010-10-24DebbieForrayIlyaFurman
Debbie Forray,Ilya Furman
(汉高公司)
Strong consumer demand for increased stored content on cell phones,MP3 players,and digital cameras continues to drive the memory market to higher production volumes.This is,indeed,an intensely competitive marketplace which pushed selling prices lower in 2007 versus 2006,and even lower still in late 2008 and early 2009.In light of these market developments,semiconductor companies are seeking lower-cost die attach material solutions to replace the higher-cost,film-based adhesive materials used for certain applications.
Fortunately,recent product developments in the field of controlled flow die attach technology have resulted in a low-cost,high-reliability,high–volume-compatible solution to the cost quandary for die stacking production.This latest material advance offers performance comparable to film without the adverse effects of potentially damaged wirebonds,warpage problems or reduced machine throughput–all issues that often accompany film-based processes.In addition,the competitive material price of Ablestik? Self-Filleting? die attach paste and required material investment in only known good die (film covers the entire wafer,including known bad die),results in some packaging firms saving as much as 25%in die attach materials cost as compared to that of current film adhesives.Furthermore,if one factors in the equipment investment required to facilitate a film process,the savings–as high as 50% comparatively–are even more profound,making this an increasingly appealing alternative.
1 Defining Controlled Flow Die Attach
As die become thinner and design rules for new package types become tighter,traditional die attach methods and processes reach a point of diminishing returns.For example,a standard paste die attach material process requires that material is dispensed and a bondforce applied that is large enough to force the adhesive to form a fillet around the edge of the die.Typical package assembly specifications require 100%coverage of die attach paste under the die and the presence of a fillet surrounding the entire die.When the package requires very tight assembly tolerances(100 μm or less) or very thin die (75μmor less),it is difficult to control the fillet height and fillet length consistently.In such a scenario,the traditional die attach process can result in adhesive contamination of the die top (Figure 1) or wirebond pads.Because of this,device assemblers have historically turned to adhesive film technology but it,too,has challenges which are discussed later in this article.
New developments in the form of Self-Filleting die attach adhesives address the limitations of traditional die attach pastes,while also providing a lower cost alternative to film.Self-Filleting adhesive provides many of the same benefits of traditional die attach pastes without the problematic issue of inconsistent fillet control.The Self-Filleting dispense process follows that of traditional paste whereby a dot or pattern is drawn on the substrate and the die is placed with some bondforce.(Figure 2)
However,the die placement process for Self-Filleting paste deviates from standard die attach methods:the bondforce needs to be high enough to start the flow of the material but low enough so the maximum coverage under the die is approximately 80-90% upon release of the die from the pick and place tool.After the die is released,the capillary force of the material enables controlled flow to the edge of the die,where it stops and forms a bondline fillet,but not a bulky fillet.

Figure 1 The large fillets on the daughter die increase the probability of die top contamination from the standard paste.The fillets formed from the controlled flow process on the mother die are comparable to a film adhesive.The cross section shows the applicability of using Self-Filleting adhesives for thin die and tight design rules packages.

Figure 2 Capillary force along with surface tension keeps the paste from flowing beyond the edge of the die or up the die kerf.The result from the controlled flow process is a fillet typically less than 50% of the die height and a fillet width consistent around the entire die perimeter.The cross section in figure 2 shows a 75 micron mother die (bottom die) attached using a controlled flow process,and a 75 micron daughter die (stacked die)using a traditional die attach process.
2 Controlled Flow Process Parameters
In order to fullly realize the advantages of Self-Filleting adhesives,the materials need to be processed slightly differently than traditional pastes.The initial goal of the dispense and die attach processes is to make sure there is no overflow or fillet creation upon die placement,which allows the material to flow and fillet on its own and,in the process,minimize fillet length.
The most important process parameter is dispense volume,as it will control overflow of paste and set the bondline thickness.In addition,dispense pattern shape and centering are important,as pattern shape can determine the flow speeds and also have an effect on the fillet length.Dispense pattern is somewhat dependent on die size but,in most cases,a double cross pattern is recommended,with the material distributed towards the edges of the die.Bondforce should be set as low as is possible to achieve full coverage,with bondforces of 100g or less being sufficient for most applications.
While die attach temperature can be used to decrease coverage time,this technique is not recommended as a temperature that is too high may cause the material to cure before the fillet is formed according to the self-filleting mechanisms.Actual time to achieve full coverage is primarily dependent on the coverage percentage immediately after die attach and the rheological properties of the given adhesive.
3 Controlling Bondline and Tilt with Spacers
Bo ndline control in tradional die attach is accomplished by using bondforce and time to distribute the material until the desired bondline is reached.In the case of Self-Filleting pastes and a controlled flow process,bondline control is established through volume alone.Although a bondforce is still required to start the flow of the material,the force needed is significantly less as compared to standard die attach pastes:a traditional die attach may require a bondforce of 3-4 Newtons in comparison to approximately 1 Newton for Self-Filleting materials.
Die attach spacers --typically spherical particles with a very tight distribution–are often used to control the bondline .Organic or metallic in nature,spacers in such applications not only to establish bondline thickness,but also help control die attach tilt as well.Generally,spacers ar e used at a very low quantity in a die attach adhesive–approximately 200 spacers in a 10x10 mm area,for example.
The second advantage of spacers is their ability to control bondline tilt.Bondline tilt occurs when a silicon die is placed non-paralell to the substrate either by improper equipment set-up or inconsistent paste dispense.In Self-Filleting adhesives,the spacers can act as pillars that flow out with the paste to ensure that the silicon is set parallel to the substrate.Figure 3 below shows a cross section of a same die stack set up using a spacer to control bondline and tilt.

Figure 3 Spacers are used to control bondline tilt in die attach pastes
4 Self-Filleting vs.Film
As referenced previouisly,because of the inherent drawbacks of traditioanl die attach pastes,many packaging firms have migrated to film die attach materials to achieve the processability and performance required for today’s memory and stacked die applications.There are several benefits to film,one of which is the managed flow of the material when attached.
Now with the advent of Self-Filleting paste,some of film’s advantages can be achieved with the use of die attach paste at a fraction of the cost.Paste manufacturing costs are lower than that of film and the savings,therefore,passed on to the consumer.In addition,there are also process-related cost reductions that are realized through the use of Self-Filleting pastes:
*Reduced material waste:Film covers the entire wafer–both known good and known bad die–with adhesive.In a well-defineed process,yield will range from 80-90%,which means that 10-20% of the film product is wasted.Paste is only used on the known good die,reducing the quantity needed and saving cost.
*Reduced capital equipment expenditure:The standard manufacturing process for dispensing paste is well defined,with required equipment already in place in virtually every global packaging house.Film requires the purchase of new equipment and the adoption of different processes.
However,it’s not just cost savings,but reliaiblity advantages that may be achieved when employing Self-Filleting pastes in place of film-based materials.One of the more predominant reliaibility issuess associated with film technologies are defects caused by void entrapment during the lamination process.Undelations in substrates and/or die can present challenges to film materials,as they have difficulties filling or flowing into or around these obstacles.As pastes are liquid mediums,fill and flow are not limiting factors.
With the industry moving toward ever thinner die,the pressure required in the film lamination process may also pose challenges.When placed under enough force,today’s very fragile wafers can crack.With Self-Filleting die attach paste,on the other hand,minimal bondforce is required to dispense and place the die and die cracking is significantly reduced or eliminated.In same size die stacking designs,film’s effectiveness is also somewhat limited.Although advances have been made using flow-over-wire films (FOW),few have been exceptionally successful in resolving problems such as trapping voids between the wires and/or bending the wires.A Self-Filleting paste may eliminate some of these film-related issues.
5 Summary
With the development of Self-Filleting die attach pastes and controlled flow technology,packaging specialists now have an ef fective film alternative for certain applications.(Figure 4) The lower cost and processability of Self-Filleting materials make them an attractive alternative for many manufacturers who may currently use film-based technologies.
To facilitate the stacking of die for more applications such as memory,traditional die attach pastes have steadily been replaced with film-type die attach,as die stacking designs make it difficult to use traditional paste materials.Now,however,Self-Filleting materials may mark the re-emergence of die attach paste as the material of choice for packaging firms seeking to lower costs and maximize the life of existing capital without sacrificing performance.Though Self-Filleting materials are not a film replacement for all die attach applications,they are indeed a groundbreaking advance for many.
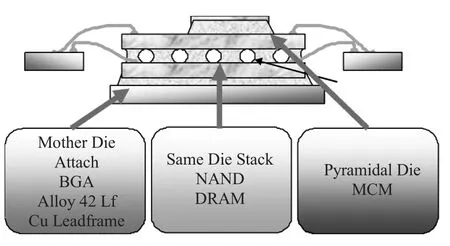
Figure 4 Self-Filleting paste has been used success fully on many applications as an alternative to die attach film adhesives
